Recombinant Rat Voltage-dependent P/Q-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1A (Cacna1a), partial
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Rat Voltage-dependent P/Q-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1A(Cacna1a) ,partial
-
貨號:CSB-YP004397RA
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Rat Voltage-dependent P/Q-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1A(Cacna1a) ,partial
-
貨號:CSB-EP004397RA
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Rat Voltage-dependent P/Q-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1A(Cacna1a) ,partial
-
貨號:CSB-EP004397RA-B
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Rat Voltage-dependent P/Q-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1A(Cacna1a) ,partial
-
貨號:CSB-BP004397RA
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Rat Voltage-dependent P/Q-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1A(Cacna1a) ,partial
-
貨號:CSB-MP004397RA
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:Cacna1a; Cach4; Cacn3; Cacnl1a4; Voltage-dependent P/Q-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1A; Brain calcium channel I; BI; Calcium channel; L type; alpha-1 polypeptide; isoform 4; Rat brain class A; RBA-I; Voltage-gated calcium channel subunit alpha Cav2.1
-
種屬:Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
蛋白長度:Partial
-
蛋白標簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復(fù)溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質(zhì)期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶點詳情
-
功能:Voltage-sensitive calcium channels (VSCC) mediate the entry of calcium ions into excitable cells and are also involved in a variety of calcium-dependent processes, including muscle contraction, hormone or neurotransmitter release, gene expression, cell motility, cell division and cell death. The isoform alpha-1A gives rise to P and/or Q-type calcium currents. P/Q-type calcium channels belong to the 'high-voltage activated' (HVA) group and are specifically blocked by the spider omega-agatoxin-IVA (AC P30288). They are however insensitive to dihydropyridines (DHP).
