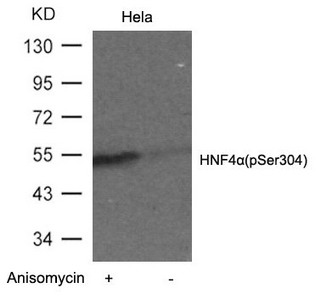
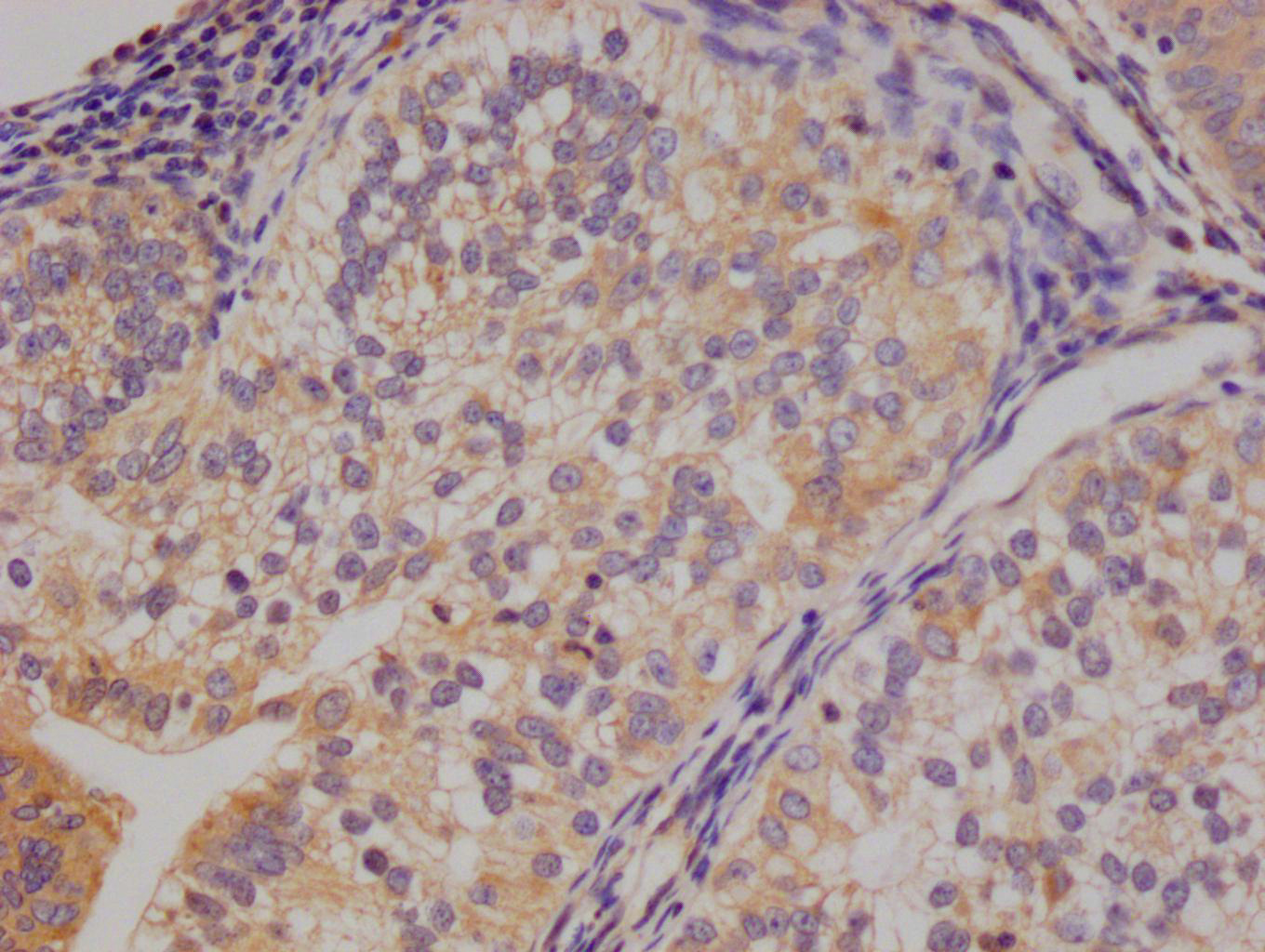
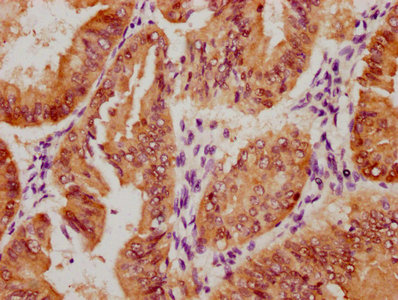
Phospho-HNF4A (Ser304) Antibody
-
中文名稱:磷酸化-HNF4A (Ser304)兔多克隆抗體
-
貨號:CSB-PA443636
-
規格:¥2454
-
圖片:
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
產品名稱:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) HNF4A Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反應種屬:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Peptide sequence around phosphorylation site of serine 304 (L-R-S(p)-Q-V)derived from Human HNF4a.
