DKK1:經典的Wnt/β-catenin通路拮抗劑,癌癥雙向調控靶點?
日期:2023-07-26 14:11:06
近年來,DKK1在腫瘤治療中引起關注!臨床研究顯示其廣泛應用前景。君實生物(Junshi Biosciences)的JS015注射液已于去年獲得IND受理,一種用于晚期惡性實體瘤的重組人源化抗DKK1單克隆抗體。此外,Leap Therapeutics公司的Sirexatamab(DKN-01,曾名LY-2812176)正在肝癌、膽管癌、胃癌等腫瘤中進行臨床II期研究,而另一款DKK1抗體BHQ-880已在2020年完成了多發性骨髓瘤的II期臨床試驗。目前,DKK1作為經典Wnt信號通路的拮抗劑,不僅是腫瘤診斷和預后評價的血清學標志物,更是重要的腫瘤治療新靶點!
1. 什么是DKK1?
1.1 DKK1的結構
Dickkopf相關蛋白1(Dickkopf-related protein 1,DKK1)是Wnt/B-catenin信號通路的典型抑制劑,屬于DKK家族(其余包括DKK2、DKK3和DKK4)。DKK1由人類DKK1基因編碼,位于10q11.2,長度約為3.5kb,編碼一種分子量約為28.7KDa的分泌型糖蛋白,含約266個氨基酸。DKK1的結構包括:一個N端的信號序列、兩個保守的富半胱氨酸區域(Dkk_N和輔脂肪酶折疊區域)以及一個靠近蛋白C端的N-糖化位點。其信號序列由20~30個氨基酸組成,負責定位DKK1肽鏈在內質網,并介導DKK1的細胞外分泌。輔脂肪酶折疊區域是由多個短的β疊和二硫鍵構成的類指結構,能與Wnt受體LRP5/LRP6及穿膜蛋白Kremen1/2結合成三聚體,從而誘導內吞作用并抑制Wnt信號通路。Dkk_N區域還含有一個保守的富胱氨酸序列(圖1) [1-3]。
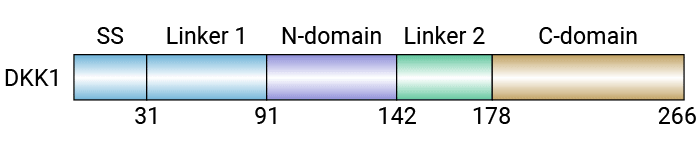
圖1. DKK1的結構示意圖 [1]
1.2 DKK1的表達和功能
DKK1主要由成骨細胞、骨細胞分泌,其次也表達于很多組織和細胞類型,包括胎盤、皮膚、前列腺、血管內皮、腎臟、成骨細胞和骨細胞等多個部位。DKK1作為一種分泌型糖蛋白,主要通過與Wnt蛋白競爭性結合LRP5/6受體,拮抗Wnt/β-catenin信號通路活性,調節細胞增殖、分化及癌變,影響細胞凋亡、瘤細胞侵襲和轉移。越來越多的研究證實DKK1在腫瘤發生發展中呈現多樣化的特點,甚至在同一種細胞中,因生理環境不同表現出相反的調節作用,其功能相對較復雜 [3-6]。
2. DKK1拮抗Wnt/β-catenin信號通路的調節機制
DKK1被視為Wnt/β-catenin信號通路的典型抑制因子,對細胞生命活動具有重要調控作用,在多種腫瘤的發展中扮演不可替代的角色。最新研究表明,盡管DKK1通常作為傳統Wnt/β-catenin信號通路的抑制劑,但在某些研究中未能發揮其抑制劑的作用,這可能與β-catenin基因的變異有關。
目前的研究認為,DKK1通過至少兩種方式抑制經典Wnt信號通路。首先,它與Frizzled相關蛋白質競爭性地阻止Frizzled與Wnt結合。其次,DKK1可以與細胞膜的Wnt受體LRP5/6和共受體Kremen1/2結合,形成聚合物并使其內吞,從而關閉Wnt信號,終止靶基因異常轉錄進程。此外,DKK1本身也是經典Wnt信號通路的靶基因,其啟動子區域含有β-catenin結合位點。一些研究認為轉錄生成的DKK1能通過負反饋機制抑制上游基因的表達,與信號鏈上的其他因子共同維持內環境的穩態(圖2) [7-12]。
