Recombinant Mouse Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G (i) subunit alpha-1 (Gnai1)
-
中文名稱:小鼠Gnai1重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-YP009588MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Gnai1重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-EP009588MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Gnai1重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-EP009588MO-B
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Gnai1重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-BP009588MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Gnai1重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-MP009588MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來(lái)源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:Gnai1; Gnai-1Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(i) subunit alpha-1; Adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G alpha protein
-
種屬:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白長(zhǎng)度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
表達(dá)區(qū)域:2-354
-
氨基酸序列GCTLSAEDK AAVERSKMID RNLREDGEKA AREVKLLLLG AGESGKSTIV KQMKIIHEAG YSEEECKQYK AVVYSNTIQS IIAIIRAMGR LKIDFGDSAR ADDARQLFVL AGAAEEGFMT AELAGVIKRL WKDSGVQACF NRSREYQLND SAAYYLNDLD RIAQPNYIPT QQDVLRTRVK TTGIVETHFT FKDLHFKMFD VGGQRSERKK WIHCFEGVTA IIFCVALSDY DLVLAEDEEM NRMHESMKLF DSICNNKWFT DTSIILFLNK KDLFEEKIKK SPLTICYPEY AGSNTYEEAA AYIQCQFEDL NKRKDTKEIY THFTCATDTK NVQFVFDAVT DVIIKNNLKD CGLF
-
