Recombinant Mouse Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein (Mlkl)
-
中文名稱:小鼠Mlkl重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-EP861529MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Mlkl重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-EP861529MO-B
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Mlkl重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-BP861529MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:小鼠Mlkl重組蛋白
-
貨號(hào):CSB-MP861529MO
-
規(guī)格:
-
來源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
純度:Greater than 85% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:MlklMixed lineage kinase domain-like protein
-
種屬:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白長(zhǎng)度:Full length
-
表達(dá)區(qū)域:1-472aa
-
氨基酸序列MDKLGQIIKLGQLIYEQCEKMKYCRKQCQRLGNRVHGLLQPLQRLQAQGKKNLPDDITAALGRFDEVLKEANQQIEKFSKKSHIWKFVSVGNDKILFHEVNEKLRDVWEELLLLLQVYHWNTVSDVSQPASWQQEDRQDAEEDGNENMKVILMQLQISVEEINKTLKQCSLKPTQEIPQDLQIKEIPKEHLGPPWTKLKTSKMSTIYRGEYHRSPVTIKVFNNPQAESVGIVRFTFNDEIKTMKKFDSPNILRIFGICIDQTVKPPEFSIVMEYCELGTLRELLDREKDLTMSVRSLLVLRAARGLYRLHHSETLHRNISSSSFLVAGGYQVKLAGFELSKTQNSISRTAKSTKAERSSSTIYVSPERLKNPFCLYDIKAEIYSFGIVLWEIATGKIPFEGCDSKKIRELVAEDKKQEPVGQDCPELLREIINECRAHEPSQRPSVDGRSLSGRERILERLSAVEESTDKKV
-
蛋白標(biāo)簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復(fù)溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲(chǔ)存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質(zhì)期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項(xiàng):Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相關(guān)產(chǎn)品
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
功能:Pseudokinase that plays a key role in TNF-induced necroptosis, a programmed cell death process. Does not have protein kinase activity. Activated following phosphorylation by RIPK3, leading to homotrimerization, localization to the plasma membrane and execution of programmed necrosis characterized by calcium influx and plasma membrane damage. In addition to TNF-induced necroptosis, necroptosis can also take place in the nucleus in response to orthomyxoviruses infection: following ZBP1 activation, which senses double-stranded Z-RNA structures, nuclear RIPK3 catalyzes phosphorylation and activation of MLKL, promoting disruption of the nuclear envelope and leakage of cellular DNA into the cytosol. Binds to highly phosphorylated inositol phosphates such as inositolhexakisphosphate (InsP6) which is essential for its necroptotic function.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 deficiency negates chronic low-to-moderate alcohol consumption-induced cardioprotecion possibly via ROS-dependent apoptosis and RIP1/RIP3/MLKL-mediated necroptosis. PMID: 27840306
- M. tuberculosis and TNFalpha synergise to induce necroptosis in murine fibroblasts via RIPK1-dependent mechanisms and characterized by phosphorylation of Ser345 of the MLKL necroptosis death effector. PMID: 28892415
- hydrostatic pressure (EHP)-induced RGC-5 cell necroptosis was mediated by MLKL PMID: 28981598
- Biological events and molecular signaling following MLKL activation during necroptosis have been reported. PMID: 28854080
- The authors report here that male reproductive organs of both Ripk3- and Mlkl-knockout mice retain 'youthful' morphology and function into advanced age, while those of age-matched wild-type mice deteriorate. Feeding of wild-type mice with an RIPK1 inhibitor prior to the normal onset of age-related changes in their reproductive organs blocked the appearance of signs of aging. PMID: 28807105
- Data indicate that mixed-lineage kinase domain-like protein (MLKL) oligomerization, membrane translocation, and cell death occur simultaneously with NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) activation in bone marrow-derived macrophages. PMID: 28096356
- Pull down experiments with biotinylated Sorafenib show that it binds independently RIPK1, RIPK3 and MLKL. Moreover, it inhibits RIPK1 and RIPK3 kinase activity. In vivo Sorafenib protects against TNF-induced systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and renal ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI). PMID: 28661484
- Knock-out mice deficient in MLKL or RIP3 had increased survival and reduced pulmonary injury during Serratia marcescens pneumonia. PMID: 28387756
- Our findings reveal that MLKL and FADD play critical roles in preventing lymphoproliferative disease and activating the NLRP3 inflammasome PMID: 27498868
