Recombinant Mouse Transcription factor AP-1 (Jun)
In Stock-
中文名稱:小鼠Jun重組蛋白
-
貨號:CSB-EP011972MO
-
規格:¥2328
-
圖片:
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
純度:Greater than 85% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
種屬:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白長度:Full Length
-
來源:E.coli
-
分子量:41.9 kDa
-
表達區域:1-334aa
-
氨基酸序列MTAKMETTFYDDALNASFLQSESGAYGYSNPKILKQSMTLNLADPVGSLKPHLRAKNSDLLTSPDVGLLKLASPELERLIIQSSNGHITTTPTPTQFLCPKNVTDEQEGFAEGFVRALAELHSQNTLPSVTSAAQPVSGAGMVAPAVASVAGAGGGGGYSASLHSEPPVYANLSNFNPGALSSGGGAPSYGAAGLAFPSQPQQQQQPPQPPHHLPQQIPVQHPRLQALKEEPQTVPEMPGETPPLSPIDMESQERIKAERKRMRNRIAASKCRKRKLERIARLEEKVKTLKAQNSELASTANMLREQVAQLKQKVMNHVNSGCQLMLTQQLQTF
Note: The complete sequence may include tag sequence, target protein sequence, linker sequence and extra sequence that is translated with the protein sequence for the purpose(s) of secretion, stability, solubility, etc.
If the exact amino acid sequence of this recombinant protein is critical to your application, please explicitly request the full and complete sequence of this protein before ordering. -
蛋白標簽:N-terminal 6xHis-tagged
-
產品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
緩沖液:If the delivery form is liquid, the default storage buffer is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 5%-50% glycerol. If the delivery form is lyophilized powder, the buffer before lyophilization is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose.
-
復溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:3-7 business days
-
注意事項:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Transcription factor that recognizes and binds to the enhancer heptamer motif 5'-TGA[CG]TCA-3'. Promotes activity of NR5A1 when phosphorylated by HIPK3 leading to increased steroidogenic gene expression upon cAMP signaling pathway stimulation. Involved in activated KRAS-mediated transcriptional activation of USP28. Binds to the USP28 promoter.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- NOS1 inhibition prevents nuclear translocation of the AP1 transcription factor subunits. PMID: 29605772
- these results highlight the metabolic oversight of the nerve injury response via the regulation of JUN activity by O-GlcNAcylation, a pathway that could be important in the neuropathy associated with diabetes and aging. PMID: 30012597
- These results suggest JUN and DDIT3 are independently regulated pro-death signaling molecules in retinal ganglion cells and together account for the vast majority of apoptotic signaling in retinal ganglion cells after axonal injury PMID: 28969695