蛋白標(biāo)簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復(fù)溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲(chǔ)存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質(zhì)期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項(xiàng):Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
功能:Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) function as transducers downstream of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) in numerous signaling cascades. The alpha chain contains the guanine nucleotide binding site and alternates between an active, GTP-bound state and an inactive, GDP-bound state. Signaling by an activated GPCR promotes GDP release and GTP binding. The alpha subunit has a low GTPase activity that converts bound GTP to GDP, thereby terminating the signal. Both GDP release and GTP hydrolysis are modulated by numerous regulatory proteins. Signaling is mediated via effector proteins, such as adenylate cyclase. Inhibits adenylate cyclase activity, leading to decreased intracellular cAMP levels. The inactive GDP-bound form prevents the association of RGS14 with centrosomes and is required for the translocation of RGS14 from the cytoplasm to the plasma membrane. Required for normal cytokinesis during mitosis. Required for cortical dynein-dynactin complex recruitment during metaphase.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- LGN and Galphai participate in a long-inferred signal that originates outside the bundle to model its staircase-like architecture, a property that is essential for direction sensitivity to mechanical deflection and hearing. PMID: 27660326
- stimulation of GPR17 by the small molecule agonist MDL29,951 (2-carboxy-4,6-dichloro-1H-indole-3-propionic acid) decreases myelin basic protein expression levels mainly by triggering the Galphai/o signaling pathway. PMID: 26620557
- Gnai1 missense mutation is responsible of hyperpigmentation in mouse model. PMID: 26763459
- acidosis in inflamed tissues may be a decisive factor to regulate switching of PKA and PKCepsilon dependence via proton-sensing G-protein-coupled receptors. PMID: 25933021
- By using mice deficient in individual Galphai/o G-protein subunits, authors demonstrate that Galphai1 and Galphai3 are the critical in vivo targets of ADP-ribosylation underlying vasoactive amine sensitization elicited by pertussis toxin exposure. PMID: 24478091
- leucine can directly facilitate insulin signaling through a Galphai protein-dependent intracellular signaling pathway PMID: 23404499
- Inactive Galpha(i1)-GDP enhances the affinity of RGS14 for H-Ras-GTP in live cells, resulting in a ternary signaling complex that is further regulated by G protein-coupled receptors. PMID: 23250758
- Mice with mutations of Gnai1 or Gnai2 have neither fusions of ribs nor lumbar vertebrae, but loss of both Gnai3 and one of the other two genes increases the number and severity of rib fusions without affecting the lumbar fusions. PMID: 23236180
- Results suggest a model in which the Gbetagamma dimer that is released as a result of the dissociation from Galpha(o) upon activation of mGluR6 closes the TRPM1 channel, perhaps via a direct interaction. PMID: 22586107