-
免疫原種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
克隆類型:Polyclonal
-
純化方式:Antibodies were produced by immunizing rabbits with synthetic phosphopeptide and KLH conjugates. Antibodies were purified by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific phosphopeptide. Non-phospho specific antibodies were removed by chromatogramphy usi
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
產品提供形式:Liquid
-
應用范圍:ELISA,WB
-
推薦稀釋比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:1000 -
Protocols:
-
儲存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
用途:For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Transcriptional regulator which controls the expression of hepatic genes during the transition of endodermal cells to hepatic progenitor cells, facilitating the recruitment of RNA pol II to the promoters of target genes. Activates the transcription of CYP2C38. Represses the CLOCK-ARNTL/BMAL1 transcriptional activity and is essential for circadian rhythm maintenance and period regulation in the liver and colon cells.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- genetic association studies in population of children in Japan: Data suggest that mutations in INS, HNF1A, HNF4A, and HNF1B likely play critical roles in children with insulin-requiring autoantibody-negative type 1 diabetes in the population studied. (INS = insulin; HNF1A = HNF1 homeobox A; HNF4A = hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha; HNF1B = HNF1 homeobox B) PMID: 28597946
- Our findings highlight the regulatory networks among TFs, lncRNAs, miRNAs, and mRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Several key molecules, such as hsa-miR-195, lncRNA MALAT1 and TFs TAF1 and HNF4alpha, may contribute to the progression of HCC. PMID: 30249878
- Of the 465,447 CpG sites analyzed, 12 showed differential methylation (false discovery rate <0.15), including markers within genes associated with monogenic diabetes (HNF4A) or obesity (RREB1). The overall methylation at HNF4A showed inverse correlations with mRNA expression levels, though non significant PMID: 29099273
- DDX3 regulates MTP gene expression and lipid homeostasis through interplay with HNF4 and SHP. PMID: 28128295
- These findings suggest that GATA6 might interact with HNF4alpha and contribute to the development of mucinous-type lung adenocarcinomas PMID: 29469192
- HNF4-alpha and particularly SATB2 may be helpful in the differential diagnosis of pulmonary adenocarcinoma and metastases of colorectal adenocarcinomas PMID: 29243296
- Study identified for the first time that HNF4alpha and C/EBPalpha are important transcriptional regulators for FBP1 expression in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. PMID: 29566023
- Although DNA methylation (5mC) and hydroxymethylation (5hmC) are highly dynamic during early embryonic development, less is known about their roles at later stages of differentiation. 5hmC marks HNF4A promoter 1 previous to terminal hepatocyte differentiation. TET1-dependent 5hmC is required to activate promoter 1-driven HNF4A expression. PMID: 28648900
- HNF4A alone could be a gold standard marker for distinguishing primary gastric cancer from breast metastasis PMID: 28583188
- This work suggested that OA increased PKM1/PKM2 ratio, resulting in HNF-4alpha activation and hepatoma differentiation. PMID: 28726775
- HNF-4A plays a critical role in lipid and glucose homeostasis in second trimester of pregnancy PMID: 28591938
- These results indicate a critical and conserved role for HNF4A in maintaining intestinal homeostasis in response to microbiota. PMID: 28385711
- this is the first report to clarify the expression pattern and function of HNF4alpha during the definitive endoderm differentiation. PMID: 28000155
- HNF4A is central to the pathogenesis of NASH. This adds to previous literature demonstrating that HNF4A regulates the transcription of genes involved in the progression of NAFLD, and that HNF4A genetic variants play a potential role in NASH progression PMID: 29216278
