Recombinant Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype ayw Capsid protein (C)
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype ayw Capsid protein(C)
-
貨號:CSB-YP360972HEM
-
規格:
-
來源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype ayw Capsid protein(C)
-
貨號:CSB-EP360972HEM
-
規格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype ayw Capsid protein(C)
-
貨號:CSB-EP360972HEM-B
-
規格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype ayw Capsid protein(C)
-
貨號:CSB-BP360972HEM
-
規格:
-
來源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype ayw Capsid protein(C)
-
貨號:CSB-MP360972HEM
-
規格:
-
來源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:C
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:C; Capsid protein; Core antigen; Core protein; HBcAg; p21.5
-
種屬:Hepatitis B virus genotype D subtype ayw (isolate France/Tiollais/1979) (HBV-D)
-
蛋白長度:full length protein
-
表達區域:1-183
-
氨基酸序列MDIDPYKEFG ATVELLSFLP SDFFPSVRDL LDTASALYRE ALESPEHCSP HHTALRQAIL CWGELMTLAT WVGVNLEDPA SRDLVVSYVN TNMGLKFRQL LWFHISCLTF GRETVIEYLV SFGVWIRTPP AYRPPNAPIL STLPETTVVR RRGRSPRRRT PSPRRRRSQS PRRRRSQSRE SQC
-
蛋白標簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶點詳情
-
功能:Self assembles to form an icosahedral capsid. Most capsids appear to be large particles with an icosahedral symmetry of T=4 and consist of 240 copies of capsid protein, though a fraction forms smaller T=3 particles consisting of 180 capsid proteins. Entering capsids are transported along microtubules to the nucleus. Phosphorylation of the capsid is thought to induce exposure of nuclear localization signal in the C-terminal portion of the capsid protein that allows binding to the nuclear pore complex via the importin (karyopherin-) alpha and beta. Capsids are imported in intact form through the nuclear pore into the nuclear basket, where it probably binds NUP153. Only capsids that contain the mature viral genome can release the viral DNA and capsid protein into the nucleoplasm. Immature capsids get stuck in the basket. Capsids encapsulate the pre-genomic RNA and the P protein. Pre-genomic RNA is reverse-transcribed into DNA while the capsid is still in the cytoplasm. The capsid can then either be directed to the nucleus, providing more genomes for transcription, or bud through the endoplasmic reticulum to provide new virions.