Recombinant Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B Gag-Pol polyprotein (gag-pol), partial
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B Gag-Pol polyprotein(gag-pol) ,partial
-
貨號:CSB-YP361033HKM
-
規格:
-
來源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B Gag-Pol polyprotein(gag-pol) ,partial
-
貨號:CSB-EP361033HKM
-
規格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B Gag-Pol polyprotein(gag-pol) ,partial
-
貨號:CSB-EP361033HKM-B
-
規格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B Gag-Pol polyprotein(gag-pol) ,partial
-
貨號:CSB-BP361033HKM
-
規格:
-
來源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B Gag-Pol polyprotein(gag-pol) ,partial
-
貨號:CSB-MP361033HKM
-
規格:
-
來源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:gag-pol
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:gag-pol; Gag-Pol polyprotein; Pr160Gag-Pol) [Cleaved into: Matrix protein p17; MA); Capsid protein p24; CA); Spacer peptide 1; SP1; p2); Nucleocapsid protein p7; NC); Transframe peptide; TF); p6-pol; p6*); Protease; EC 3.4.23.16; PR; Retropepsin); Reverse transcriptase/ribonuclease H; EC 2.7.7.49; EC 2.7.7.7; EC 3.1.26.13; Exoribonuclease H; EC 3.1.13.2; p66 RT); p51 RT; p15; Integrase; IN; EC 2.7.7.-; EC 3.1.-.-)]
-
種屬:Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 group M subtype B (isolate BRU/LAI) (HIV-1)
-
蛋白長度:Partial
-
蛋白標簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶點詳情
-
功能:Gag-Pol polyprotein and Gag polyprotein may regulate their own translation, by the binding genomic RNA in the 5'-UTR. At low concentration, Gag-Pol and Gag would promote translation, whereas at high concentration, the polyproteins encapsidate genomic RNA and then shutt off translation.; Matrix protein p17 targets Gag and Gag-pol polyproteins to the plasma membrane via a multipartite membrane-binding signal, that includes its myristoylated N-terminus. Matrix protein is part of the pre-integration complex. Implicated in the release from host cell mediated by Vpu. Binds to RNA.; Forms the conical core that encapsulates the genomic RNA-nucleocapsid complex in the virion. Most core are conical, with only 7% tubular. The core is constituted by capsid protein hexamer subunits. The core is disassembled soon after virion entry. Host restriction factors such as TRIM5-alpha or TRIMCyp bind retroviral capsids and cause premature capsid disassembly, leading to blocks in reverse transcription. Capsid restriction by TRIM5 is one of the factors which restricts HIV-1 to the human species. Host PIN1 apparently facilitates the virion uncoating. On the other hand, interactions with PDZD8 or CYPA stabilize the capsid.; Nucleocapsid protein p7 encapsulates and protects viral dimeric unspliced genomic RNA (gRNA). Binds these RNAs through its zinc fingers. Acts as a nucleic acid chaperone which is involved in rearangement of nucleic acid secondary structure during gRNA retrotranscription. Also facilitates template switch leading to recombination. As part of the polyprotein, participates in gRNA dimerization, packaging, tRNA incorporation and virion assembly.; The aspartyl protease mediates proteolytic cleavages of Gag and Gag-Pol polyproteins during or shortly after the release of the virion from the plasma membrane. Cleavages take place as an ordered, step-wise cascade to yield mature proteins. This process is called maturation. Displays maximal activity during the budding process just prior to particle release from the cell. Also cleaves Nef and Vif, probably concomitantly with viral structural proteins on maturation of virus particles. Hydrolyzes host EIF4GI and PABP1 in order to shut off the capped cellular mRNA translation. The resulting inhibition of cellular protein synthesis serves to ensure maximal viral gene expression and to evade host immune response. Also mediates cleavage of host YTHDF3. Mediates cleavage of host CARD8, thereby activating the CARD8 inflammasome, leading to the clearance of latent HIV-1 in patient CD4(+) T-cells after viral reactivation; in contrast, HIV-1 can evade CARD8-sensing when its protease remains inactive in infected cells prior to viral budding.; Reverse transcriptase/ribonuclease H (RT) is a