- persistent distention/stretch on colonic smooth muscle cells could suppress SCF production probably through Ca(2+) -ERK-AP-1-miR-34c deregulation. PMID: 28580775
- Jun is a major regulator of RGC somal degeneration after glaucomatous ocular hypertensive injury. These results suggest in glaucomatous neurodegeneration, JNK-JUN signaling has a major role as a pro-death signaling pathway between axonal injury and somal degeneration. PMID: 28726785
- Loss of epidermal AP1 reduces filaggrin level, alters chemokine expression and produces an ichthyosis-related phenotype. PMID: 28569792
- Study provide evidence that c-jun expression is regulated by WDR13. PMID: 28222755
- The positive feedback regulation of OCT4 and c-JUN, resulting in the continuous expression of oncogenes such as c-JUN, seems to play a critical role in the determination of the cell fate decision from induced pluripotent stem cells to cancer stem cells in liver cancer. PMID: 27341307
- In transgenic mice with graded elevation of Schwann cell c-Jun, high c-Jun elevation is a potential pathogenic mechanism because it inhibits myelination. There was no link between c-Jun elevation and tumorigenesis. Modest c-Jun elevation, which is beneficial for regeneration, is well tolerated during Schwann cell development and in the adult and is compatible with restoration of myelination and function after injury. PMID: 29109239
- Overall, our results provide the first evidence that HDAC6 is capable of inducing expression of pro-inflammatory genes by regulating the ROS-MAPK-NF-kappaB/AP-1 pathways and serves as a molecular target for inflammation. PMID: 27208785
- c-jun expression patterns suggest that c-jun has a pivotal role in the proliferation of embryonic neural precursor cells, but it has also other roles in adult neurogenesis PMID: 28091742
- Data show that miR-200b and miR-200c could directly bind the 3' UTR of JUN, and JUN activated the transcription of srebp1 to increase lipid accumulation. PMID: 27166182
- transgenic mice overexpressing sPLA2 -IIA keratinocytes showed enhanced activation of EGFR and JNK1/2 that led to c-Jun activation. PMID: 27299855
- ths work provides transcriptional catalog for the developing inner circular smooth muscle and suggests that cJun regulates gene expression in the ICM downstream of Hh signaling. PMID: 26930384
- Jun is required to upregulate a programme of genes associated with cell adhesion as Embryonic stem cells exit the pluripotent ground state. PMID: 26850660