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- Conclude that expression of the Cacna1a mRNA increased before the onset of alcohol withdrawal syndrome susceptibility, suggesting that altered CaV2.1 channel expression may play a role in AWS pathogenesis. PMID: 29277284
- postulate that the N-terminus of the truncated channel plays an essential part in its interaction with the full-length CaV2.1, which prevents the correct folding of the wild-type channel PMID: 27260834
- Thus, GHSR1a differentially inhibits CaV2 channels by Gi/o or Gq protein pathways depending on its mode of activation. PMID: 26283199
- the consensus motifs of S-nitrosylation were much more abundant in Cav2.2 than in Cav1.2 and Cav2.1. PMID: 26507659
- data suggest that the different roles that Ca(V)2.1 and Ca(V)2.2 play in MNC secretion may be a result of the different levels of expression of Ca(V)2.1 in VP and OT MNCs PMID: 24344901
- the contribution of Ca(V)2.1 to complex cognitive functions PMID: 24205277
- By transducing presynaptic action potential firings into unique Ca(2+) signals and vesicle release profiles, Cav2.1 channels contribute to the encoding and processing of neural information PMID: 24453334
- Calcium currents are enhanced by alpha2delta-1 lacking its membrane anchor PMID: 22869375
- Gem contains two candidate inhibitory sites, each capable of producing full inhibition of P/Q-type Ca(2+) channels. PMID: 22589533
- Lowering glucose level enhances the activity of P/Q type Ca(2+)channels and elevates [Ca(2+)](i) level in hypothalamic arcuate nucleus neurons via inhibition of GSK3beta. PMID: 22504905
- Cav2.1 channels, along with dopamine D3 receptors, mediate upregulation of dopamine D2 receptors in dopamine-denervated striatum. PMID: 21389298
- The invertebrate LCav2 channel does not exhibit any of the hallmarks of mammalian voltage-dependent G-protein inhibition. PMID: 20511524
