Recombinant Rat Sodium channel protein type 4 subunit alpha (Scn4a), partial
-
中文名稱:大鼠Scn4a重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-YP020841RA
-
規格:
-
來源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:大鼠Scn4a重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-EP020841RA
-
規格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:大鼠Scn4a重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-EP020841RA-B
-
規格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:大鼠Scn4a重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-BP020841RA
-
規格:
-
來源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:大鼠Scn4a重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-MP020841RA
-
規格:
-
來源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Scn4a
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:Scn4a; Sodium channel protein type 4 subunit alpha; Mu-1; SkM1; Sodium channel protein skeletal muscle subunit alpha; Sodium channel protein type IV subunit alpha; Voltage-gated sodium channel subunit alpha Nav1.4
-
種屬:Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
蛋白長度:Partial
-
蛋白標簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶點詳情
-
功能:PPore-forming subunit of a voltage-gated sodium channel complex through which Na(+) ions pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. Alternates between resting, activated and inactivated states. Required for normal muscle fiber excitability, normal muscle contraction and relaxation cycles, and constant muscle strength in the presence of fluctuating K(+) levels.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- Intramolecular distances computed from the LRET signals define a geometrical map of Nav1.4 with the bound toxins, and reveal voltage-dependent structural changes related to channel gating PMID: 28202723