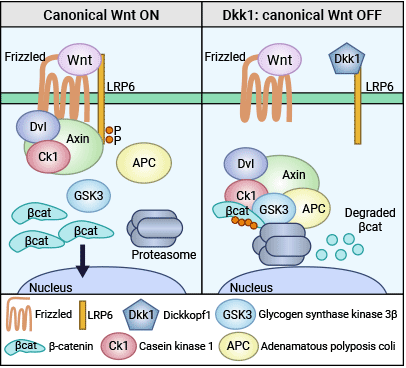
圖2. DKK1拮抗Wnt/β-catenin信號通路的調節機制 [12]
3. DKK1在腫瘤等其它疾病中的作用
DKK1主要通過Wnt/β-catenin信號通路發揮作用,以往研究表明DKK1通過該通路參與了多種疾病的發病機制。尤其在腫瘤中,DKK1在不同研究條件下呈現出截然不同的結果。據報道,在多發性骨髓瘤 [11]、肝胞癌 [12]、肝/腎母細胞癌 [13]、非小細胞肺癌 [14]、頭頸部癌 [15]、食管癌 [16]、胰腺癌 [17]等腫瘤中DKK1往往表達增高,呈現促癌基因的特征;在胃癌 [18]、膀胱癌 [19]、黑色素瘤 [20]、結直腸癌 [21]中,DKK1表達降低,呈現抑癌基因特征。
3.1 DKK1和多發性骨髓瘤
DKK1在多發性骨髓瘤MM中的作用是促進骨破壞,而抑制DKK1可以減輕骨破壞程度。高表達的DKK1與廣泛的骨破壞相關,因為它抑制了骨髓干細胞向成骨細胞的分化。近年來,抑制DKK1的抗體和疫苗成為治療多發性骨髓瘤的新方法。研究發現,抗DKK1疫苗能夠引發CD4+和CD8+T細胞反應,而保護裸鼠免受MM侵襲。DKK1聯合MMSA-1的多表位抗原疫苗比DKK1/MMSA-1單抗原疫苗誘導的T細胞免疫反應更強,增強了對骨髓瘤細胞及MM骨破壞的抑制作用 [22]。因此,靶向DKK1可能為多發性骨髓瘤治療帶來新的方向。
3.2 DKK1和胃癌
研究發現,胃癌細胞中DKK1表達強,正常胃黏膜中表達較弱。DKK1高表達與胃癌晚期、遠處轉移、淋巴侵潤和血管侵犯相關。敲除DKK1可減弱胃癌細胞的增殖、遷移和侵襲能力。DKK1陽性的胃癌患者存活期較低。因此,血清中DKK1含量增加和胃癌組織中DKK1表達增加有助于胃癌的診斷和預測。Sirexatamab(DKN-01)是一種針對DKK1的靶向藥物,在臨床治療胃癌方面顯示出潛力。數據顯示,Sirexatamab通過結合DKK1降低血管增生,并上調關鍵細胞因子IFNγ、IL-15和IL-33的水平,促進腫瘤細胞死亡。它還可以激活Wnt信號通路,重編程免疫抑制細胞MDSC,降低其免疫抑制活性(圖3) [23-25]。
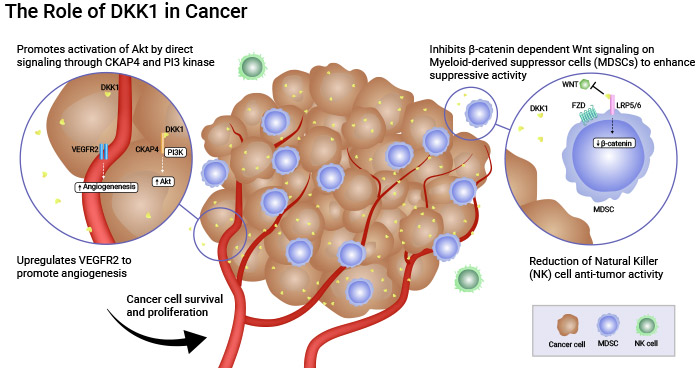
圖3. Sirexatamab(DKN-01)在臨床治療胃癌方面顯示出潛力 [25]
3.3 DKK1和結直腸癌
血管生成擬態(Vasculogenic Mimicry,VM)是腫瘤細胞在特定條件下形成的類似血管壁結構,可輸送血液,促進腫瘤生長和血管構建。參與VM的腫瘤細胞容易發生血道轉移,對化療和抗血管生成治療不敏感,導致患者預后差。研究發現,存在VM的結腸癌組織中DKK1表達較低,DKK1過表達的HCT116細胞形成管狀結構能力明顯減弱,且VE-cadherin表達降低。此外,DKK1可抑制裸鼠移植瘤組織中HCT116細胞形成VM。因此,DKK1過表達可抑制結直腸癌VM形成 [26]。
3.4 DKK1和乳腺癌
DKK1在乳腺癌中的作用是復雜的,既可能具有抑制腫瘤的效果,也可能具有促進腫瘤的效果。在某些情況下,DKK1被認為是抑制乳腺癌的因素,特別是對于骨轉移的抑制。它可以增強破骨細胞的活性,并抑制乳腺癌細胞向骨骼進行轉移。因此,高血清DKK1水平可以作為乳腺癌骨轉移的特異性診斷指標 [27]。然而,有研究表明,DKK1在乳腺癌中也可能具有促進血管生成、促進乳腺癌細胞遷移和侵襲的能力。DKK1可以通過VEGFR2信號級聯反應誘導血管生成,增加乳腺癌細胞的侵襲和血管生成能力 [28-29]。
