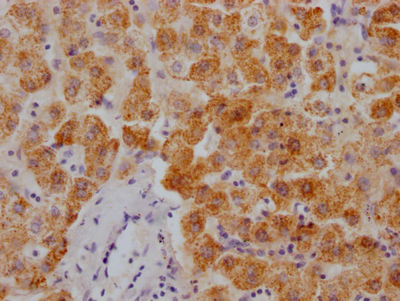
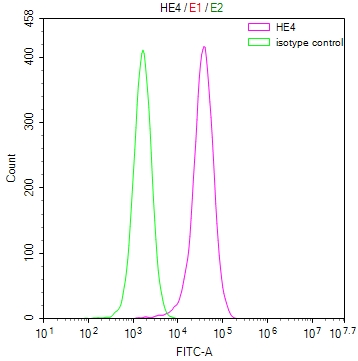
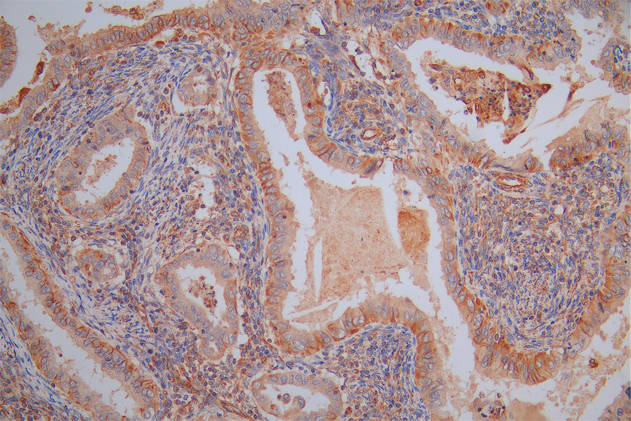
FLCN Antibody, Biotin conjugated
-
中文名稱:FLCN兔多克隆抗體, Biotin偶聯
-
貨號:CSB-PA008711HD01HU
-
規格:¥880
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
產品名稱:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) FLCN Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:
-
別名:BHD antibody; BHD skin lesion fibrofolliculoma protein antibody; Birt Hogg Dube syndrome protein antibody; Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome protein antibody; DKFZp547A118 antibody; FLCL antibody; Flcn antibody; FLCN_HUMAN antibody; FLJ45004 antibody; FLJ99377 antibody; Folliculin antibody; MGC17998 antibody; MGC23445 antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反應種屬:Human
-
免疫原:Recombinant Human Folliculin protein (291-579AA )
-
免疫原種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
標記方式:Biotin
-
克隆類型:Polyclonal
-
抗體亞型:IgG
-
純化方式:Antigen Affinity Purified
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300
Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4 -
產品提供形式:Liquid
-
應用范圍:ELISA
-
Protocols:
-
儲存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
用途:For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:GTPase-activating protein that plays a key role in the cellular response to amino acid availability through regulation of the mTORC1 signaling cascade controlling the MiT/TFE factors TFEB and TFE3. Activates mTORC1 by acting as a GTPase-activating protein: specifically stimulates GTP hydrolysis by RRAGC/RagC or RRAGD/RagD, promoting the conversion to the GDP-bound state of RRAGC/RagC or RRAGD/RagD, and thereby activating the kinase activity of mTORC1. The GTPase-activating activity is inhibited during starvation and activated in presence of nutrients. Acts as a key component for mTORC1-dependent control of the MiT/TFE factors TFEB and TFE3, while it is not involved in mTORC1-dependent phosphorylation of canonical RPS6KB1/S6K1 and EIF4EBP1/4E-BP1. In low-amino acid conditions, the lysosomal folliculin complex (LFC) is formed on the membrane of lysosomes, which inhibits the GTPase-activating activity of FLCN, inactivates mTORC1 and maximizes nuclear translocation of TFEB and TFE3. Upon amino acid restimulation, RRAGA/RagA (or RRAGB/RagB) nucleotide exchange promotes disassembly of the LFC complex and liberates the GTPase-activating activity of FLCN, leading to activation of mTORC1 and subsequent cytoplasmic retention of TFEB and TFE3. Indirectly acts as a positive regulator of Wnt signaling by promoting mTOR-dependent cytoplasmic retention of MiT/TFE factor TFE3. Required for the exit of hematopoietic stem cell from pluripotency by promoting mTOR-dependent cytoplasmic retention of TFE3, thereby increasing Wnt signaling. Acts as an inhibitor of browning of adipose tissue by regulating mTOR-dependent cytoplasmic retention of TFE3. In response to flow stress, regulates STK11/LKB1 accumulation and mTORC1 activation through primary cilia: may act by recruiting STK11/LKB1 to primary cilia for activation of AMPK resided at basal bodies, causing mTORC1 down-regulation. Together with FNIP1 and/or FNIP2, regulates autophagy: following phosphorylation by ULK1, interacts with GABARAP and promotes autophagy. Required for starvation-induced perinuclear clustering of lysosomes by promoting association of RILP with its effector RAB34.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- Two FLCN mutations have been identified in Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome patients: One is an insertion mutation previously reported in three Asian families; while the other is the first mutation (originally found in Asian populations) that has ever been detected in a French family. PMID: 29357828
- FLCN gene analysis revealed a heterozygous FLCN{NM_144997.5}:c.1285dupC mutation in all affected members. The clinical features of BHD syndrome are heterogeneous with wide intra-familial and interfamilial variation. It is caused by mutations of the FLCN gene. PMID: 28775225
- The molecular insight into the folliculin dynamics in the presence and absence of mutations may provide valuable information regarding the interactions essential for normal functioning of cellular process and the molecular basis of Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome PMID: 27484154