- the role of the intracellular IFM motif of rNav1.4 (skeletal muscle isoform of the rat Na(+) channel) on the alpha-beta1 functional interaction PMID: 28012039
- Role of Asparagines in Coupling the Pore and Votage-Sensor Domain in Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels PMID: 26636939
- The study constructs a homology model for the pore domain of the NaV1.4 channel and uses the functional data for the binding of micro-conotoxin GIIIA to NaV1.4 to validate the model. PMID: 25133704
- The relationships between voltage sensors and pore conformations in an inactivation deficient Nav1.4 channel, were investigated. PMID: 23322038
- Effectiveness of SkM1-based antiarrhythmic therapy critically depends on the delivery vehicle, with viral gene delivery seeming to be superior. PMID: 22722661
- SkM1 gene transfer reduces the incidence of inducible ventricular tachycardia / ventricular fibrillation. PMID: 22374989
- Anthopleurin elicited opposing effects on the gating mode, kinetics and charge immobilized during open- versus closed-state fast inactivation of Nav1.4 channels. PMID: 21099342
- amino acid Ile-1575 in the middle of transmembrane segment 6 of domain IV in the adult rat skeletal muscle isoform of rNa(V)1.4 may act as molecular switch allowing for interaction between outer and inner vestibules PMID: 20926383
- Our results demonstrated the unique permeability of guanidine through NaV1.4 gating pores, and defined voltage-dependent and voltage-independent block by divalent and trivalent cations, respectively. PMID: 20660662
- To examine the block by mu-conotoxin KIIIA and its analogs of a sodium channel isoform, nine disulfide-depleted KIIIA-peptides are tested on NaV1.4. When mu-conotoxin binds to NaV1.4, it blocks the sodium current essentially completely. PMID: 20459109