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- In conclusion, the authors identify filamin B as a novel host factor that can interact with core protein to promote hepatitis B virus replication in hepatocytes. PMID: 29594956
- highly prevalent naturally occurring BCP and preCore mutations modulate HBV-induced autophagy. PMID: 29738548
- RBM24 interacted with the 5' TR of HBV pregenomic RNA to block 80S ribosome assembly on HBV pgRNA and thus inhibited core protein translation, whereas the interaction between RBM24 and the 3' TR enhanced the stability of HBV RNA. PMID: 29760415
- HBV basal core promoter variants was the strongest predictor of significant fibrosis in Hepatitis B virus infected patients PMID: 27988305
- HBc promoted hepatocellular carcinoma cells motility by regulating the miR-382-5p/DLC-1 axis, which might provide a novel target for clinical diagnosis and treatment. PMID: 28982593
- Together, these results indicate that Rab33B is an important player in intracellular hepatitis B virus trafficking events, guiding core transport to nucleocapsid assembly sites and/or nucleocapsid transport to budding sites. PMID: 28635671
- Basal core promoter A1762T/G1764A dual mutations increase the risk of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma, particularly in an HBV genotype C population, even without progression to cirrhosis (meta-analysis). PMID: 26848866
- The basal core promoter and preCore mutants induced higher levels of apoptosis in human hepatocytes than the wt virus. PMID: 29096158
- KIR content genotypes associate with carriage of hepatitis B surface antigen, e antigen and HBV viral load in Gambians. PMID: 29149205
- Western blotting and MS results indicated that rHBeAg and HBeAg are essentially structurally identical, although HBeAg from different patients exhibits minor carboxyl-terminal heterogeneity. PMID: 28842495
- IL-15 mRNA and protein levels significantly increased in rhHBcAg stimulation group compared with non-stimulated group. PMID: 28274303