3.5 DKK1和胰腺癌
采用無創血清學檢測胰腺癌血清中CA19-9、s-ULBP2、DKK1表達水平與良性胰腺病患者及健康人群的差別,實驗結果顯示,胰腺癌患者血清CA19-9、s-ULBP2、DKK1含量明顯高于良性胰腺病組及健康對照組。通過Logistic回歸分析及ROC曲線分析,提示CA19-9的敏感度最高,DKK1的特異性最高。研究認為,三者聯合檢測可提高胰腺癌診斷準確率且可評估胰腺癌的臨床治療效果 [30]。
3.6 DKK1和膀胱癌
基于GEPIA數據庫,DKK1在膀胱癌組織中相對于癌旁組織表達量下降,DKK1高表達者總體生存率較DKK1低表達者要減小。ELISA檢測血清中DKK1濃度顯示,膀胱癌中血清濃度顯著高于健康者,且淋巴結轉移的膀胱癌DKK1血清濃度顯著高于未轉移者。III期+IV期膀胱癌患者DKK1濃度明顯高于I期+II期患者。然而,實驗與數據庫中的結果相矛盾。可能的原因是測量對象不同(血清蛋白水平vs.組織中基因水平) [19, 31]。因此,需要進一步的驗證DKK1在膀胱癌發展中的具體用機制,探索其作為新的治療靶點的可能性。
3.7 DKK1和其它疾病
除了與腫瘤相關,DKK1還與多種疾病有關。在帕金森病的6-OHDA損傷大鼠模型中,DKK1被誘導表達于腹側中腦,敲低DKK1可以減輕MPP+誘導的PC12細胞凋亡,并促進β-catenin和p-Ser9-GSK-3β的表達 [32]。臨床前研究顯示,DKK1不僅抑制成骨細胞,同時還激活破骨細胞,導致骨穩態破壞和抑制骨形成。研究表明DKK1可能參與強直性脊柱炎(Ankylosing Spondylitis,AS)等新骨形成的過程 [33]。
在牙周炎研究中,下調DKK1可以抑制促炎細胞因子IL-1β、IL-6、IL-8的表達,促進成骨標志物BMP-2、OCN、RunX2的mRNA表達以及鈣結節生成,同時促進人牙周膜干細胞(hPDLSCs)成骨分化,從而抑制牙周炎的發展。進一步研究DKK1在這些疾病中的作用,有助于發現新的治療方法和藥物 [34-35]。
4. DKK1的臨床在研藥物
來自Pharmsnap的數據表明(表1),BHQ-880和Sirexatamab等藥物作為DKK1抑制劑,正在進行臨床研究,用于治療多發性骨髓瘤等多種腫瘤。同時,DKK1負載的樹突狀細胞疫苗和JS015單克隆抗體也顯示出潛力。值得一提的是,Sirexatamab在一線治療晚期胃癌和胃食道結合部癌的2a期臨床試驗初步結果顯示,客觀緩解率(ORR)達到68.2%,DKK1高表達腫瘤患者的ORR更高達90% [36]。
此外,還有其它DKK1抑制劑和調節劑處于臨床前或藥物發現階段,用于肝癌,卵巢癌,子宮內膜癌,前列腺癌,免疫球蛋白a腎病等疾病治療。因此,通過針對DKK1的靶向治療方法,利用不同類型的藥物,如單克隆抗體、重組多肽和小分子化藥物,有望開發出更有效的選擇,為腫瘤或自身免疫性疾病的治療帶來新的希望。
| 藥物 | 靶點 | 作用機制 | 在研適應癥 | 藥物最高研發狀態(全球) | 藥物類型 | 在研機構 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BHQ-880 | DKK1 | DKK1抑制劑 | 多發性骨髓瘤 | 臨床2期 | 單克隆抗體 | Novartis AG; MorphoSys AG; Novartis Pharma AG |