- Role of a conserved neighbouring tryptophan residue at position 736 (W736) of Na(V)1.4 in the pore formation was examined. W736 contributes to the formation of the pore, close to the mouth of the channel, but is not part of the selectivity filter. PMID: 12397382
- Chimeric channels of NaV1.4 and NaV1.5 also indicated that the C-terminal domain is largely responsible for calmodulin effects on inactivation PMID: 15746172
- We studied the properties of a sodium channel comprised only of S5-P-S6 region of the rat sodium channel alpha-subunit Nav1.4 (micro1pore). PMID: 15992775
- low but significant levels of heme-specific transcriptional activity were observed at the hmuO promoter in the chrAS mutants, suggesting that an additional heme-dependent activator is involved in hmuO expression PMID: 16239540
- Data suggest that modulation of the sodium current by the expression of the highly sialylated beta1-subunit may alter the channel gating by increasing the density of surface negative charges in the vicinity of the sodium channel voltage sensing machinery. PMID: 16432696
- We demonstrate that a pH-independent current is found in Na(V)1.4, but not in the cardiac isoform (Na(V)1.5). PMID: 16873405
- an energetically equivalent cation-pi interaction underlies both use-dependent and tonic block of Nav1.4 by TTX PMID: 17237232
- The mutation R663H permits transmembrane permeation of protons, but not larger cations, similar to the conductance displayed by histidine substitution at Shaker K(+) channel S4 sites. PMID: 17591984
- Binding of beta-scorpion toxin modifies Nav1.4 channel function and provides insight into early gating transitions of sodium channels. PMID: 17698594