- RIPK3 and/or MLKL may exert functions independently of necroptosis. PMID: 27523270
- Data suggest that necroptotic cells externalize phosphatidylserine (PS) after translocation of phosphorylated Mlkl to cell membrane; necroptotic cells with exposed PS release extracellular vesicles containing Mlkl; inhibition of Mlkl after PS exposure can reverse process of necroptosis and restore cell viability. PMID: 28650960
- results reveal a pathway for MLKL-dependent programmed necrosis that is executed in the absence of RIPK3 and potentially drives the pathogenesis of severe liver diseases. PMID: 27756058
- Mice deficient in RIPK3 or doubly deficient in MLKL and FADD, but not MLKL alone, are more susceptible to influenza A virus than their wild-type counterparts, revealing an important role for RIPK3-mediated apoptosis in antiviral immunity. PMID: 27321907
- MLKL octamer formation depends on alpha-helices 4 and 5. PMID: 27920255
- The findings reported here indicate that palmitate induces RIP1/RIP3-dependent necrosis via MLKL-mediated pore formation of RAW 264.7 cells in the plasma membrane, which could provide a new mechanism to explain the link between elevated levels of free fatty acids (FFAs), palmitate in particular, and macrophage death. PMID: 27856241
- The results indicate that RIP1 and MLKL contribute to necroptotic cell death after HCoV-OC43 infection to limit viral replication. PMID: 27795420
- In AML, Mlkl expression is reduced. This leads to reduced activation of the inflammasome and reduced myeloid differentiation. PMID: 27411587
- we demonstrate that the phosphorylation of Ser345 is not required for the interaction between RIPK3 and MLKL in the necrosome, but is essential for MLKL translocation, accumulation in the plasma membrane, and consequent necroptosis. PMID: 26024392
- deficiency of RIPK3 or MLKL prevents oxalate crystal-induced acute kidney injury. PMID: 26817517
- RIPK3 can promote NLRP3 inflammasome and IL-1beta inflammatory responses independent of MLKL and necroptotic cell death PMID: 25693118
- Cisplatin stimulates RIP1/RP3/MLKL-dependent necrotic cell death in renal tubules, which finally causes renal dysfunction PMID: 25788533
- These data reveal a potential role for RIPK3 as a suppressor of MLKL activation and indicate that phosphorylation can fine-tune the ability of MLKL to induce necroptosis. PMID: 26283547
- MLKL acctivation unleashes the four-helix bundle domain to induce membrane localization and necroptotic cell death PMID: 25288762
- Ectopic expression of ICP6, but not RHIM mutant ICP6, directly activated RIP3/MLKL-mediated necrosis. PMID: 25316792
- Knockdown of RIPK3 or MLKL blocks TNF-induced necroptosis. PMID: 24434512
- [review] Although studies have demonstrated that mixed lineage kinase domain-like (MLKL) protein is the only substrate of RIP3 kinase that is essential for necroptotic death, the molecular determinants acting downstream of MLKL remain ambiguous. PMID: 24556404
- Data suggest that nucleotide- (ATP-) binding residues of human MLKL have divergently evolved from mouse Mlkl and conventional protein kinases; studies include small-angle X-ray scattering, thermal shift of nucleotide binding, and sequence alignment. PMID: 24219132
- Neither Mlkl nor Rip3 deficiency provided protection against polymicrobial sepsis-induced animal death in the study of septic shock induced by CLP. PMID: 23835476
- Toll-like receptor 3-mediated necrosis via TRIF, RIP3, and MLKL. PMID: 24019532
- crystal structure determined; structure-guided mutation of the MLKL pseudoactive site resulted in constitutive, RIPK3-independent necroptosis, demonstrating that modification of MLKL is essential for propagation of the necroptosis pathway downstream of RIPK3 PMID: 24012422
- the importance of the RIP3-MLKL interaction in the formation of functional necrosomes and suggest that translocation of necrosomes to mitochondria-associated membranes is essential for necroptosis signaling. PMID: 23612963
- Findings implicate MLKL as a key mediator of necrosis signaling downstream of the kinase RIP3. PMID: 22265413
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細(xì)胞定位:Cytoplasm. Cell membrane. Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:Protein kinase superfamily
-
組織特異性:Highly expressed in thymus, colon, intestine, liver, spleen and lung. Expressed at much lower level in skeletal muscle, heart and kidney. Not detected in brain.