- ANXA11 level regulates lymph node metastases and 5-FU resistance of Hca-P murine hepatocarcinoma cells via c-Jun pathway PMID: 26908448
- Taken together, these findings indicate that LT reduces c-Jun protein levels via two distinct mechanisms, thereby inhibiting critical cell functions, including cellular proliferation. PMID: 28893904
- Ca(2+) signaling pathway increases Nr4a1 expression in MA-10 Leydig cells, at least in part, by enhancing the recruitment of coactivator most likely through the MEF2, AP1, and CREB transcription factors thus demonstrating an important interplay between the Ca(2+) and cAMP pathways in regulating Nr4a1 expression. PMID: 26647388
- we performed cotransfections of AP-1 expression plasmids with different mouse Gja1 promoter/luciferase reporter constructs within TM3 Leydig and TM4 Sertoli cells.We showed that a functional cooperation between cJun and cFos activates Gja1 expression and requires an AP-1 DNA regulatory element located between -132 and -26 bp PMID: 28903063
- AP1 factors are important regulators of adult taste cell renewal and their downregulation negatively impacts taste maintenance. PMID: 27787515
- these data indicate that MEF2 and AP-1 confer antagonistic regulation of Hspb7 gene expression in skeletal muscle, with implications for autophagy and muscle atrophy. PMID: 27632998
- results suggest that fibroblasts, c-Jun, and IGF-1 play key roles in mediating stromal-epithelial interactions that are required for the therapeutic effects of finasteride in benign prostate epithelial cells PMID: 28196103
- These findings highlight a key role of the TLR4-NOS1-AP1 signaling axis in regulating macrophage polarization PMID: 28013342
- Data suggest that Sf1 and c-jun interact and cooperate to activate the Fdx1 promoter in MA-10 (tumorigenic cell line) and TM3 (non-tumorigenic cell line) Leydig cells; such activation requires different regulatory elements located between -124 and -306 bp of Fdx1 promoter and involves recruitment of Sf1 to this region. (Sf1 = splicing factor 1; c-jun = proto-oncogene c-jun; Fdx1 = ferredoxin 1) PMID: 28274746
- NF-kappaB and c-Jun coregulate lipopolysaccharide-induced Fra-1 transcription. PMID: 27286066
- BATF/JUN-B and BATF/C-JUN complexes play important roles in OA cartilage destruction through regulating anabolic and catabolic gene expression in chondrocytes. PMID: 27147707
- this study shows that c-Jun regulates the activation state of macrophages and promotes arthritis via differentially regulating cyclooxygenase-2 and arginase-1 levels PMID: 28298526