- The present identification of two mutations not only further supports the important role of tumor suppressor FLCN in Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome and primary spontaneous pneumothorax, but also expands the spectrum of FLCN mutations. PMID: 28785590
- In the folliculin gene, a similar genotype spectrum but different mutant loci was determined in Chinese patients with Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome compared with European and American patients. PMID: 28558743
- Germline mutations in the FLCN gene are responsible for the autosomal dominant inherited disorder Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome. PMID: 28970150
- Seventy-six of 156 FLCN mutation carriers (120 probands and 36 sibs, 48.7%) had skin papules; however, cutaneous manifestations were so subtle that only one patient voluntarily consulted dermatologists. Japanese Asian BHD families have three FLCN mutational hotspots. PMID: 27220747
- A nonsense mutation of FLCN was found in a spontaneous pneumothorax family. The results expand the mutational spectrum of FLCN in patients with Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome. PMID: 27486260
- the study describes the FLCN mutation spectrum in Danish Birt-Hogg-Dube (BHD) syndrome patients, and contributes to a better understanding of BHD syndrome and management of BHD patients. PMID: 27734835
- We report Smith-Magenis syndrome who presents bilateral renal tumors. This is most likely related to haploinsufficiency of FLCN gene, located in the deleted region PMID: 27633572
- For patients whose clinical features are atypical, detection of germline mutation in FLCN gene would help confirm diagnosis. The 2 mutations we reported would expand the mutation spectrum of FLCN gene associated with BHD syndrome PMID: 27258496
- DNA sequence analyses determined that there was a two base pair deletion in exon 4 of the FLCN gene, confirming the diagnosis of BHD syndrome. PMID: 27780965
- We identified a hitherto unreported pathogenic FLCN frameshift deletion c.563delT (p.Phe188Serfs*35) in a family of a 46-year-old woman presented with macrohematuria due to bilateral chromophobe renal carcinomas PMID: 26342594
- FLCN irregulation in lung cysts of primary spontaneous pneumothorax is not associated with promoter methylation. PMID: 26398834
- mTOR inhibitor, sirolimus, suppresses the tumor's growth, suggesting that mTOR inhibitors might be effective in control of FLCN-deficient RCC. PMID: 26418749
- we show that glycogen accumulates in kidneys from mice lacking FLCN and in renal tumors from a BHD patient PMID: 26439621
- Case Report: FLCN deletion mutation in members of Indian Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome family. PMID: 25827758
- This report documents the first identification of founder mutations in FLCN, as well as expands mutation spectrum of the gene PMID: 25807935
- FLCN-related renal cell carcinomas showed overexpression of GPNMB and underexpression of FLCN, whereas sporadic tumors showed inverted patterns. PMID: 25594584
- The FLCN-GABARAP association is modulated by the presence of either folliculin-interacting protein (FNIP)-1 or FNIP2 and further regulated by ULK1. PMID: 25126726
- Two predominant genes, ephrin type A receptor 6 (EPHA6) and folliculin (FLCN), with mutations exclusive to African American CRCs, are by genetic and biological criteria highly likely African American CRC driver genes. PMID: 25583493
- Findings suggest that folliculin deficient renal cell carcinoma cells are highly sensitive to irradiation due to increased autophagic cell death, unlike other types of renal cell carcinoma. PMID: 24434776
- A rare mutation of the folliculin gene was detected in the patient and family members with Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome with pulmonary cysts or pneumothorax, but no skin or renal lesions. PMID: 24346394
- Birt-Hogg-Dube (BHD) syndrome is a recently discovered autosomal-dominant disease caused by a mutation in the folliculin gene. PMID: 24996715
- loss of FLCN constitutively activates AMPK, resulting in PGC-1alpha-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis and increased ROS production PMID: 24762438
- FLCN germ-line mutation is associated with spontaneous pneumothorax and renal cancer PMID: 23264078
- Results suggest that Birt-Hogg-Dube (BHD)syndrome-causing FLCN mutants may retain partial functionality. Thus, several BHD symptoms may be due to abnormal levels of FLCN rather than its complete loss. PMID: 23784378
- Tumor suppression function of FLCN may be linked to its impact on the cell cycle. PMID: 23874397