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫鏈接:
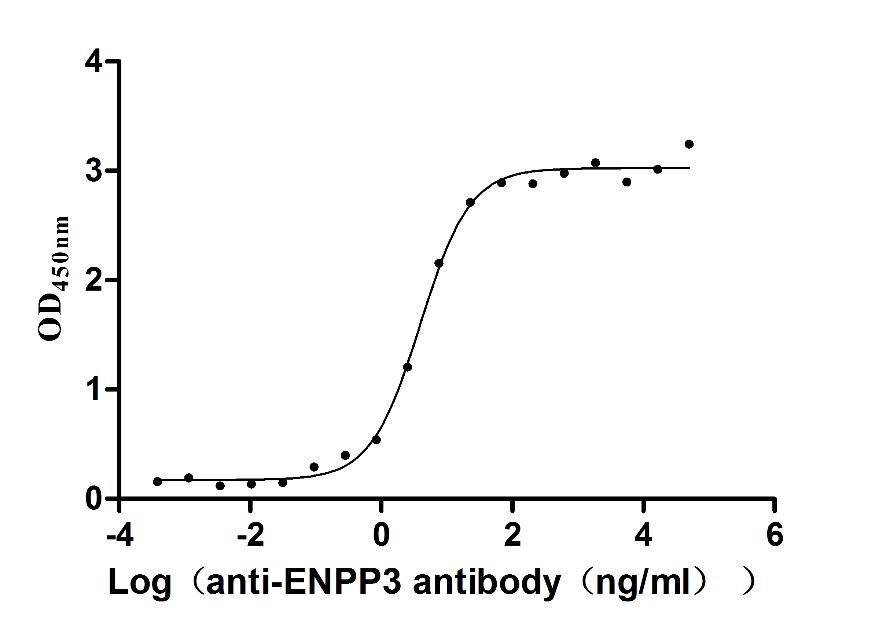
Most popular with customers
-
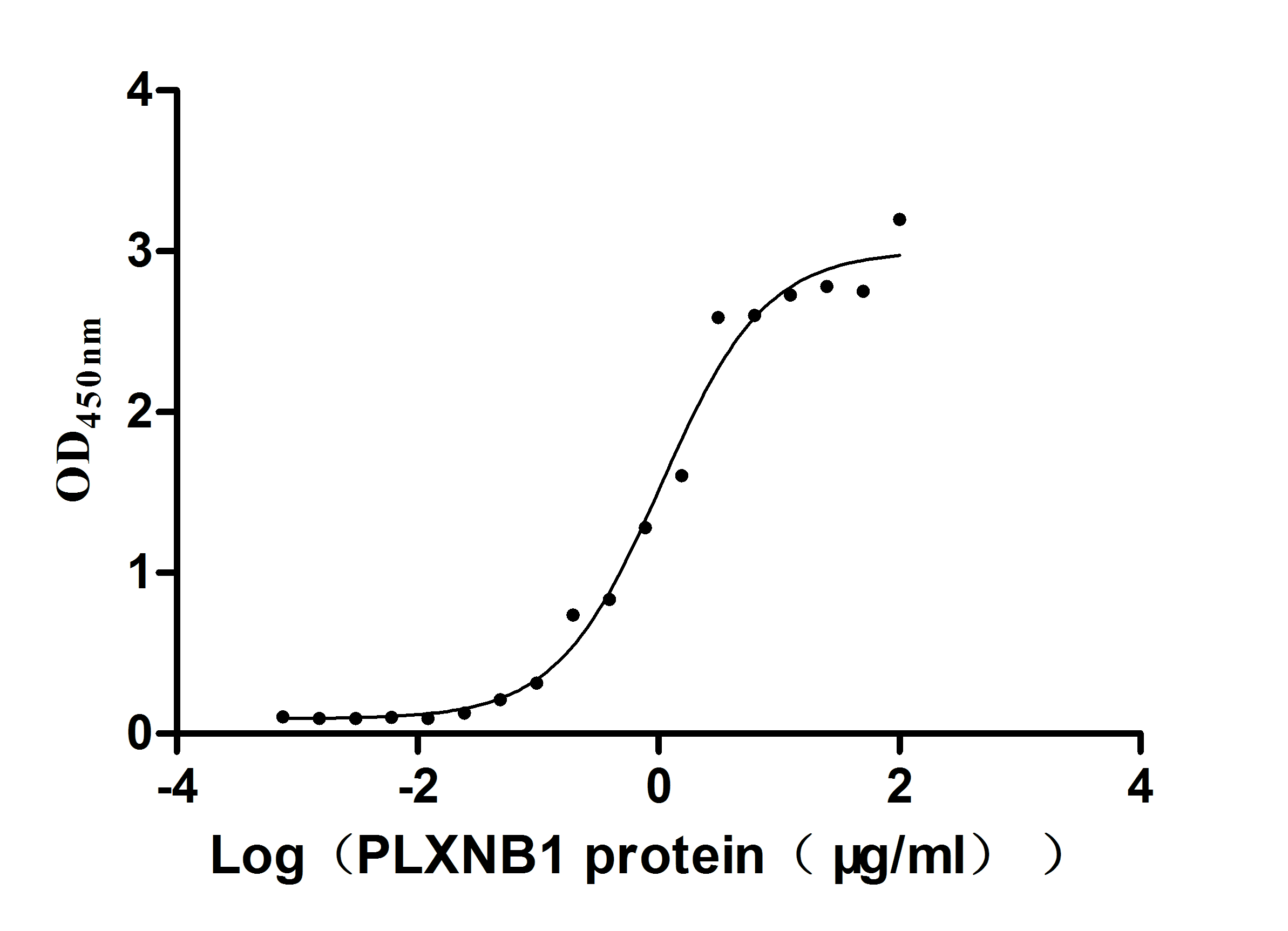
Recombinant Human Plexin-B1 (PLXNB1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
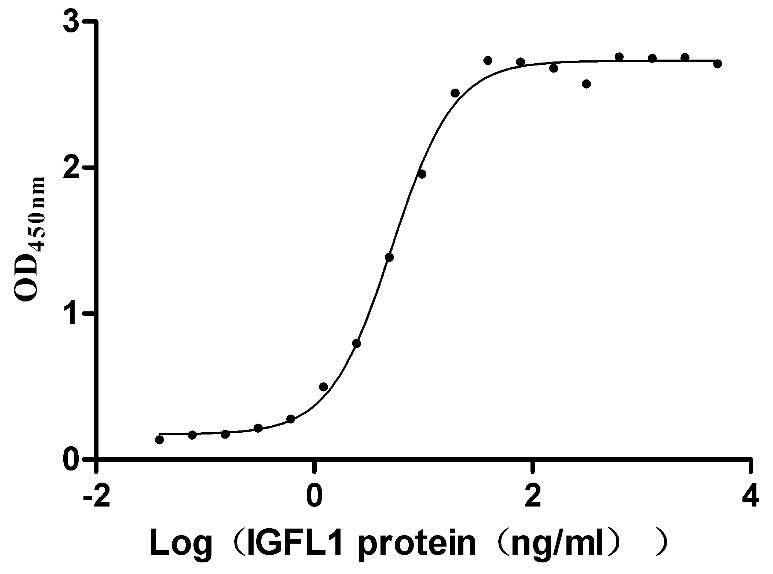
Recombinant Human IGF-like family receptor 1 (IGFLR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