- Data show that failure to achieve Hepatitis B e Antigens (HBeAg) seroclearance were the factors significantly associated with virological breakthrough (VBT). PMID: 28350873
- In HBeAg (+) subjects, the AUROC of hepatitis B core antibody (anti-HBc) levels for predicting significant fibrosis was 0.734, while in HBeAg (-) subjects, the AUROC was 0.707. PMID: 28052021
- HBeAg and its precursors promote HDM2-mediated degradation and impair transcriptional activity of p53 by interacting with NUMB, consequently contributing to hepatocellular carcinoma development. PMID: 27106262
- Therefore, it is evident that the presence of G1862T in subgenotype A1 hepatitis B virus does not completely abolish HBeAg expression, but affects the rate of HBeAg maturation, its passage through the secretory pathway and activation of the unfolded protein response. PMID: 28678685
- hepatitis B virus mutations in the basal core promoter/precore region are associated with an increase in the risk of hepatitis B-related acute-on-chronic liver failure (meta-analysis). PMID: 26984835
- HBcAg contributes to the decrease of myeloid dendritic cells during chronic hepatitis B infection. PMID: 27617403
- Among 124,865 patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB)infection, 324 (0.3%) were concurrently positive for hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), and 206 (0.2%) were concurrently positive for hepatitis B surface E antigen (HBeAg). PMID: 28252163
- HBeAg negative hepatitis B patients tend to have HBV pre-core mutations. However, these mutations do not cause increased DNA copies, but associate with damage of liver function. PMID: 27004005
- Patients with HBV genotype C viruses, high viral load and having mutations in the Hepatitis B virus basal core promoter/precore region, were more susceptible to developing liver cirrhosis. PMID: 26577140
- study found that individuals infected with HBV withwith basal core promoter (BCP) double mutations (A1762T, G1764A)have lower concentrations of serum DLD than those with the wild-type BCP PMID: 27303803