| Sirexatamab (DKN-01) | DKK1 | DKK1抑制劑 | 結直腸癌;胃腺癌;食管癌;胃食管交界處癌;膽道腫瘤;肝癌;卵巢癌;子宮內膜癌;前列腺癌;胃癌;多發性骨髓瘤;非小細胞肺癌;肉瘤;鱗狀細胞癌 | 臨床2期 | 單克隆抗體 | 飛躍治療公司 (Leap Therapeutics, Inc.);禮來制藥 Eli Lilly & Co. |
| DKK1 loaded dendritic cell vaccine(Case Comprehensive Cancer Center) | DKK1 | 免疫刺激劑 | 淀粉樣變性; 免疫球蛋白a腎病; 意義不明的單克隆丙種球蛋白病;多發性骨髓瘤;陰燃多發性骨髓瘤 |
早期臨床1期 | 預防性疫苗 | The Case Comprehensive Cancer Center |
| JS015 | DKK1 | DKK1抑制劑 | 晚期惡性實體瘤 | 臨床申請批準 | 單克隆抗體 | 上海君實生物醫藥科技股份有限公司 (Shanghai Junshi Biosciences Co., Ltd.) |
| DKK1-CAR-iNKT | DKK1 | / | 腫瘤 | 臨床前 | 單克隆抗體 | 蘇達有限公司 (Arovella Therapeutics Ltd.) |
| anti-DKK1 antibodies | DKK1 | DKK1調節劑 | 腫瘤 | 臨床前 | 生物藥 | 扭轉生物科技有限公司 (Twist Bioscience Corp.) |
| APC-002 | DKK1 | DKK1抑制劑 | 食管癌;胃癌 | 臨床前 | 生物藥 | 安沛治療有限公司 (Aptacure Therapeutics Ltd.) |
| Recombinant human R-spondin 1 | DKK1 | DKK1調節劑 | / | 臨床1期 | 重組多肽 | / |
| RN-564 | DKK1 | DKK1抑制劑 | / | 臨床1期 | 單克隆抗體 | / |
| IIIC3 (Enzo Biochem, Inc.) | DKK1 | DKK1抑制劑 | / | 藥物發現 | 小分子化藥 | / |
| Mab-B3 | DKK1 | DKK1抑制劑 | / | 藥物發現 | 單克隆抗體 | / |
表1:DKK1的在研臨床藥物
為鼎力協助科研和藥企人員針對DKK1在腫瘤和自身免疫等疾病相關的臨床應用研究,CUSABIO推出DKK1活性蛋白(Code: CSB-MP006920HU(A4))產品,助力您在DKK1機制方面的研究或其潛在臨床價值的探索(點擊查看DKK1全系列產品:蛋白;抗體;試劑盒)。
DKK1蛋白
Recombinant Human Dickkopf-related protein 1(DKK1) (Active) (Code: CSB-MP006920HU(A4))
-SDS.jpg)
The purity was greater than 95% as determined by SDS-PAGE. (Tris-Glycine gel) Discontinuous SDS-PAGE (reduced) with 5% enrichment gel and 15% separation gel.
