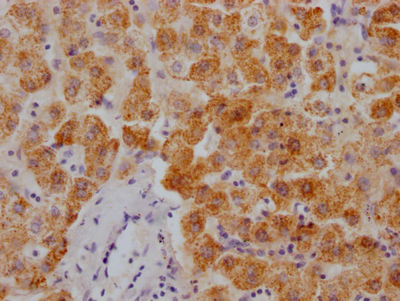
CENPJ Antibody, FITC conjugated
-
中文名稱:CENPJ兔多克隆抗體, FITC偶聯(lián)
-
貨號:CSB-PA005213LC01HU
-
規(guī)格:¥880
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
產(chǎn)品名稱:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) CENPJ Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:CENPJ
-
別名:BM032 antibody; CENP-J antibody; CENPJ antibody; CENPJ_HUMAN antibody; Centromere protein J antibody; Centrosomal P4.1-associated protein antibody; CPAP antibody; LAG-3-associated protein antibody; LAP antibody; LIP1 antibody; LYST interacting protein LIP1 antibody; LYST interacting protein LIP7 antibody; LYST-interacting protein 1 antibody; MCPH6 antibody; Sas 4 antibody; SASS4 antibody; SCKL4 antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反應(yīng)種屬:Human
-
免疫原:Recombinant Human Centromere protein J protein (1082-1248AA)
-
免疫原種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
標(biāo)記方式:FITC
-
克隆類型:Polyclonal
-
抗體亞型:IgG
-
純化方式:>95%, Protein G purified
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300
Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4 -
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Liquid
-
儲存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
用途:For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
相關(guān)產(chǎn)品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Plays an important role in cell division and centrosome function by participating in centriole duplication. Inhibits microtubule nucleation from the centrosome. Involved in the regulation of slow processive growth of centriolar microtubules. Acts as microtubule plus-end tracking protein that stabilizes centriolar microtubules and inhibits microtubule polymerization and extension from the distal ends of centrioles. Required for centriole elongation and for STIL-mediated centriole amplification. Required for the recruitment of CEP295 to the proximal end of new-born centrioles at the centriolar microtubule wall during early S phase in a PLK4-dependent manner. May be involved in the control of centriolar-microtubule growth by acting as a regulator of tubulin release.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- CPAP regulates delivery of its bound beta-tubulin to define the size of microtubule-based cellular structures using a "clutch-like" mechanism. PMID: 27306797
- Data suggest that alcohol/ethanol exposure diminishes pool of proliferative neurons (Neuro2a cell line) through disordering of spindle orientation and promotion of asymmetric cell division; these neuronal abnormalities appear to be due to reduced CENPJ protein expression level. PMID: 29778912
- CPAP-S467D protein has a low affinity for microtubule binding but a high affinity for pericentriolar material proteins. PMID: 26997271
- CPAP promotes timely cilium disassembly to maintain neural progenitor pool. CPAP mutation causes Seckel syndrome with microcephaly. PMID: 26929011
- Data suggest that the single G-box domain (that appears to fold into 14-20 antiparallel beta-strands) of CENPJ has stable but dynamic structure; CRAP forms multimers (in solution and in crystals) of elongated fibrils similar to amyloid fibrils. [REVIEW] PMID: 26517891
- Centrobin plays a role in the stability and centriole elongation function of CPAP and limits the centriole length. PMID: 25616662
- studies provide the first structural insight into how the malfunction of centriole proteins results in human disease and also reveal that the CPAP-STIL interaction constitutes a conserved key step in centriole biogenesis PMID: 24052813
- The results showed a human-specific hypomethylation in the 5' UTR of CENPJ in the brain, where methylation levels among humans are only about one-third of those found among nonhuman primates. PMID: 24288161
- Centrobin-CPAP interaction is critical for the recruitment of CPAP to procentrioles to promote the elongation of daughter centrioles and for the persistence of CPAP on preexisting mother centrioles. PMID: 24700465
- CPAP depletion results in asymmetric spindle poles with uneven distribution of pericentriolar material. PMID: 24491538