- muO conotoxins inhibit NaV1.4 channels by interfering with their voltage sensors in domain-2. PMID: 18698149
- Missense mutations R666G, R663H,R666S and R666C (respectively) result in a low-amplitude inward current at the resting potential that may lead to the pathological sarcolemmal depolarization during attacks of weakness in hypokalemic periodic paralysis . PMID: 18824591
- Expression of skeletal SkM1 but not cardiac SCN5A Na+ channel isoform preserves normal conduction in a depolarized cardiac syncytium. PMID: 18977767
- Potassium-sensitive normokalemic periodic paralysis mutations in rat Na(V)1.4 (R669Q/G/W) cause gating pore current that is activated by depolarization and therefore is conducted in the activated state of the voltage sensor. PMID: 19052238
- Data demonstrate that arachidonic acid (AA), but not the metabolic products of AA, can voltage-dependently modulate rNa(V)1.4 currents. PMID: 19097141
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Sodium channel (TC 1.A.1.10) family, Nav1.4/SCN4A subfamily
-
組織特異性:Detected in skeletal muscle.
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
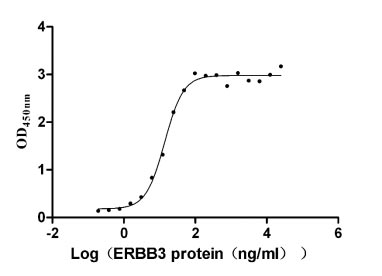
Recombinant Human Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-3 (ERBB3), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
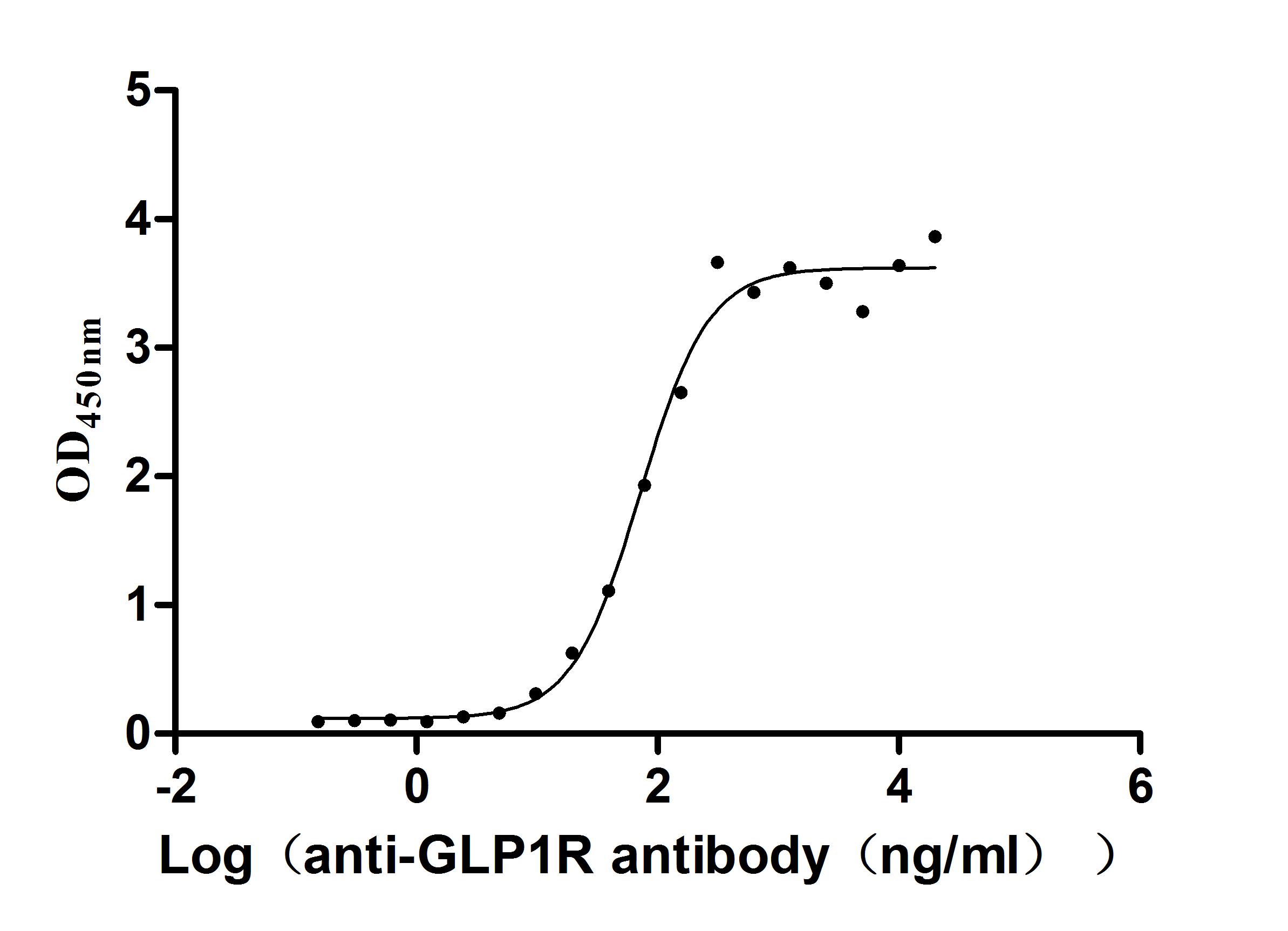
Recombinant Human Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP1R), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
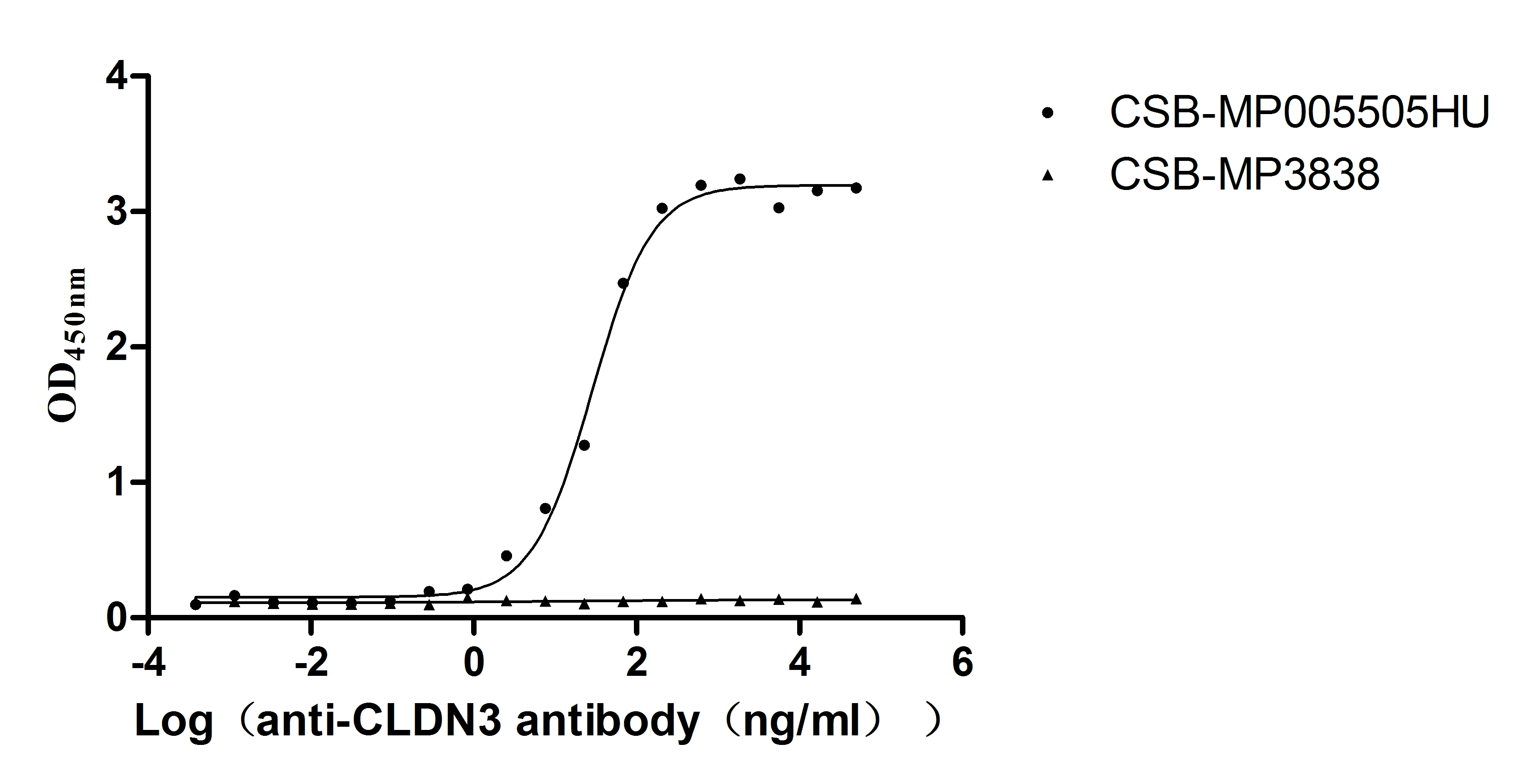
Recombinant Human Claudin-3 (CLDN3)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
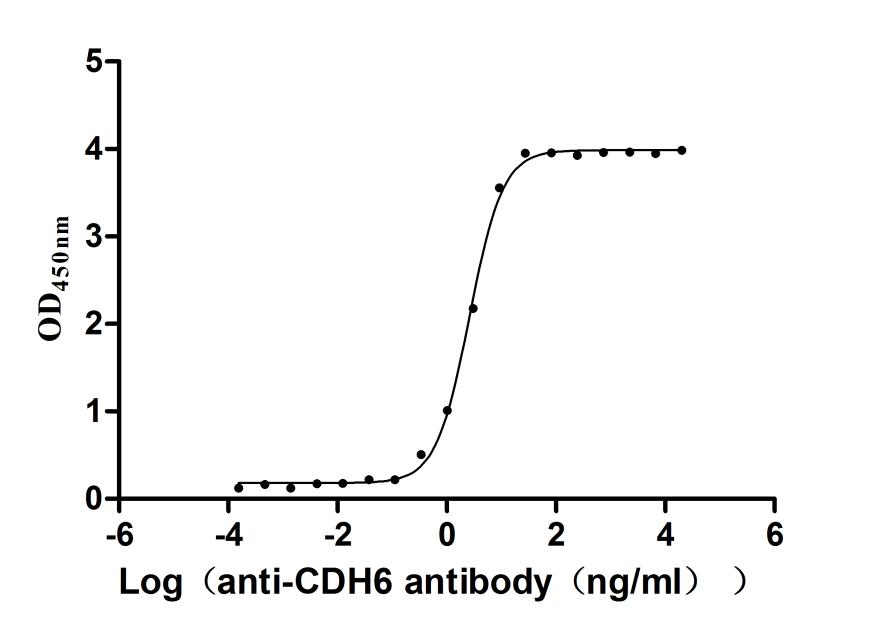
Recombinant Human Cadherin-6 (CDH6), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)