- PLIO treatment inhibited nuclear factorkappaB (NFkappaB) nuclear translocation in B16F10 cells. In addition, PLIO treatment inhibited the phosphorylation of c-Jun Nterminal kinases and AKT PMID: 27666322
- Anxa5 mediates the in vitro malignant behaviours of murine hepatocarcinoma Hca-F cells via ERK2/c-Jun/p-c-Jun(Ser73) and ERK2/E-cadherin pathways. PMID: 27697636
- These findings indicate that c-Jun has important functions during HBV-associated tumorigenesis by promoting hepatocyte proliferation as well as progression of dysplasia PMID: 26470729
- The TLR4 pathway may play an important role in regulating AP-1 activation PMID: 26803521
- These observations suggest that the antiinflammatory properties of crebanine may stem from the inhibition of proinflammatory mediators via suppression of the NF-kappaB, AP-1, MAPKs, and Akt signaling pathways. PMID: 26499331
- In a model of heavy metal poisoning, copper contamination of drinking water (as can occur with corrosion in aging plumbing systems) up-regulates binding of transcription factor AP-1 in neurons of brain, even in low concentrations. PMID: 23719850
- Transplant-induced reactivation of murine cytomegalovirus immediate early gene expression is associated with recruitment of NF-kappaB and AP-1 to the major immediate early promoter. PMID: 26795571
- ERK contributes to the morphine-induced hyperalgesia by regulating the activation of c-JUN PMID: 26165762
- These results indicate that both NF-kappaB and c-Jun/AP-1 are involved in regulating anti-beta2GPI-induced expression of prothrombotic and proinflammatory molecules in vivo. PMID: 26829121
- Tumorigenesis by Meis1 overexpression is accompanied by a change of DNA target-sequence specificity which allows binding to the AP-1 element. PMID: 26259236
- BMP7 and FGF9 coordinately regulate AP-1 transcription to promote G1-S cell cycle progression and nephron progenitor cells proliferation. PMID: 26634297
- Our findings conclude that pharmacological actions of CoQ0 are mediated via inhibition of NFkappaB/AP-1 activation and induction of Nrf2/ARE-signaling. PMID: 26548719
- Taken together, our results suggest that LPS induces PDK4 expression and alters glucose metabolism via the JNK pathway. PMID: 26740179
- In the heterologous mouse model loss of c-Jun expression led to ablation of dissemination of Theileria annulata-infected and transformed macrophages. PMID: 25375322
- Our results demonstrate that c-Jun can suppress adipocyte differentiation through the down-regulation of KLF15 at the transcriptional level. PMID: 26692489