- Neurons in the inferior colliculus express Ca(2+) channel alpha(1A), alpha(1B), alpha(1C), alpha(1D), and alpha(1E) subunits. PMID: 12895521
- Regulation of Cav2.1 channel in response to local Ca2+ increases calmodulin binding and negative regulation during more global Ca2+ increases calcium inactivation. PMID: 14673106
- Cacna1a subunit is apparently associated with the glutamatergic synapses and may play a role in the regulation of excitatory neurotransmission and contribute to the generation of postsynaptic calcium transport. PMID: 15090043
- The PP2calpha-Ca2+ channel complex is responsible for rapid dephosphorylation of Ca2+ channels and may contribute to regulation of synaptic transmission in neurons. PMID: 15728831
- Differential regulation of CaV2.1 channels by CaM, VILIP-2, CaBP1, and other neurospecific Ca2+-binding proteins is a potentially important determinant of Ca2+ entry in neurotransmission. PMID: 16049183
- nonmyristoylated CaBP1 and VILIP-2 bind to CaV2.1 channels and regulate them like CaM, whereas myristoylation allows differential, Ca2+-independent regulation by the inactive EF-hands of CaBP1 and VILIP-2 PMID: 16049184
- These results expand the known diversity of CaV2.1 transcripts in cerebellar Purkinje cells, and propose the selective expression of distinct assortments of CaV2.1 transcripts in different brain neurons and species. PMID: 16278278
- Ca2+-dependent inactivation of Ca(v)2.1 depends on a subplasmalemmal Ca2+ microdomain that is affected by the amplitude of the Ca2+ current and differentially modulated by distinct Ca2+ buffers PMID: 16373336
- Data show that the Drosophila cacophony ts2 mutation reduces presynaptic Ca2+ entry and defines an important element in Cav2.1 channel inactivation PMID: 16820014
- brain BKCa channels are assembled into complexes with calcium channels Cav1.2, Cav2.1 & Cav2.2; complex formation with Cav channels enables BKCa-mediated membrane hyperpolarization controlling neuronal firing & release of hormones & transmitters PMID: 17068255