multifunctional enzyme that converts the viral RNA genome into dsDNA in the cytoplasm, shortly after virus entry into the cell. This enzyme displays a DNA polymerase activity that can copy either DNA or RNA templates, and a ribonuclease H (RNase H) activity that cleaves the RNA strand of RNA-DNA heteroduplexes in a partially processive 3' to 5' endonucleasic mode. Conversion of viral genomic RNA into dsDNA requires many steps. A tRNA(3)-Lys binds to the primer-binding site (PBS) situated at the 5'-end of the viral RNA. RT uses the 3' end of the tRNA primer to perform a short round of RNA-dependent minus-strand DNA synthesis. The reading proceeds through the U5 region and ends after the repeated (R) region which is present at both ends of viral RNA. The portion of the RNA-DNA heteroduplex is digested by the RNase H, resulting in a ssDNA product attached to the tRNA primer. This ssDNA/tRNA hybridizes with the identical R region situated at the 3' end of viral RNA. This template exchange, known as minus-strand DNA strong stop transfer, can be either intra- or intermolecular. RT uses the 3' end of this newly synthesized short ssDNA to perform the RNA-dependent minus-strand DNA synthesis of the whole template. RNase H digests the RNA template except for two polypurine tracts (PPTs) situated at the 5'-end and near the center of the genome. It is not clear if both polymerase and RNase H activities are simultaneous. RNase H probably can proceed both in a polymerase-dependent (RNA cut into small fragments by the same RT performing DNA synthesis) and a polymerase-independent mode (cleavage of remaining RNA fragments by free RTs). Secondly, RT performs DNA-directed plus-strand DNA synthesis using the PPTs that have not been removed by RNase H as primers. PPTs and tRNA primers are then removed by RNase H. The 3' and 5' ssDNA PBS regions hybridize to form a circular dsDNA intermediate. Strand displacement synthesis by RT to the PBS and PPT ends produces a blunt ended, linear dsDNA copy of the viral genome that includes long terminal repeats (LTRs) at both ends.; Catalyzes viral DNA integration into the host chromosome, by performing a series of DNA cutting and joining reactions. This enzyme activity takes place after virion entry into a cell and reverse transcription of the RNA genome in dsDNA. The first step in the integration process is 3' processing. This step requires a complex comprising the viral genome, matrix protein, Vpr and integrase. This complex is called the pre-integration complex (PIC). The integrase protein removes 2 nucleotides from each 3' end of the viral DNA, leaving recessed CA OH's at the 3' ends. In the second step, the PIC enters cell nucleus. This process is mediated through integrase and Vpr proteins, and allows the virus to infect a non dividing cell. This ability to enter the nucleus is specific of lentiviruses, other retroviruses cannot and rely on cell division to access cell chromosomes. In the third step, termed strand transfer, the integrase protein joins the previously processed 3' ends to the 5' ends of strands of target cellular DNA at the site of integration. The 5'-ends are produced by integrase-catalyzed staggered cuts, 5 bp apart. A Y-shaped, gapped, recombination intermediate results, with the 5'-ends of the viral DNA strands and the 3' ends of target DNA strands remaining unjoined, flanking a gap of 5 bp. The last step is viral DNA integration into host chromosome. This involves host DNA repair synthesis in which the 5 bp gaps between the unjoined strands are filled in and then ligated. Since this process occurs at both cuts flanking the HIV genome, a 5 bp duplication of host DNA is produced at the ends of HIV-1 integration. Alternatively, Integrase may catalyze the excision of viral DNA just after strand transfer, this is termed disintegration.
-
亞細胞定位:[Gag-Pol polyprotein]: Host cell membrane; Lipid-anchor. Host endosome, host multivesicular body.; [Matrix protein p17]: Virion membrane; Lipid-anchor. Host nucleus. Host cytoplasm.; [Capsid protein p24]: Virion.; [Nucleocapsid protein p7]: Virion.; [Reverse transcriptase/ribonuclease H]: Virion.; [Integrase]: Virion. Host nucleus. Host cytoplasm.