- The presence of BCP variant(s) was associated with aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet index ratio >/=0.7 (P=0.029), but it was not associated with abnormal imagingbiopsy results in chronic hepatitis B patients. PMID: 26401823
- Daata show that the empty patitis B virus (HBV) core (HBc) virus-like particles (VLPs) were able to effectively package the added DNA and RNA sequences. PMID: 26113394
- Point mutation in Hepatitis B core Antigen is associated with acute on chronic liver failure. PMID: 25849554
- Hepatitis B virus core protein activates Enhancer I through its binding to cAMP response element (CRE), increasing the concurrent accumulation of CREB/CBP on CRE, and thus increases CRE transcriptional activation. PMID: 25936964
- PC/BCP mutants become predominant in a dynamic and continuous process in hepatitis B. PMID: 26074702
- The basal core promoter/pre-core mutations T1753V, A1762T, G1764A, C1766T, T1768A, A1846T, G1896A and G1899A, and an HBeAg-negative status correlate with an increased risk of acute-on-chronic liver failure. PMID: 26063382
- The naturally occurring mutations P5T/H/L of the HBV core antigen induced endoplasmic reticulum stress. PMID: 25828947
- These findings highlight the role of HBeAg in regulating hepatitis B virus replication fitness and transcription efficiency and new insights on the early steps of replication in the G1896A mutant. PMID: 26119876
- nine residues in HBV core under selection pressure in the presence of 10 different HLA class I alleles PMID: 25720337
- Studied the prevalence of basal core promoter (BCP) and precore gene (PC) mutations in hepatitis B virus (HBV) isolates among the Nicobarese tribe and their relationship with genotypes and HBeAg status. PMID: 25323975
- Capsid proteins plays a role in regulating genome replication. PMID: 25568211
- These results revealed that carboxyl-terminal domain can inhibit multiple stages of viral replication, and its effects may be mediated at least in part through specific host interactions. PMID: 25540387
- In conclusion, the expression of hepatitis B virus core protein sensitized hepatocytes to TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis by disrupting the interaction between MKK7 and RACK1. PMID: 25428880