-AC1.jpg)
Immobilized Human DKK1 at 2 μg/mL can bind Anti-DKK1 recombinant antibody (CSB-RA006920MA1HU), the EC50 is 1.283-2.544 ng/mL.
參考文獻:
[1] Chu, Hang Yin, et al. "Dickkopf-1: A promising target for cancer immunotherapy." Frontiers in Immunology 12 (2021): 658097.
[2] Diarra, Danielle, et al. "Dickkopf-1 is a master regulator of joint remodeling." Nature medicine 13.2 (2007): 156-163.
[3] Bafico, Anna, et al. "Novel mechanism of Wnt signalling inhibition mediated by Dickkopf-1 interaction with LRP6/Arrow." Nature cell biology 3.7 (2001): 683-686.
[4] Zhu, Guohua, et al. "Expression and role of Dickkopf-1 (Dkk1) in tumors: from the cells to the patients." Cancer Management and Research (2021): 659-675.
[5] Yamaguchi, Yuji, et al. "Regulation of skin pigmentation and thickness by Dickkopf 1 (DKK1)." Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings. Vol. 14. No. 1. Elsevier, 2009.
[6] Ke, Hua Zhu, et al. "Sclerostin and Dickkopf-1 as therapeutic targets in bone diseases." Endocrine reviews 33.5 (2012): 747-783.
[7] Leijten, Jeroen Christianus Hermanus, et al. "Gremlin 1, frizzled‐related protein, and Dkk‐1 are key regulators of human articular cartilage homeostasis." Arthritis & Rheumatism 64.10 (2012): 3302-3312.
[8] Dun, Xiaoyi, et al. "Differential expression of DKK-1 binding receptors on stromal cells and myeloma cells results in their distinct response to secreted DKK-1 in myeloma." Molecular cancer 9.1 (2010): 1-9.
[9] Niida, Atsushi, et al. "DKK1, a negative regulator of Wnt signaling, is a target of the β-catenin/TCF pathway." Oncogene 23.52 (2004): 8520-8526.
[10] Zhou, Yu-Xin, et al. "Nomogram Incorporating the WNT/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway for Predicting the Survival of Cutaneous Melanoma." International Journal of General Medicine (2021): 2751-2761.
[11] Purro, Silvia A., Soledad Galli, and Patricia C. Salinas. "Dysfunction of Wnt signaling and synaptic disassembly in neurodegenerative diseases." Journal of molecular cell biology 6.1 (2014): 75-80.
[12] Fulciniti, Mariateresa, et al. "Anti-DKK1 mAb (BHQ880) as a potential therapeutic agent for multiple myeloma." Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology 114.2 (2009): 371-379.
[13] Shen, Qiujin, et al. "Serum DKK1 as a protein biomarker for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: a large-scale, multicentre study." The lancet oncology 13.8 (2012): 817-826.
[14] Sun, Jinlin, Xudong Chen, and Yansen Wang. "Comparison of the diagnostic value of CEA combined with OPN or DKK1 in non?small cell lung cancer." Oncology Letters 20.3 (2020): 3046-3052.
[15] Gosepath, Eva M., et al. "Acquired cisplatin resistance in the head–neck cancer cell line Cal27 is associated with decreased DKK1 expression and can partially be reversed by overexpression of DKK1." International journal of cancer 123.9 (2008): 2013-2019.
[16] Song, Qingping, et al. "miR-33a-5p inhibits the progression of esophageal cancer through the DKK1-mediated Wnt/β-catenin pathway." Aging (Albany NY) 13.16 (2021): 20481.
[17] Igbinigie, Eseosaserea, et al. "Dkk1 involvement and its potential as a biomarker in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma." Clinica chimica acta 488 (2019): 226-234.