- Sas-4 acts as a vehicle to tether PCM complexes to centrioles independent of its well-known role in centriole duplication PMID: 24385583
- CEP120 associates with SPICE1 and CPAP, and depletion of any of these proteins results in short procentrioles. Furthermore, CEP120 or CPAP overexpression results in excessive centriole elongation, a process dependent on CEP120, SPICE1, and CPAP. PMID: 23810536
- SUMOylated CPAP could synergistically increase the HBx-induced NF-kappaB activity PMID: 23369793
- CEP120 is a CPAP-interacting protein that positively regulates centriole elongation. PMID: 23857771
- Authors propose that CEP135 directly connects the central hub protein, hSAS-6, to the outer microtubules, and suggest that this interaction stabilizes the proper cartwheel structure for further CPAP-mediated centriole elongation. PMID: 23511974
- CPAP degradation and function is controlled by the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase tankyrase 1. PMID: 22699936
- STIL and CPAP are essential for centriole formation and for proper spindle position. PMID: 22100914
- Results suggest that Cep152 recruits Plk4 and CPAP to the centrosome to ensure a faithful centrosome duplication process. PMID: 21059844
- Data establishes that mutation of CENPJ can lead to Seckel syndrome and calls for further investigation of the role played by other microcephaly related genes in the pathogenesis of PD. PMID: 20522431
- Results identify centrosomal P4.1-associated protein (CPAP), a human homologue of SAS-4, as a substrate of PLK2 whose activity oscillates during the cell cycle. PMID: 20531387
- cell cycle-regulated phosphorylation orchestrates the dynamics of CPAP molecular interaction and centrosome splitting to ensure genomic stability in cell division PMID: 19889632
- CPAP was found to augment Stat5-mediated transcription PMID: 12198240
- CPAP carries a novel microtubule-destabilizing motif that not only inhibits microtubule nucleation from the centrosome but also depolymerizes taxol-stabilized microtubules. PMID: 15047868
- CPAP functions as a coactivator of NF-kappaB-mediated transcription PMID: 15687488
- Mutations in CENPJ gene is associated with autosomal recessive primary microcephaly PMID: 15793586
- Together, our results reveal a structural role for CPAP to maintain centrosome integrity and normal spindle morphology during cell division. PMID: 16316625
- In summary, our results show a direct interaction between CPAP and 14-3-3, and this interaction appears to be phosphorylation and cell cycle dependent. PMID: 16516142
- discuss CENPJ, which similarly exhibits higher rate of protein evolution in primates as compared to rodents and carnivores PMID: 16631324
- High levels of LIP1 were found in serum and synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis patients, providing evidence for a cytokine-like role. PMID: 18162190
- Mutations in this conserved sequence also eliminate d-SAS-4's microtubule-destabilizing activity, suggesting that d-SAS-4 and CPAP may play similar roles within cells. PMID: 18586240
- the PN2-3 fragment of CPAP as a protein with an unprecedented tubulin sequestering mechanism distinct from that of stathmin family proteins. PMID: 19131341
- Results suggest that CPAP and CP110 play antagonistic roles in determining the extent of tubulin addition during centriole elongation, thereby controlling the length of newly formed centrioles. PMID: 19481458
- Data show that the CPAP is required for centrosome duplication in cycling human cells, and that CPAP overexpression results in the formation of abnormally long centrioles. PMID: 19481460
- Results suggest that CPAP is a new regulator of centriole length and its intrinsic tubulin-dimer binding activity is required for procentriole elongation. PMID: 19503075
- Identifies CENPJ as LYST-interacting proteins LIP1 and LIP7, which interact with the lysosomal trafficking regulator (LYST) protein. PMID: 11984006
顯示更多
收起更多
-
相關(guān)疾病:Microcephaly 6, primary, autosomal recessive (MCPH6); Seckel syndrome 4 (SCKL4)
-
亞細胞定位:Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome, centriole.
-
蛋白家族:TCP10 family
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-
-