- Hepatitis B virus e antigen downregulated interleukin-18-mediated cell signaling and interferon gamma expression. PMID: 24872585
- Authors postulate that key mutations throughout the X/preC region may be added to the basal core promoter double mutation and influence the complicated changes in genomic activity for HBeAg expression and HBV DNA replication. PMID: 24344773
- These data highlight the essential role of precores propeptide in switching between different conformations for different functions and pinpoint the propeptide tryptophan residues as central in these properties. PMID: 24999840
- Serum HBsAg levels should be monitored in the management of patients with HBeAg-seronegative chronic hepatitis B. PMID: 24700432
- The hepatitis B core antigen P135Q mutant emergence during the inflammatory phase was associated with altered HBV capsid assembly, HBeAg biosynthesis, and reduced human immune responses following HBeAg seroconversion. PMID: 24273041
- results showed the prevalence of HBc gene mutations is frequent in Iranian Hepatitis B virus (HBV)infected patients; it appears that escape from immune responses is a plausible reason for the high prevalence of HBc gene mutations among Iranian HBV infected patients PMID: 24600970
- The C-terminal arginine-rich domain (ARD) and the ARD-bound RNAs of HBV core protein are partially-ordered and connected with the outer layer through linkers positioned around the two-fold axes. PMID: 24039702
- Lower baseline levels of HBsAg might reflect the status of advanced liver fibrosis in HBeAg positive chronic hepatitis B patients. PMID: 23731848
- The structure of HBV capsid in complex with AT-130, a member of the phenylpropenamide family of assembly effectors. PMID: 23871485
- Combined HBV basal core promoter double mutations and pre-S deletion may not increase the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma, although these mutations are a risk factor of HCC when they present alone. PMID: 23517325