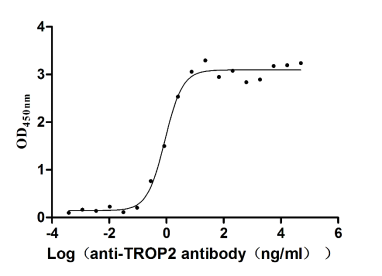
Recombinant Human Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (TACSTD2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
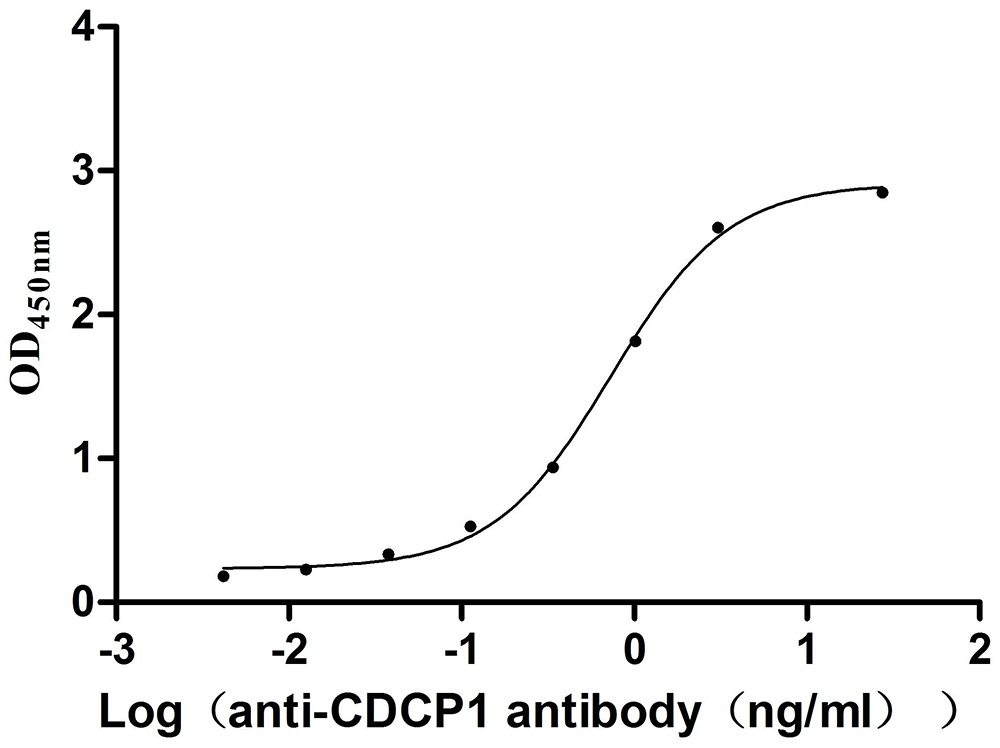