Most popular with customers
-
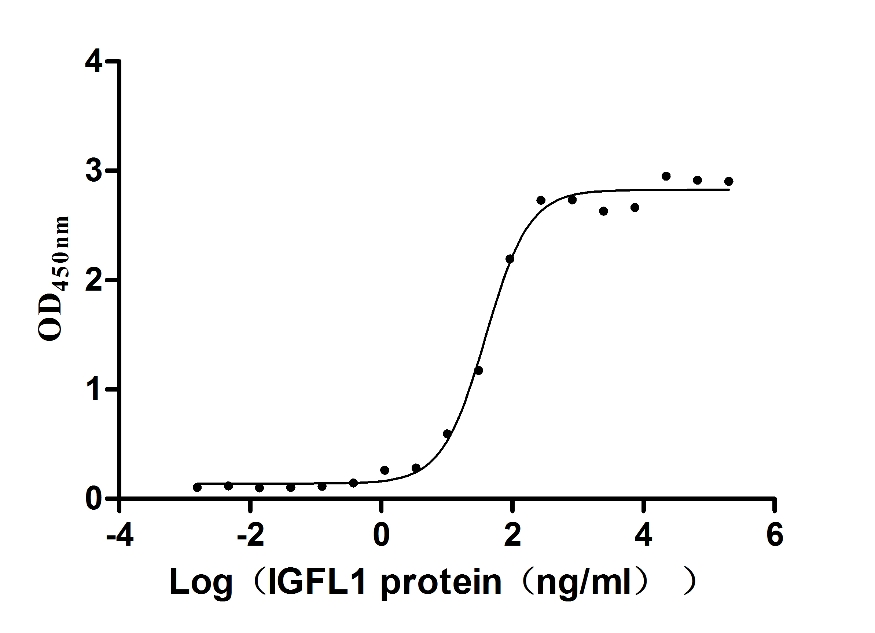
Recombinant Human Insulin growth factor-like family member 1 (IGFL1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
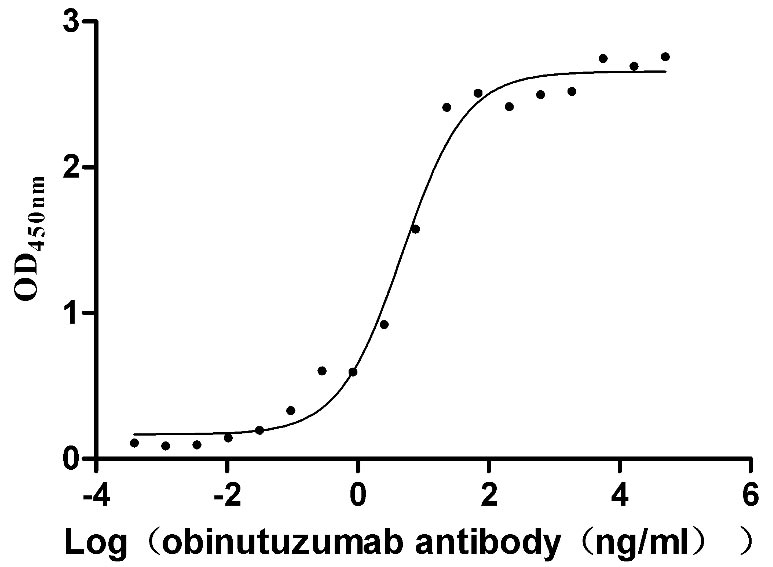
Recombinant Human B-lymphocyte antigen CD20 (MS4A1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
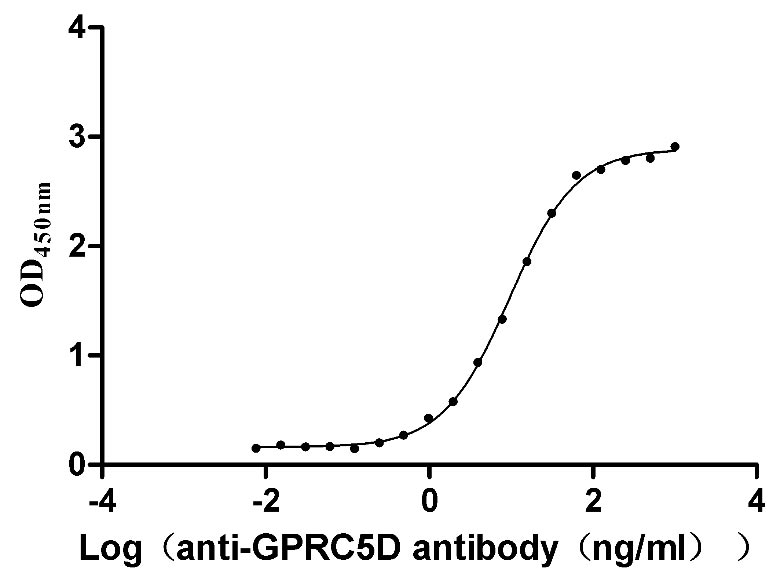