[18] Jiang, Jiang, et al. "FOXC1 negatively regulates DKK1 expression to promote gastric cancer cell proliferation through activation of Wnt signaling pathway." Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 9 (2021): 662624.
[19] Sun, D. K., et al. "Serum Dickkopf-1 levels as a clinical and prognostic factor in patients with bladder cancer." Genet Mol Res GMR 14.4 (2015): 18181-18187.
[20] Liao, Yangying, et al. "Suppressive role of microRNA-130b-3p in ferroptosis in melanoma cells correlates with DKK1 inhibition and Nrf2-HO-1 pathway activation." Human Cell 34.5 (2021): 1532-1544.
[21] Rawson, James B., et al. "Promoter methylation of Wnt antagonists DKK1 and SFRP1 is associated with opposing tumor subtypes in two large populations of colorectal cancer patients." Carcinogenesis 32.5 (2011): 741-747.
[22] Lu, Chenyang, et al. "A novel multi‐epitope vaccine from MMSA‐1 and DKK 1 for multiple myeloma immunotherapy." British journal of haematology 178.3 (2017): 413-426.
[23] Klempner, S. J., et al. "Safety and efficacy of a DKK1 inhibitor (DKN-01) in combination with pembrolizumab (P) in patients (Pts) with advanced gastroesophageal (GE) malignancies." Annals of Oncology 29 (2018): viii222.
[24] Jarman, Edward J., et al. "DKK1 drives immune suppressive phenotypes in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and can be targeted with anti‐DKK1 therapeutic DKN‐01." Liver International 43.1 (2023): 208-220.
[25] https://www.sec.gov/Archives/edgar/data/1509745/000110465921117855/tm2128111d1_ex99-2.htm
[26] Yao, Lingli, et al. "Dickkopf‐1‐promoted vasculogenic mimicry in non‐small cell lung cancer is associated with EMT and development of a cancer stem‐like cell phenotype." Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 20.9 (2016): 1673-1685.
[27] Zhuang, Xueqian, et al. "Differential effects on lung and bone metastasis of breast cancer by Wnt signalling inhibitor DKK1." Nature cell biology 19.10 (2017): 1274-1285.
[28] Niu, Jie, et al. "DKK1 inhibits breast cancer cell migration and invasion through suppression of β-catenin/MMP7 signaling pathway." Cancer cell international 19.1 (2019): 1-13.
[29] Choi, Sung Hoon, et al. "Dickkopf-1 induces angiogenesis via VEGF receptor 2 regulation independent of the Wnt signaling pathway." Oncotarget 8.35 (2017): 58974.
[30] Cui, Dapeng, et al. "Value analysis of CA19-9, s-ULBP2 and Dkk1 in the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer." The Journal of Practical Medicine (2017): 4086-4089.
[31] Wei, Ruqiong, et al. "Analyzing the prognostic value of DKK1 expression in human cancers based on bioinformatics." Annals of translational medicine 8.8 (2020).
[32] Dun, Yaoyan, et al. "Inhibition of the canonical Wnt pathway by Dickkopf-1 contributes to the neurodegeneration in 6-OHDA-lesioned rats." Neuroscience letters 525.2 (2012): 83-88.
[33] Daoussis, Dimitrios, et al. "Evidence that Dkk‐1 is dysfunctional in ankylosing spondylitis." Arthritis & Rheumatism: Official Journal of the American College of Rheumatology 62.1 (2010): 150-158.
[34] Li, Bei, et al. "GCN5 modulates osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells through DKK1 acetylation in inflammatory microenvironment." Scientific Reports 6.1 (2016): 26542.
[35] Wang, Chengze, et al. "HOXA10 inhibit the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells by regulating β-catenin localization and DKK1 expression." Connective Tissue Research 62.4 (2021): 393-401.
[36] Yamabuki, Takumi, et al. "Dikkopf-1 as a novel serologic and prognostic biomarker for lung and esophageal carcinomas." Cancer research 67.6 (2007): 2517-2525.
上一篇: 一抗和二抗的區別