- FLCN localizes to motile and non-motile cilia, centrosomes and the mitotic spindle. Alteration of FLCN levels can cause changes to the onset of ciliogenesis. In three-dimensional culture, abnormal expression of FLCN disrupts polarized growth of kidney cells and deregulates canonical Wnt signalling. Findings suggest that BHD is a ciliopathy, with symptoms at least partly due to abnormal ciliogenesis. PMID: 23784378
- Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome in a patient with melanoma and a novel mutation in the FCLN gene. PMID: 23414156
- FLCN functions as a tumor suppressor by negatively regulating rRNA synthesis. PMID: 23077212
- Germline mutation analysis of the FCLN gene in mother and daughter cases with renal cell neoplasms showed a deletion of 18 bp in exon 5(c.332_349del/p.H111_Q116del), predicting an alteration of the amino acid sequence of "HPSHPQ" replaced by a single amino acid, "L". PMID: 22211584
- Findings suggest that aspects of folliculin tumour suppressor function are linked to interaction with p0071 and the regulation of RhoA signalling. PMID: 22965878
- These data support a model in which dysregulation of the FLCN-p0071 interaction leads to alterations in cell adhesion, cell polarity, and RhoA signaling. PMID: 23139756
- These findings identify novel pathways and targets linked to folliculin tumour suppressor activity. PMID: 23155228
- FLCN deficiency and subsequent increased PPARGC1A expression result in increased mitochondrial function and oxidative metabolism as the source of cellular energy, which may drive hyperplastic transformation. PMID: 23150719
- Study reports a novel in-frame deletion mutation p.F143del (c.427_429delTTC) in exon 6 of FLCN gene in a Korean proband and her two sisters. PMID: 22446046
- confirmed a high yield of FLCN mutations in clinically defined BHD families, we found a substantially increased lifetime risk of renal cancer of 16% for FLCN mutation carriers PMID: 22146830
- FLCN mutations throughout the coding sequence, and suggest that multiple protein domains contribute to folliculin stability and tumor suppressor activity. PMID: 21538689
- Birt-Hogg-Dube (BHD) protein-deficient cells exhibited defects in cell-intrinsic apoptosis that correlated with reduced expression of the BH3-only protein Bim, which was similarly observed in all human and mouse BHD-related tumors examined. PMID: 21258407
- Data show that FLCN mutations were found in 9 of 19 (47%) families. PMID: 20618353
- This report confirms that large intragenic FLCN deletions can cause Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome and documents the first large intragenic FLCN duplication in a Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome patient PMID: 21412933
- Genetic testing for Birt-Hogg-Dube should be considered in the treatment algorithm of patients with bilateral renal masses and known oncocytoma PMID: 21496834
- FLCN tumor suppressor gene inactivation induces TFE3 transcriptional activity by increasing its nuclear localization PMID: 21209915
- plays role in tumor suppression and inhibition on rapamycin pathway PMID: 21079084
- Data show that germline FLCN mutations were not detected in 50 patients with familial non-syndromic colorectal cancer. PMID: 20522427
- An Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome protein germline mutation was found in 23 (63.9%) of the 36 patients. A large genomic deletion was identified in two of the remaining 13 patients. PMID: 20413710
- We report cases involving a new mutation in three unrelated families of Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome. PMID: 20227563
- Mutations lead to kidney tumors, lung wall defects, and benign tumors of the hair follicle in patients with the Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome PMID: 12204536
- Clinical and genetic studies of four sporadic BHD cases and four families with a total of 23 affected subjects PMID: 12471204
顯示更多
收起更多
-
相關疾病:Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome (BHD); Primary spontaneous pneumothorax (PSP); Renal cell carcinoma (RCC)
-
亞細胞定位:Lysosome membrane. Cytoplasm, cytosol. Cell projection, cilium. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle. Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:Folliculin family
-
組織特異性:Expressed in most tissues tested, including skin, lung, kidney, heart, testis and stomach.
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-