Recombinant Human G-protein coupled receptor family C group 5 member D (GPRC5D)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
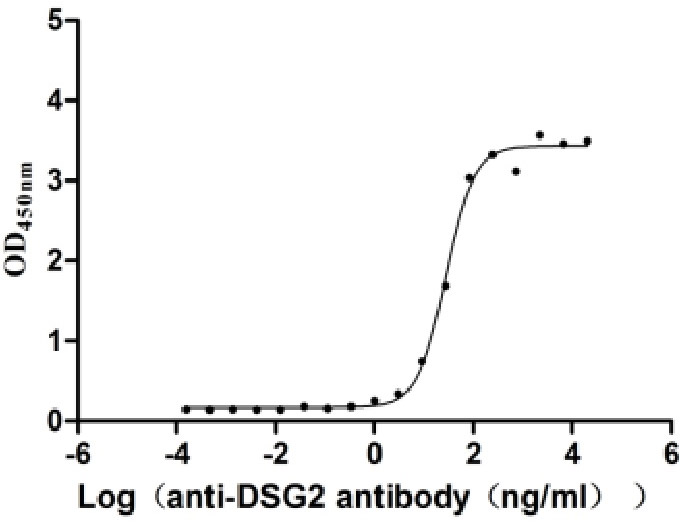
Recombinant Human Desmoglein-2 (DSG2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Cell adhesion molecule 1 (CADM1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