- hepatitis B virus core protein promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation by up-regulating the c-Ets2-dependent expression of human telomerase reverse transcriptase. PMID: 23542016
- Identification of a novel antimicrobial peptide from human hepatitis B virus core protein arginine-rich domain (ARD). PMID: 23785287
- Mutation at the aa 70 position of core protein is associated with disease progression in chronic hepatitis C. PMID: 23946458
- The L60V variation in hepatitis B virus core protein elicits new epitope-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes and enhances viral replication. PMID: 23678186
- The predominant HBV subgenotype HBV/D5 with high viral load and basal core promoter mutations was significantly associated with advanced liver disease (liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma) and might act as a predictor of severe hepatic complications. PMID: 22820088
- Structural insight into how HBeAg may establish immune tolerance for HBcAg while evading its robust immunogenicity. PMID: 23219881
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:Virion. Host cytoplasm.
-
蛋白家族:Orthohepadnavirus core antigen family
-
數據庫鏈接:
KEGG: vg:944568
Most popular with customers
-
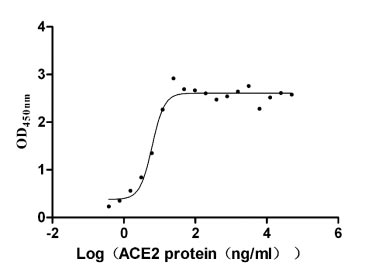
Recombinant Paguma larvata Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Paguma larvata (Masked palm civet)
-
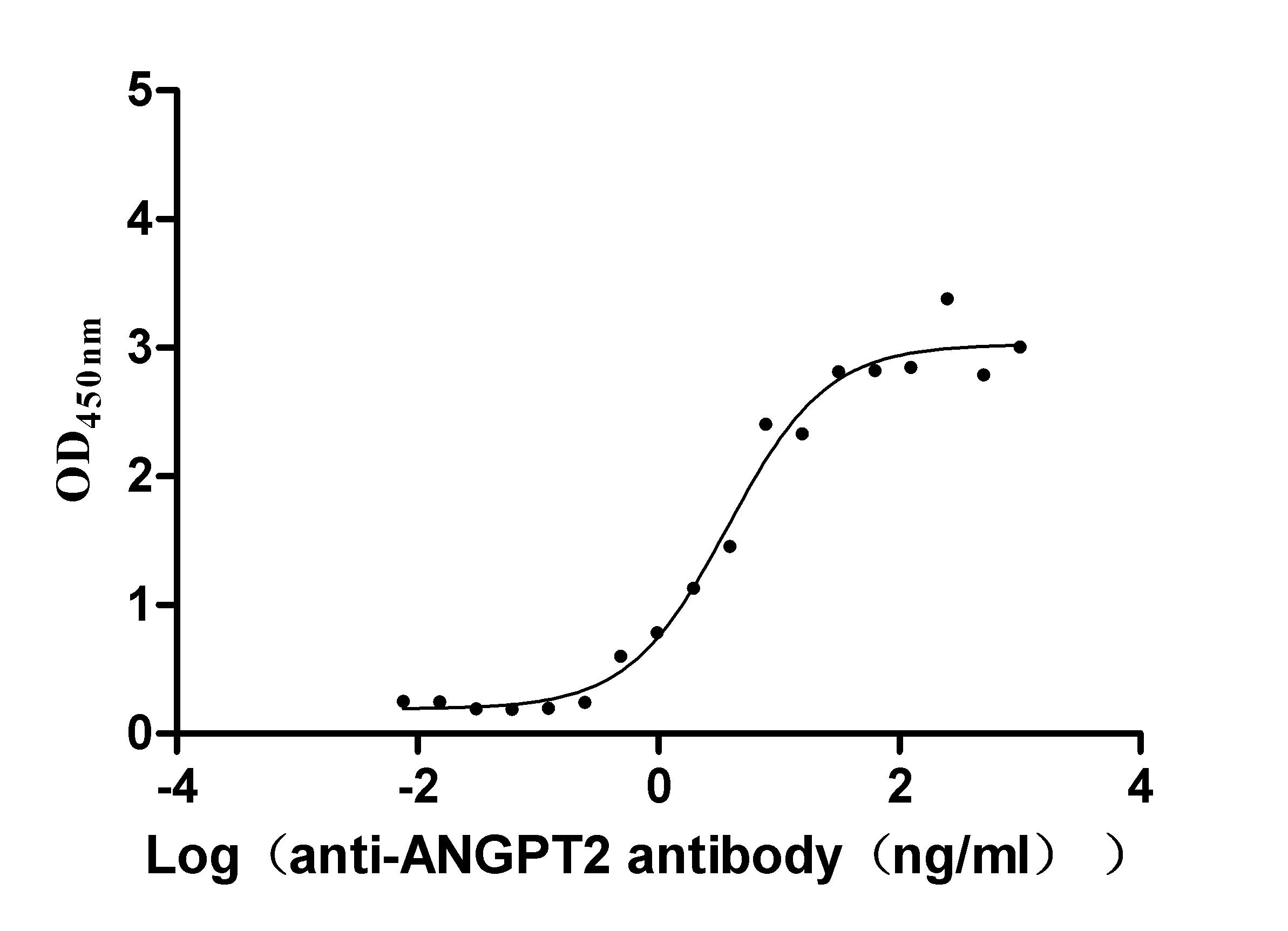
Recombinant Dog Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris)
-
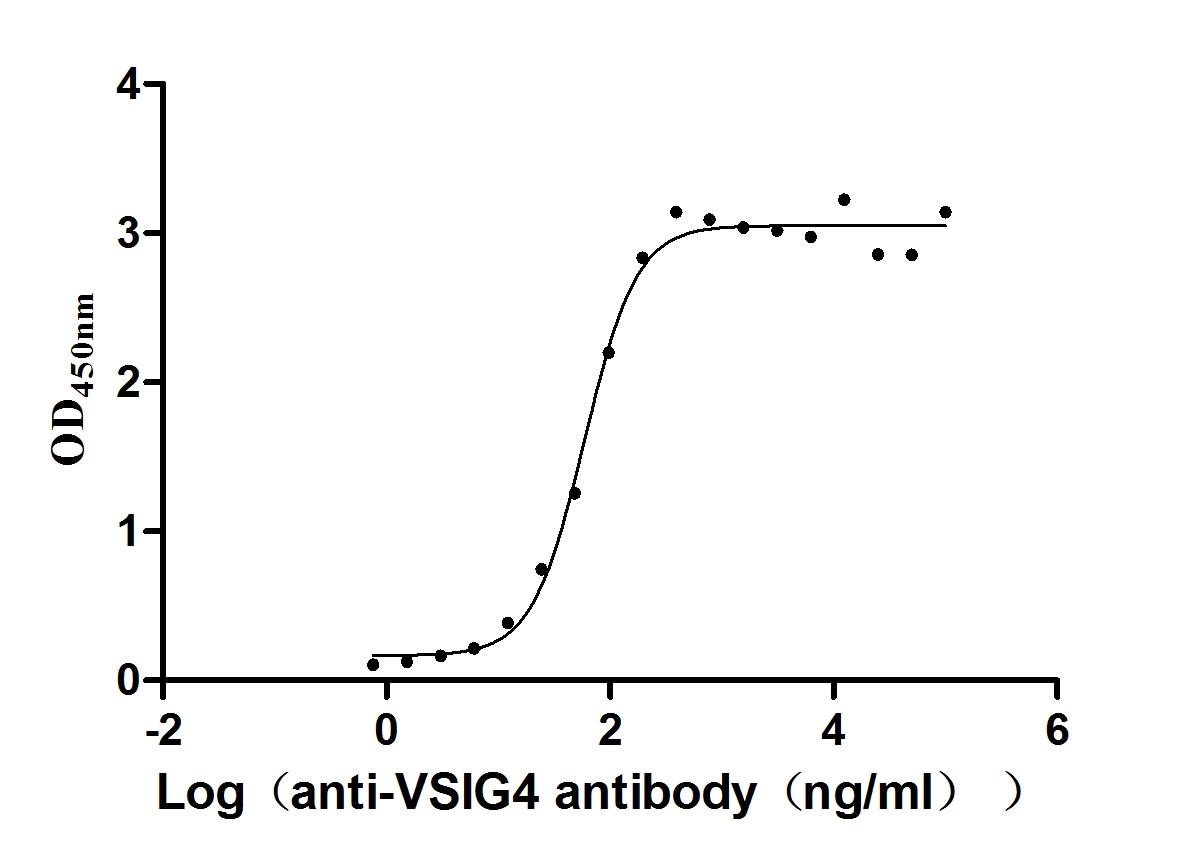
Recombinant Human V-set and immunoglobulin domain-containing protein 4 (VSIG4), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
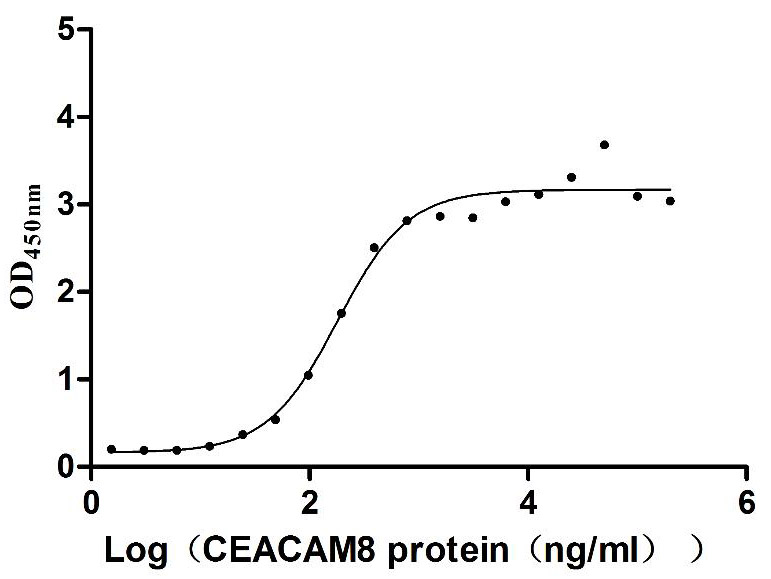
Recombinant Human Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
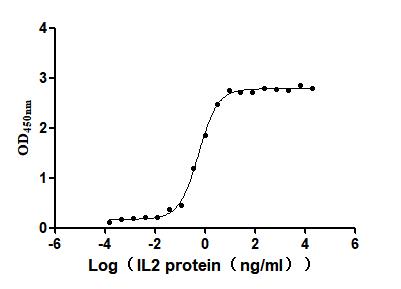
Recombinant Human Interleukin-2 (IL2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
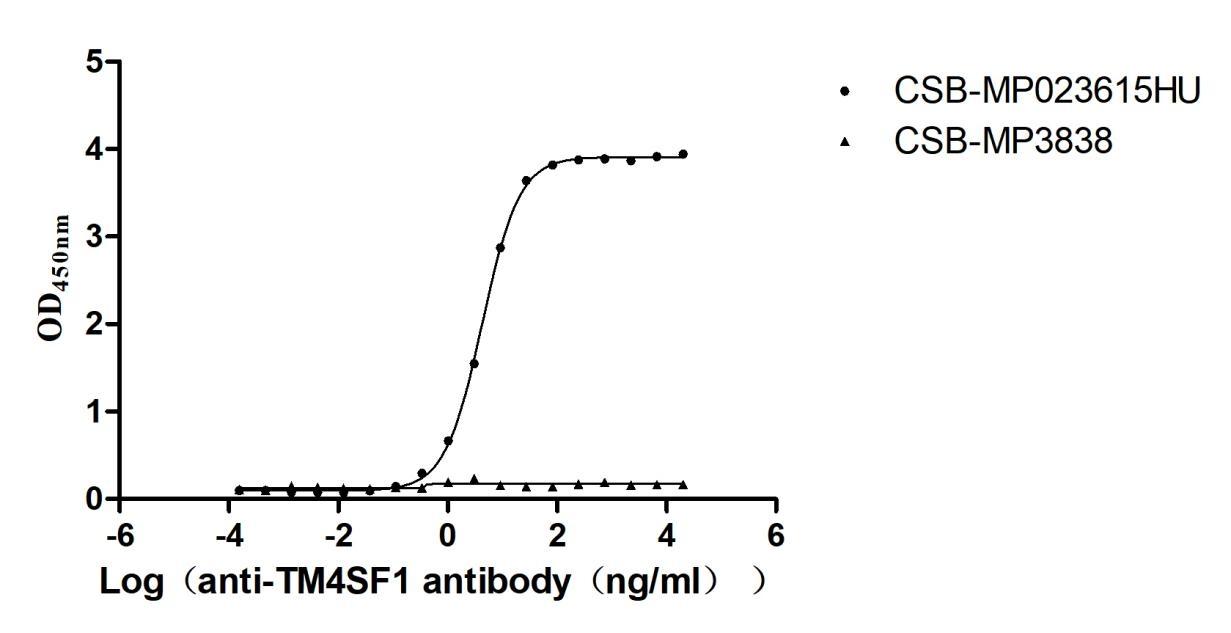
Recombinant Human Transmembrane 4 L6 family member 1(TM4SF1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
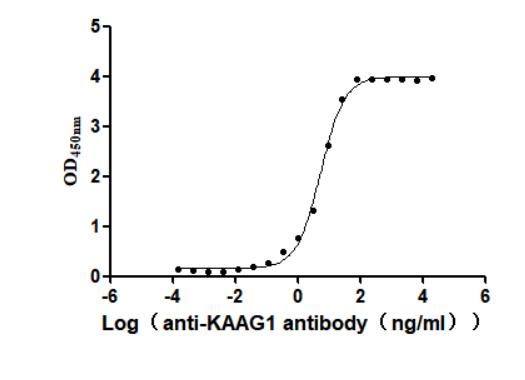
Recombinant Human Kidney-associated antigen 1(KAAG1) (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)