Recombinant Mouse CUB domain-containing protein 1 (Cdcp1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
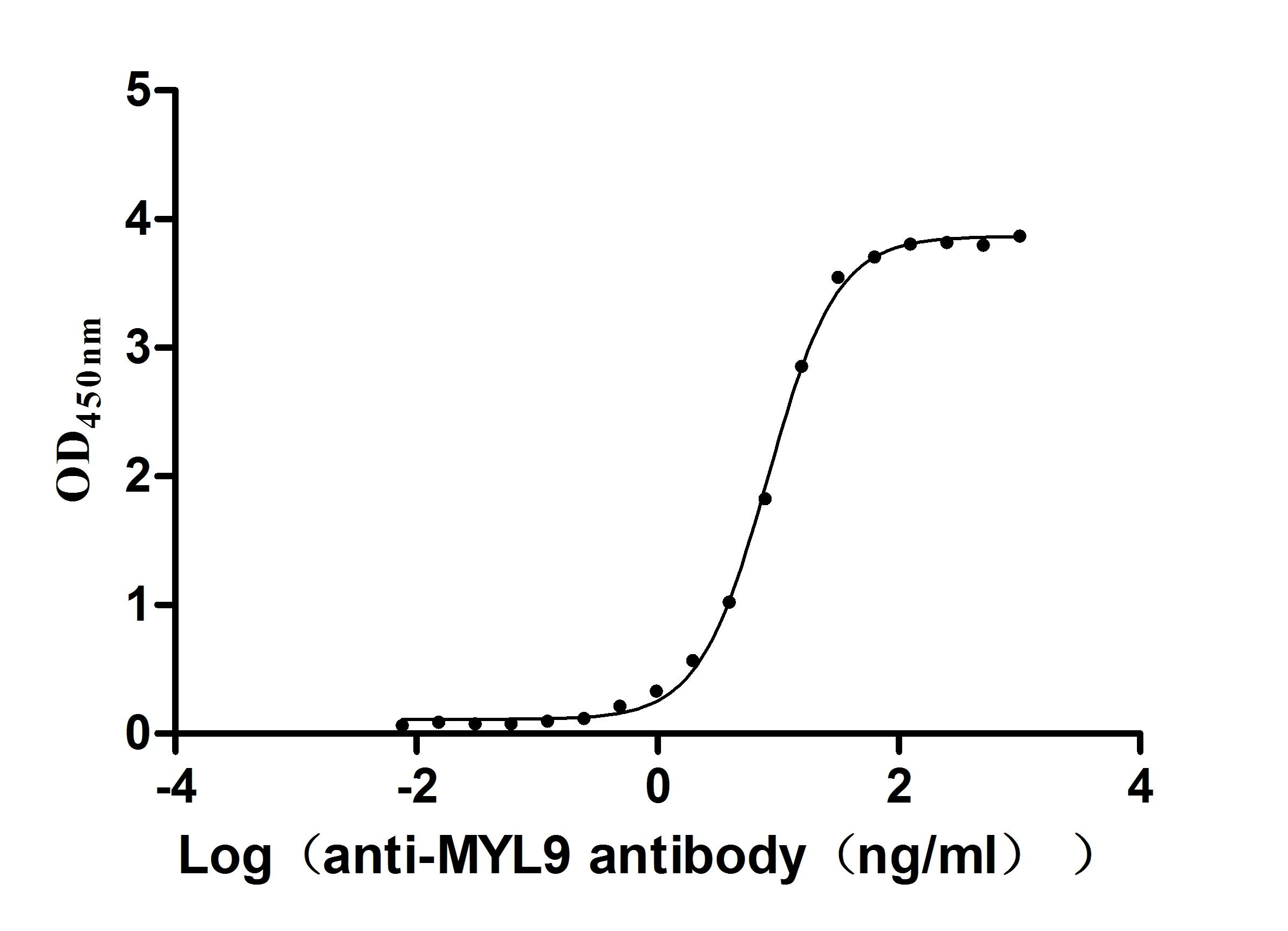
Recombinant Human Myosin regulatory light chain 12B (MYL12B) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
-
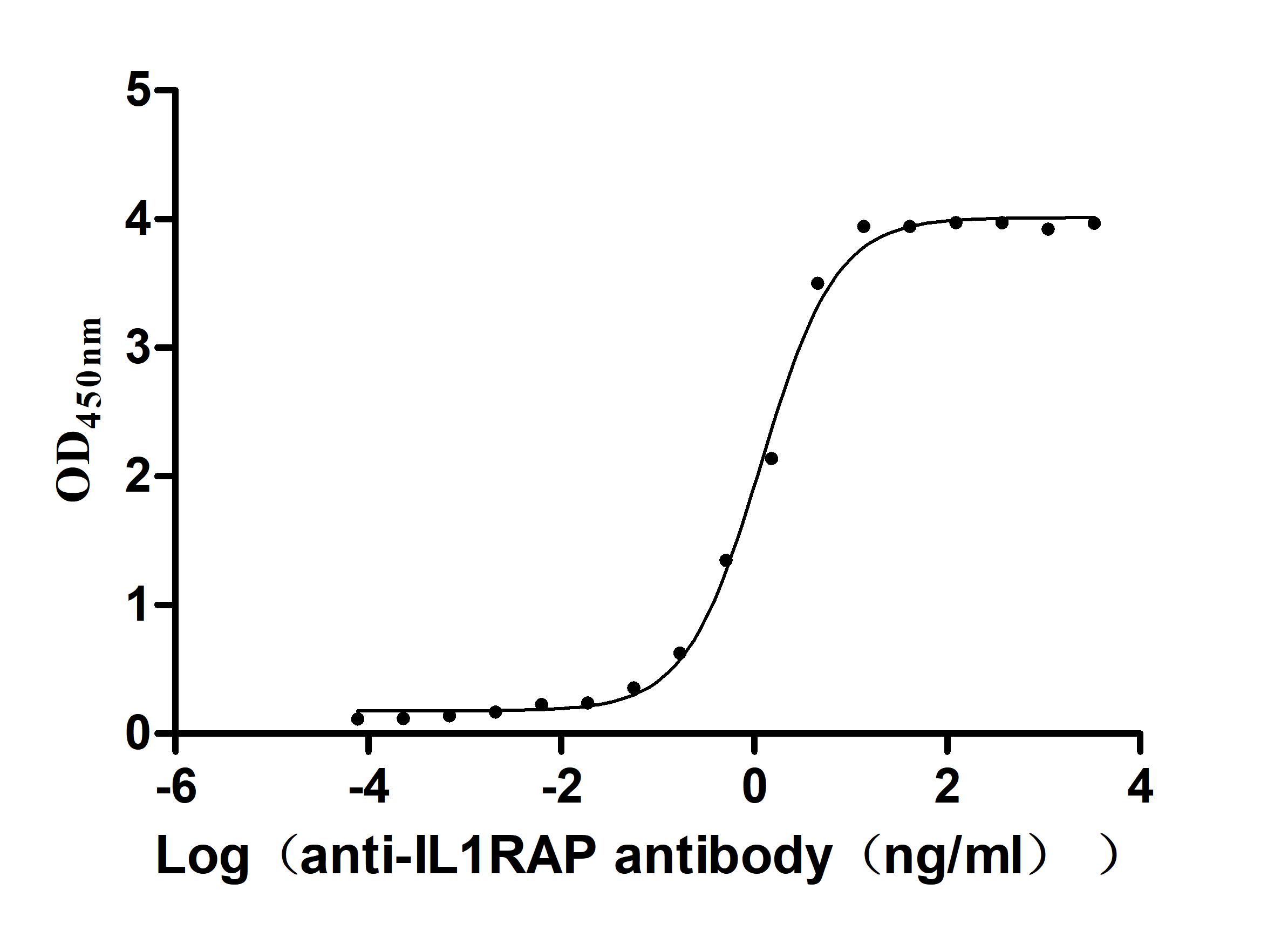
Recombinant Human Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (IL1RAP), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)