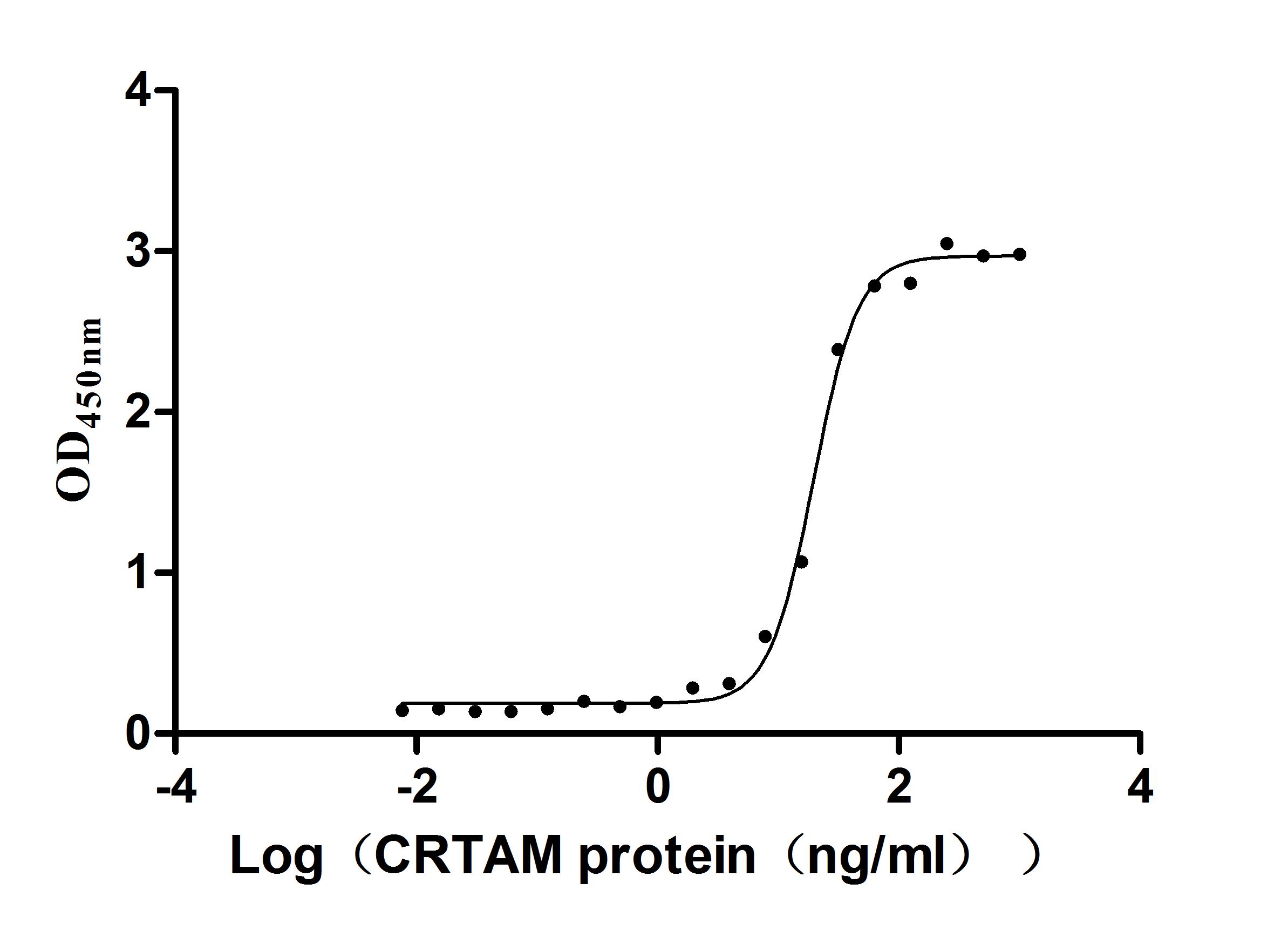
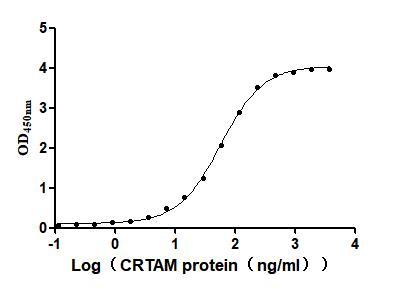
Recombinant Mouse Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule (Crtam), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
-
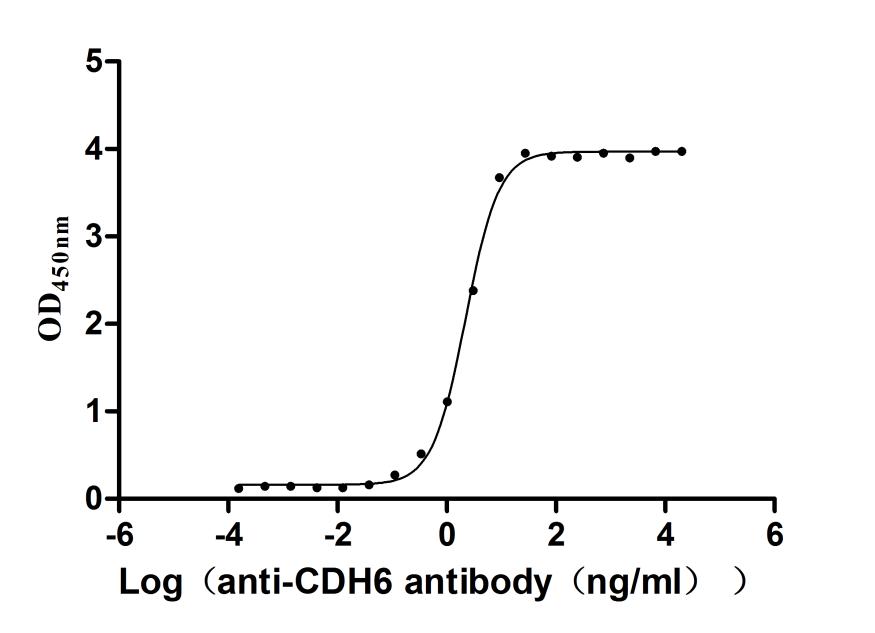
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Cadherin 6(CDH6),partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)