- RGS14 can form complexes with GPCRs in cells that are dependent on Galpha(i/o) and these RGS14.Galpha(i1).GPCR complexes may be substrates for other signaling partners such as Ric-8A PMID: 21880739
- The decrease in beta(2)-AR may account for additional relaxation impairment, given that there is no enhancement over nontransgenic after pertussis toxin, despite AC5 overexpression. PMID: 21131397
- Data show that mice lacking G(o2)alpha, but not those lacking alpha subunits of either G(o1) or any G(i) proteins, handle glucose loads more efficiently than wild-type (WT) mice. PMID: 21220323
- Activation of the Rsg14-Galphai1-GDP signaling complex is regulated by Ric8. PMID: 21158412
- analysis of a novel Gi, P2Y-independent signaling pathway mediating Akt phosphorylation in response to thrombin receptors PMID: 20586915
- CKbeta8- and CKbeta8-1-induced activation of ERK1/2 is mediated by the G(i)/G(o) protein, PLC, and PKCdelta. PMID: 20097574
- Gi-mediated signaling pathways are activated by G12/G13 and are sufficient to induce integrin alpha(IIb)beta3 activation PMID: 12183468
- Gi, but not Gq or G12/13, signaling pathways are required for activation of Akt in platelets PMID: 14623889
- Loss of G(ialpha1) amplifies the responsiveness of CA1 postsynaptic neurons to stimuli that strengthen synaptic efficacy, thereby diminishing synapse-specific plasticity required for new memory formation. PMID: 14715142
- Galpha (i) is activated and subsequently uncoupled from receptor-Galpha(i) signaling by Pasteurella multocida toxin PMID: 18583341