- the regulation of synaptic-vesicle (SV) recycling via early endosomes by the interdependent regulation of AP-2-mediated endocytosis and AP-1/sigma1B-mediated SV reformation, is reported. PMID: 25128028
- A reciprocal antagonism between the MITF and c-Jun interconnects inflammation-induced dedifferentiation with pro-inflammatory cytokine responsiveness of melanoma cells favouring myeloid cell recruitment. PMID: 26530832
- Data indicate that Sp1 and AP-1-related factors are involved in the regulation of MFG-E8 gene transcription by targeting their binding sites in the 5'-flanking region under physiological and inflammatory states. PMID: 25711369
- Data show that p38 MAP Kinase (p38MAPK)-shRNA transfection and the p38MAPK inhibitor SB203580 significantly inhibited activator protein-1 (AP-1) activity. PMID: 25966080
- AS-IV effectively inhibits LPS-induced acute inflammatory responses by modulating NF-kappaB and AP-1 signaling pathways PMID: 25960613
- suggest that TLR-mediated Sesn2 induction is dependent on AP-1, Nrf2, and the inhibition of ubiquitin-mediated degradation of Sesn2 and might protect cells against endotoxin toxicity PMID: 25637945
- Dioxin exposure markedly inhibited c-Jun phosphorylation in Map3k1-deficient embryonic eyelid epithelium, suggesting that dioxin-induced AHR pathways can synergize with gene mutations to inhibit MAP3K1 signaling. PMID: 26109068
- The NF-kappaB-to-AP-1 switch is a protective mechanism to ensure timely transition from endothelial barrier injury to repair, accelerating barrier restoration following MOI. PMID: 24986487
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:BZIP family, Jun subfamily
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 14 (TNFRSF14), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Semaphorin-4D (SEMA4D), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Nectin-4 (NECTIN4), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis CD93 molecule (CD93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Cell adhesion molecule 1 (CADM1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
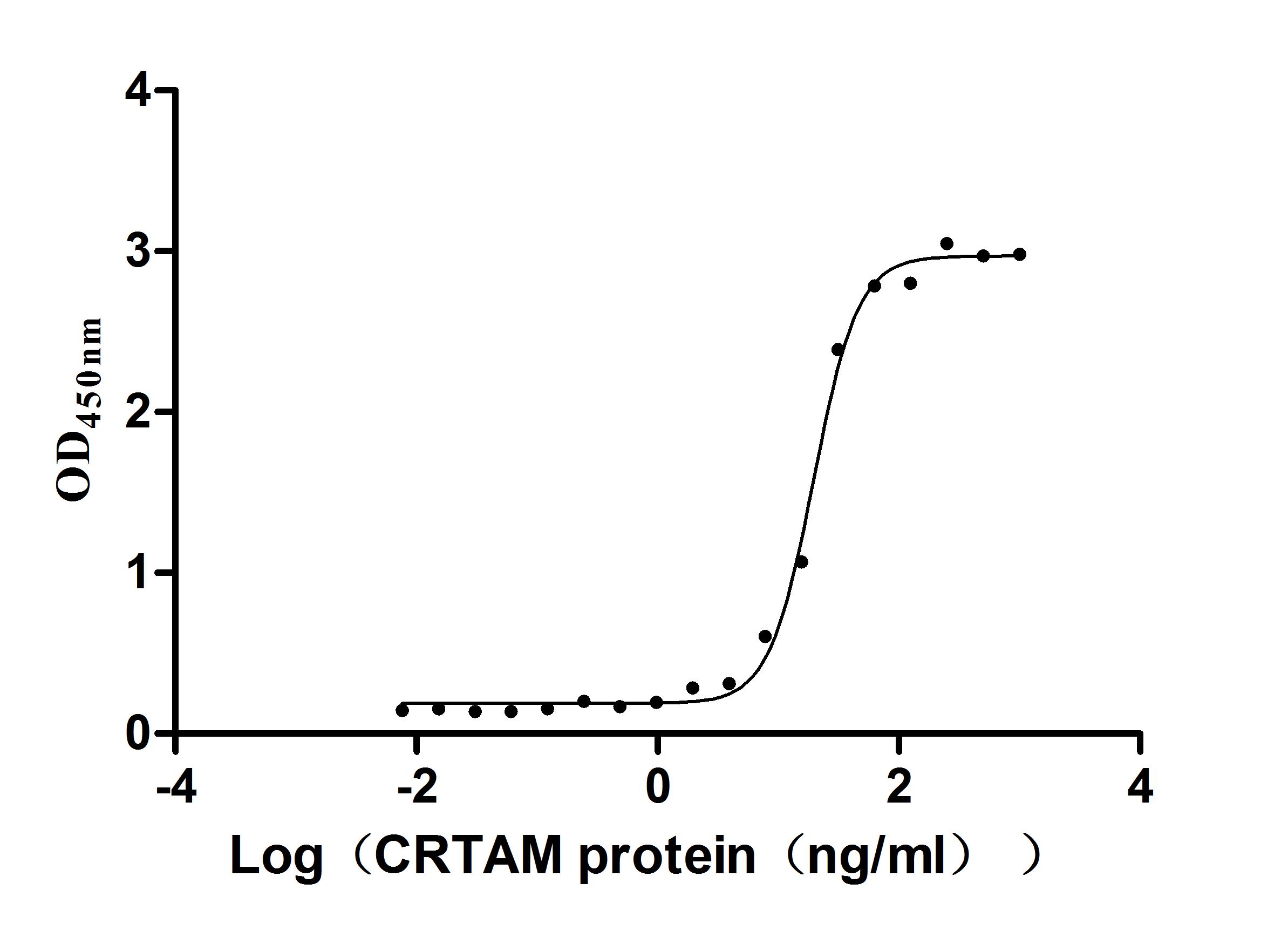
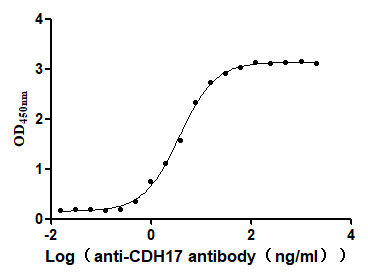
Recombinant Human Cadherin-17 (CDH17), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
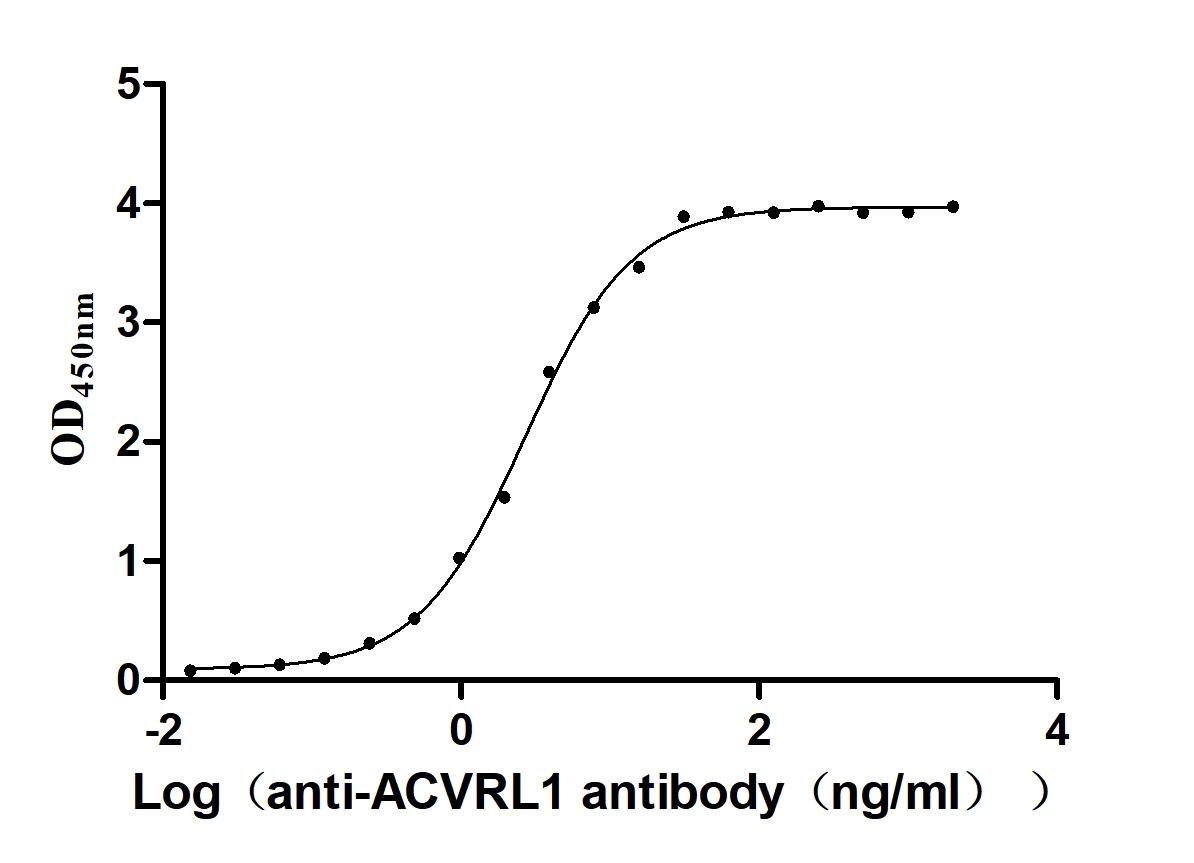
Recombinant Human Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor R3 (ACVRL1), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
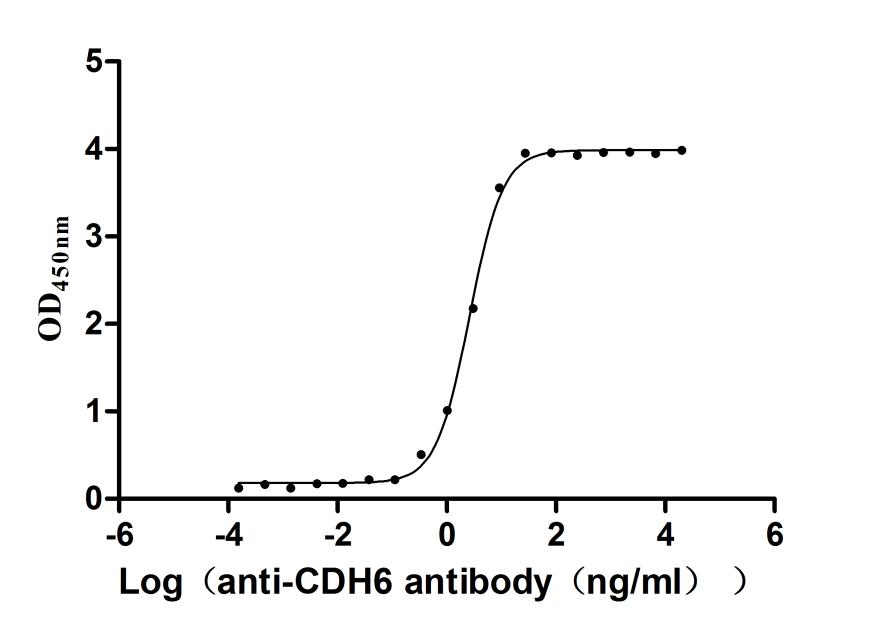
Recombinant Human Cadherin-6(CDH6),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)