- Specifically tested on two model systems, the power of iSPOT is demonstrated to accurately predict the structures of a large protein-protein complex (TGFbeta-FKBP12) and a multidomain nuclear receptor homodimer (HNF-4alpha), based on the structures of individual components of the complexes. PMID: 27496803
- Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) expression was dramatically suppressed and correlated with hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha (HNF4alpha) levels in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tissues. PMID: 27050273
- 2, 3-dihydroquinazolinone derivative, DHQZ-17, potently inhibited the expression of HNF4A, suppressing tumorigenicity of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma in vivo. PMID: 28782802
- Examination of clinical samples revealed that HNF4alpha and IL-1R1 levels increase with increasing severity of Hp-induced gastritis and reach their highest levels in Gastric Carcinoma. Co-expression of HNF4alpha and IL-1R1 was a crucial indicator of malignant transformation from gastritis to GC. PMID: 26870992
- HCV-related HCC could be mediated through HNF4alpha-microRNA deregulation PMID: 27477312
- results strongly suggest that the high frequency of the T130I polymorphism and its biological relationship with dysfunction in lipid metabolism in Mexican indigenous groups is a risk factor for the developing of T2D in Mexicans PMID: 28688048
- Transplantation of HNF4A overexpressing immortalized human hepatocytes (IHH) resulted in better liver function and survival of rats with acute liver failure (ALF) compared with IHH. HNF4A improved hepatic differentiation of IHH. Transplantation of HNF4A-overexpressing IHH could improve the liver function and survival in a rat model of ALF. PMID: 28870599
- both iron-dextran injection and a 3% carbonyl iron-containing diet led to upregulation of hepatic inflammation, which was associated with a significant reduction in HNF4alpha expression and its downstream target, miR-122. PMID: 28655781
- Analysis of differential gene expression between mesenchymal and epithelial cancer cell lines revealed that hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha (HNF4alpha), a transcriptional activator of intestinal (epithelial) differentiation, and its target genes are highly expressed in epithelial cancer cell lines PMID: 26996663
- A new organ culture system for adult murine oesophagus is described. Using this, Cdx2 and HNF4alpha were ectopically expressed by adenoviral infection. We demonstrate the expression of CDX2 and HNF4alpha in human biopsy samples. PMID: 27875772
- data suggest that the ERK1/2 pathway plays an important role in the regulation of HNF4alpha-dependent hepatic gene expression. PMID: 28196117
- HNF4alpha upregulated the expression of liver glutaminase 2 in HepG2 cells PMID: 27466601
- The Mexican genome-wide association study signal for high serum triglycerides on chromosome 18q11.2 harbors a regulatory single-nucleotide polymorphism, rs17259126, which disrupts normal hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha binding and decreases the expression of the regional TMEM241 gene. Our data suggest that decreased transcript levels of TMEM241 contribute to increased triglyceride levels in Mexicans. PMID: 27199446
- The HNF4alpha-knockdown-induced stimulation of hepcidin could be entirely blocked when BMPR1A was interfered with at the same time. PMID: 27660075
- Direct induction of hepatocyte-like cells from immortalized human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by overexpression of HNF4a has been reported. PMID: 27501760
- Data redefine p.R114W as a pathogenic mutation that causes a distinct clinical subtype of HNF4A MODY with reduced penetrance, reduced sensitivity to sulfonylurea treatment, and no effect on birth weight. PMID: 27486234
- Renal Fanconi syndrome represents the only HNF4A feature showing complete penetrance. Our cases suggest that the p.R63W HNF4A mutation must be considered in subjects with a normal birth weight and postulate the possibility of liver involvement as a part of this condition. PMID: 27245055