- Thus, the GRY rat with P/Q-type Ca(2+) channel disorders is a useful model for studying absence epilepsy and Cacna1a-related diseases. PMID: 17196942
- Essential in Ca++ selectivity over other divalent cations, at a conserved EEEE locus. PMID: 17893194
- Novel splice variants of rat CaV2.1 that lack much of the synaptic protein interaction site are expressed in neuroendocrine cells. PMID: 18390553
- Introduction into Ca(v)2.1 of the homologous mutation of Ca(v)1.2 causing the Timothy syndrome questions the role of V421 in the phenotypic definition of P-type Ca(2+) channel. PMID: 18536931
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Calcium channel alpha-1 subunit (TC 1.A.1.11) family, CACNA1A subfamily
-
組織特異性:Brain specific. Purkinje cells contain predominantly P-type VSCC, the Q-type being a prominent calcium current in cerebellar granule cells. Also found in heart, in kidney distal convoluted tubule (DCT), and in pituitary.
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
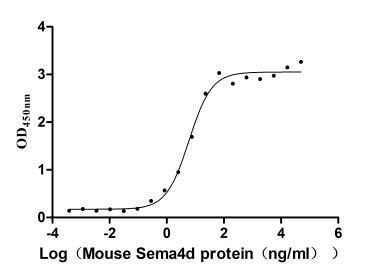
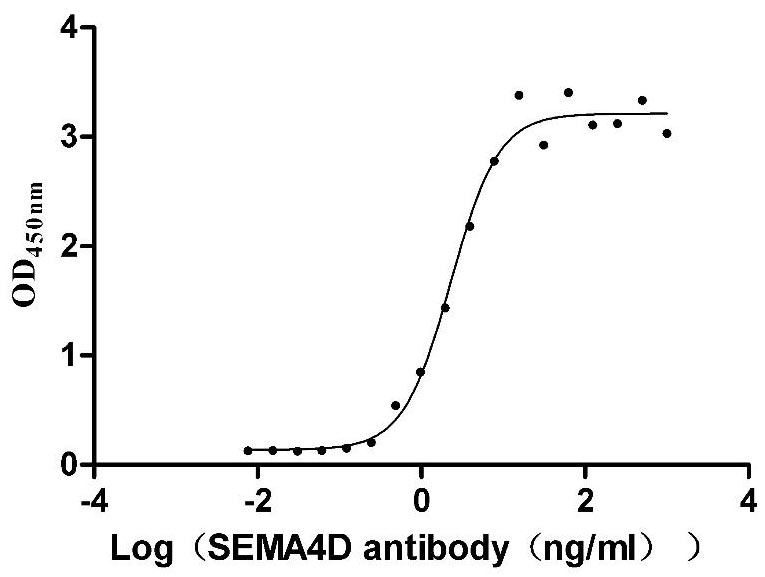
Recombinant Mouse Semaphorin-4D (Sema4d), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
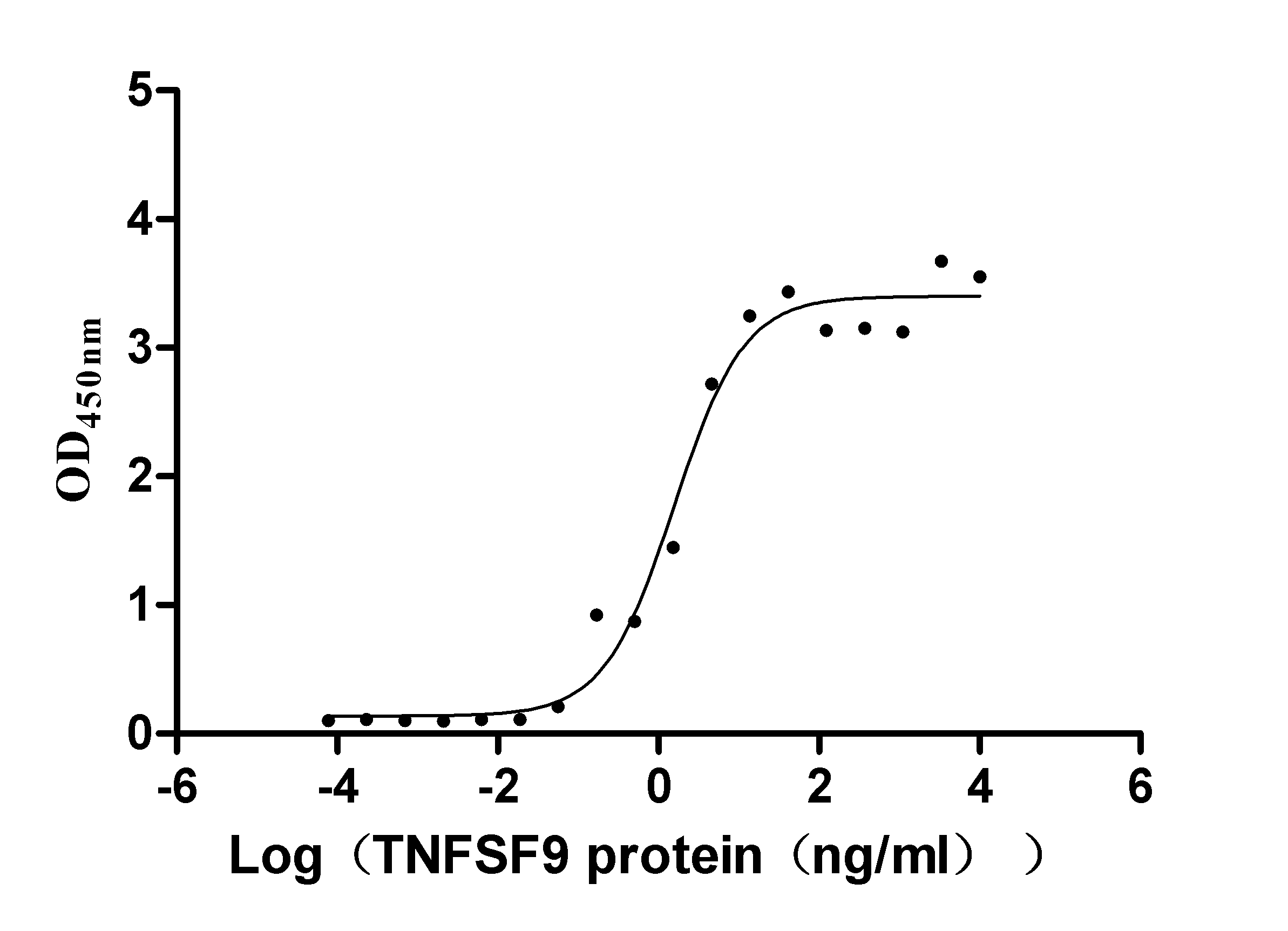
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 9 (TNFRSF9), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca mulatta Semaphorin-4D isoform 1 (SEMA4D), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)
-
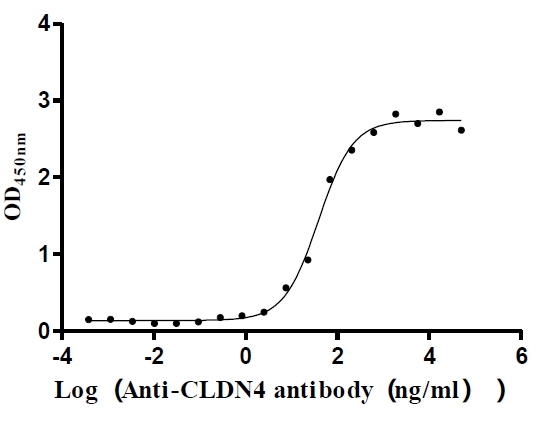
Recombinant Human Claudin-4 (CLDN4)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
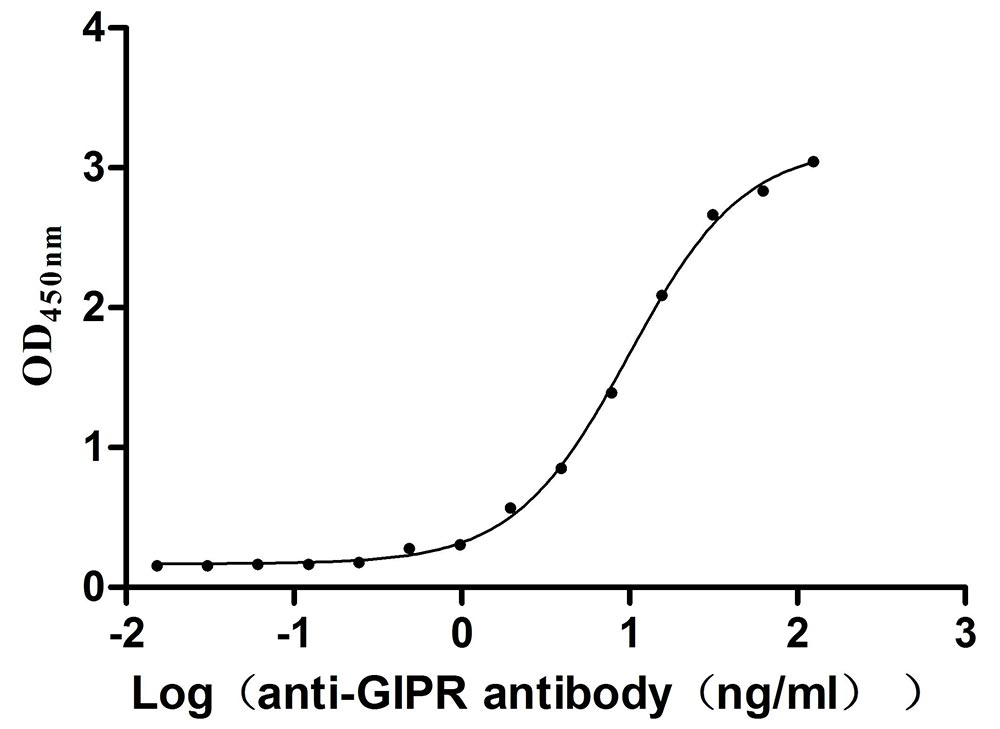
Recombinant Mouse Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (Gipr), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
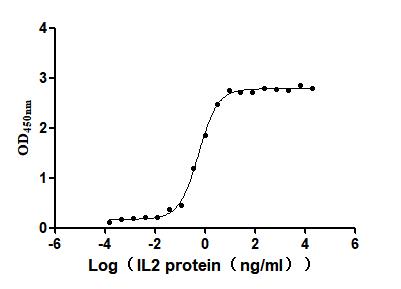
Recombinant Human Interleukin-2 (IL2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
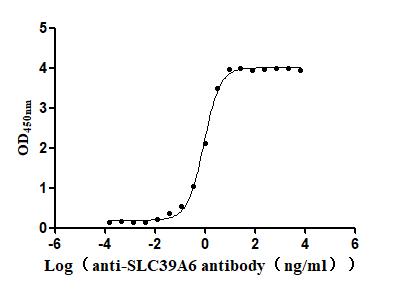
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Zinc transporter ZIP6 isoform X1(SLC39A6),partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)


-AC1.jpg)