- Report role of Gnai1 in the control of in vivo heart rate dynamics. PMID: 18832081
- PKA and GRK phosphorylation of the beta(2)AR has distinct roles for agonist dose-dependent coupling to G(i) proteins in cardiac myocytes PMID: 19706594
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細(xì)胞定位:Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cytoplasm, cell cortex. Membrane; Lipid-anchor.
-
蛋白家族:G-alpha family, G(i/o/t/z) subfamily
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte protein 4 (CTLA4), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human HLA class II histocompatibility antigen gamma chain (CD74), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Rabbit Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Oryctolagus cuniculus (Rabbit)
-
Recombinant Human Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
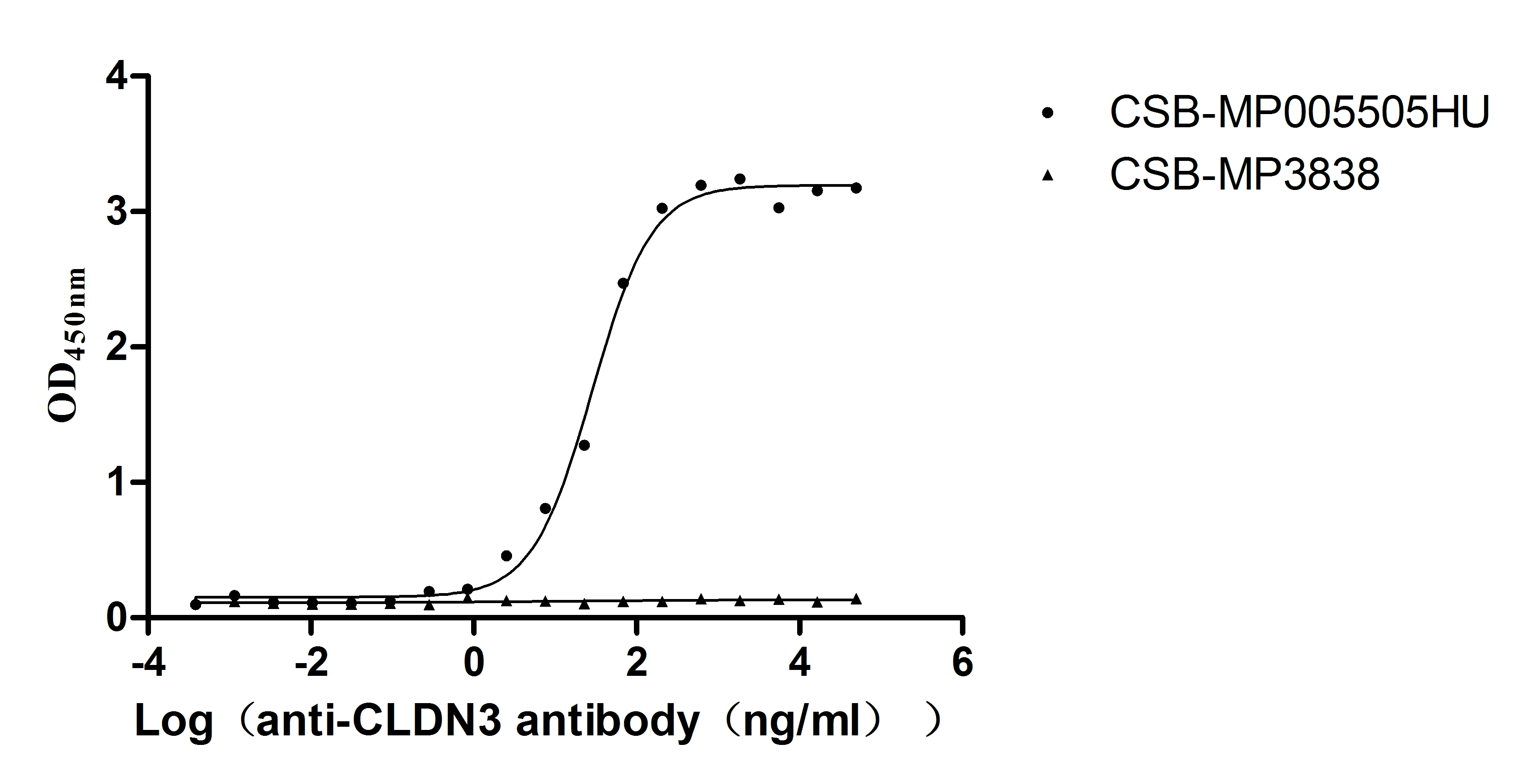
Recombinant Human Claudin-3 (CLDN3)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
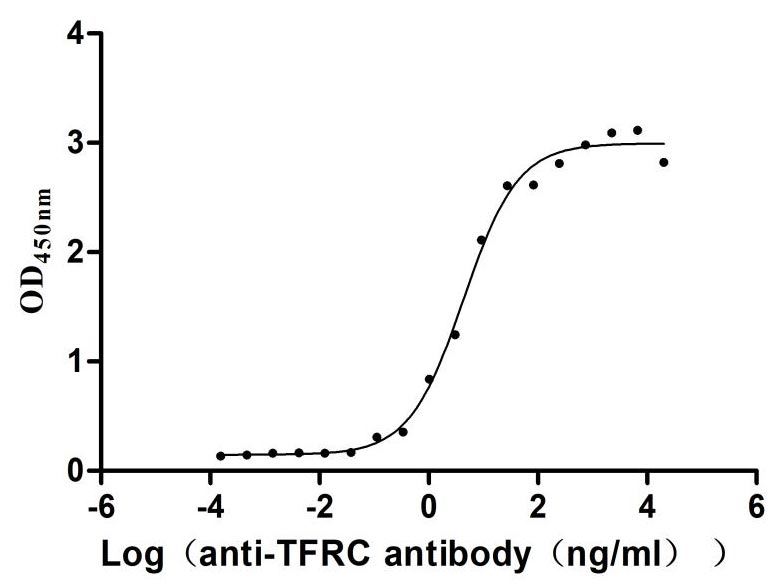
Recombinant Human Transferrin receptor protein 1 (TFRC), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
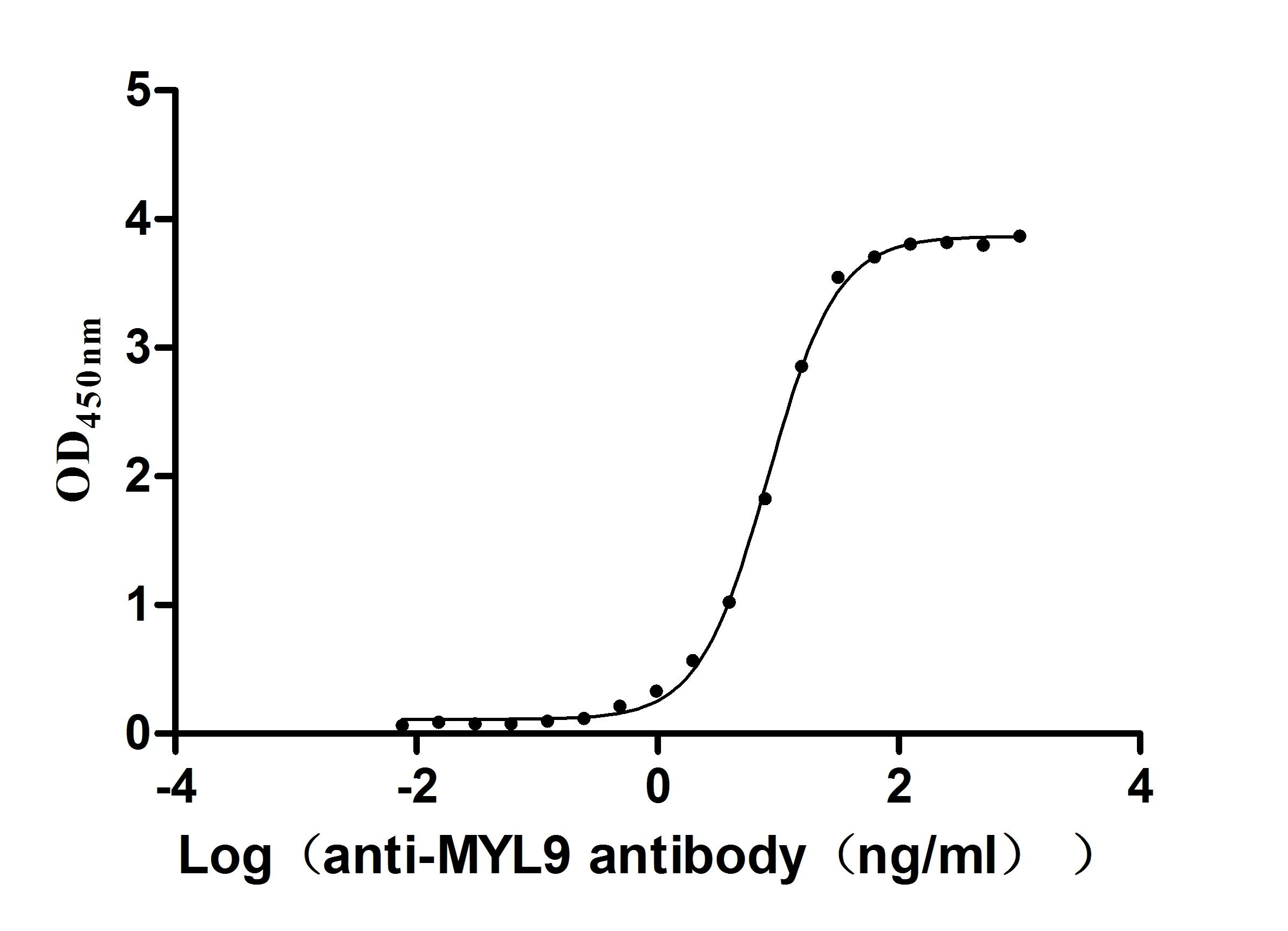
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light chain 12B (MYL12B) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
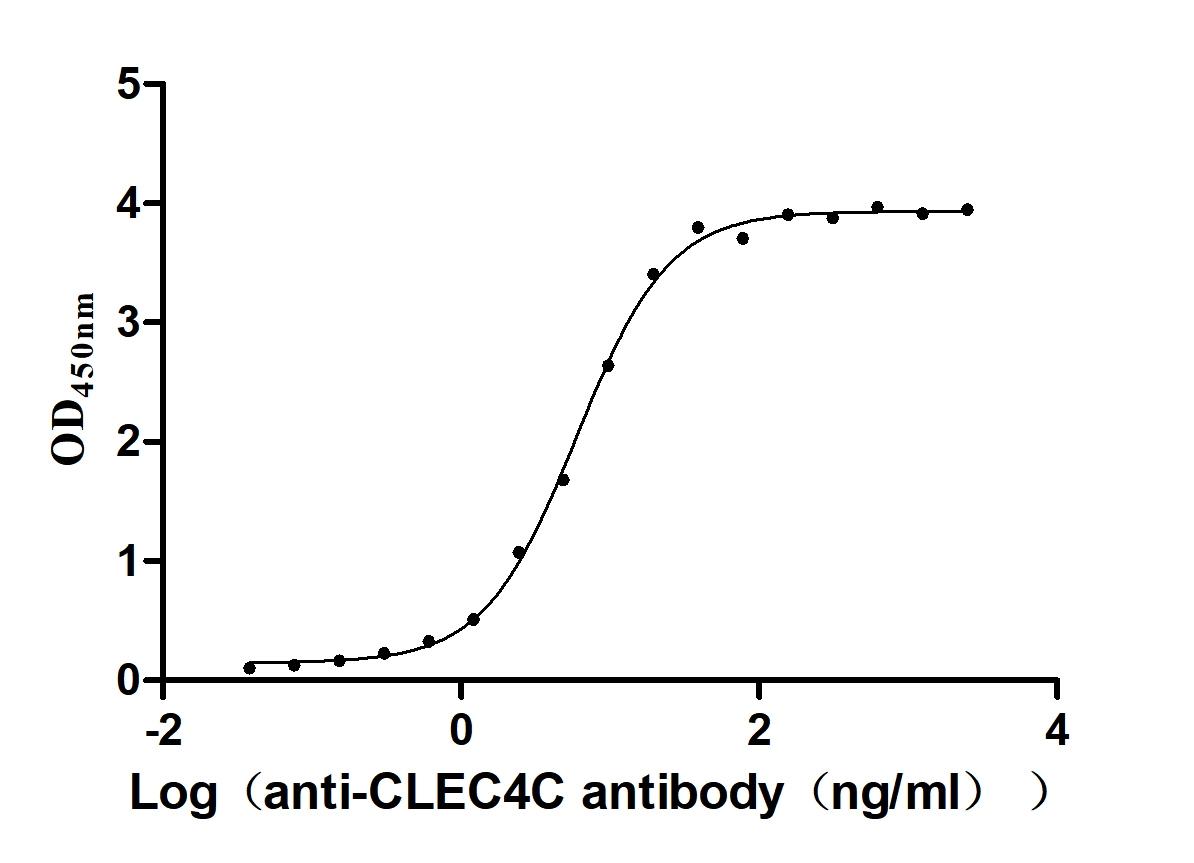
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis C-type lectin domain family 4 member C(CLEC4C), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)


-AC1.jpg)
-AC1.jpg)