- HNF-4alpha regulated miR-122 contributes to development of the gluconeogenic and lipid metabolism alterations observed in Type 2 diabetic mice and in palmitate-treated HepG2 cells PMID: 27592052
- HNF4alpha regulated CES1 expression by directly binding to the proximal promoter of CES1. PMID: 27075303
- Epigenetic alterations of the newly identified genes MC4R and HNF4a in early life might contribute to metabolic profile changes, especially increased triglyceride levels, in the cord blood of preterm infants. PMID: 27583872
- HNF4A mutations can be associated with Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young and Congenital Hyperinsulinism. Dual phenotype observed in the neonatal period progressing to diabetes in adulthood with prolonged episodes of hypoglycaemia. PMID: 27552834
- The results revealed the novel mechanism by which HNF-4alpha promoted ChREBP transcription in response to glucose, and also demonstrated that ChREBP-alpha and HNF-4alpha synergistically increased ChREBP-beta transcription. PMID: 27029511
- the results identify Exo70 as a novel transcriptional target of HNF4alpha to promote cell cycle progression in hepatoma, thus provide a basis for the development of therapeutic strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma. PMID: 26848864
- The present study aimed to explore the association between single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the hepatocyte nuclear factor4alpha (HNF4alpha) gene and the incidence of type 2 diabetes in the Chinese Bai population in Dali city, China. PMID: 26781905
- SNPs at the CETP, HNF4A and KLF14 locus are associated with HDL-C levels and type 2 diabetes (in female participants). PMID: 26670163
- The HNF1A gene encodes the transcription factor hepatocyte nuclear factor-1alpha (HNF1alpha), which is expressed in many different tissues, including the liver PMID: 26307397
- Mutations in HNF4A and HNF1A genes might account for this early-onset inherited type 2 diabetes. PMID: 26981542
- HNF4alpha expression analysis revealed that pre-exposing the cells with FGF4 was more effective in hepatocyte differentiation. PMID: 26743282
- PHD2 suppresses the activity of TGF-beta1 pathway and consequently maintains the expression of hepatocyte nuclear factor-4alpha PMID: 26624507
- rejected the hypothesis that all human MODY-associated mutations in HNF1A / HNF4A induce changes in the pharmacokinetics of sulfonylureas in humans analogically to the Hnf1a(-/-) mouse model PMID: 26446475
- Results showed that HNF4a is downregulated in colon carcinoma patients and its ectopic expression inhibited proliferation, migration and invasion of HT29, LoVo and SW480 cells. PMID: 25808746
- ETS2, HNF4A and JUNB are synergistic master regulators of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer. PMID: 26926107
- Berberine has an effect on hepatic gluconeogenesis and lipid metabolism and is mediated through HNF-4alpha and regulated downstream of miR122 PMID: 27011261
- In conclusion, our study revealed a novel mechanism by which TSH regulated the hepatic HNF-4alpha subcellular localization. PMID: 26302721
- Galpha12 overexpression in HCC inhibits MIR122 transactivation by inactivating HNF4alpha, which causes c-Met induction, contributing to cancer aggressiveness. PMID: 25965999
- We identified hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha as a regulatory factor that bound endogenous CLDN7 promoter in differentiating intestinal epithelial cells and stimulated CLDN7 promoter activity. PMID: 26216285
顯示更多
收起更多
-
相關疾病:Maturity-onset diabetes of the young 1 (MODY1); Diabetes mellitus, non-insulin-dependent (NIDDM); Fanconi renotubular syndrome 4 with maturity-onset diabetes of the young (FRTS4)
-
亞細胞定位:Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:Nuclear hormone receptor family, NR2 subfamily
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-