KLRC2
KLRC2是一種位于12號染色體的基因,其表達產物為Killer Cell Lectin Like Receptor C2,也被稱為Killer Cell Lectin Like Receptor Subfamily C, Member 2等。這種蛋白主要在自然殺傷(NK)細胞中表達,對調節NK細胞功能具有重要作用。KLRC2蛋白與某些腫瘤細胞和病毒感染細胞的裂解有關,對免疫系統的正常運作至關重要。目前,KLRC2蛋白的研究正逐漸深入,有望為相關疾病的治療提供新的思路和藥物研發方向。
熱銷產品
Recombinant Human NKG2-C type II integral membrane protein (KLRC2), partial (CSB-EP012467HU)
驗證數據
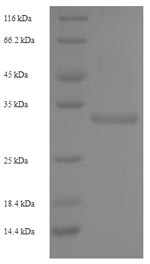
(Tris-Glycine gel) Discontinuous SDS-PAGE (reduced) with 5% enrichment gel and 15% separation gel.
KLRC2 Antibody (CSB-PA012467LA01HU)
驗證數據
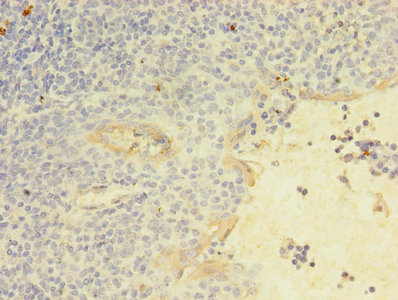
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded human tonsil tissue using CSB-PA012467LA01HU at dilution of 1:100
KLRC2 Antibodies
KLRC2 for Homo sapiens (Human)
| 產品貨號 | 產品名稱 | 種屬反應性 | 應用類型 |
|---|---|---|---|
| CSB-PA012467LA01HU | KLRC2 Antibody | Human | ELISA, IHC |
| CSB-PA012467LB01HU | KLRC2 Antibody, HRP conjugated | Human | ELISA |
| CSB-PA012467LC01HU | KLRC2 Antibody, FITC conjugated | Human |
KLRC2 Proteins
KLRC2 Proteins for Homo sapiens (Human)
| 產品貨號 | 產品名稱 | 來源 |
|---|---|---|
| CSB-YP012467HU CSB-BP012467HU CSB-MP012467HU CSB-EP012467HU-B |
Recombinant Human NKG2-C type II integral membrane protein (KLRC2), partial | Yeast Baculovirus Mammalian cell In Vivo Biotinylation in E.coli |
| CSB-EP012467HU | Recombinant Human NKG2-C type II integral membrane protein (KLRC2), partial | E.coli |
| CSB-CF012467HU | Recombinant Human NKG2-C type II integral membrane protein (KLRC2) | in vitro E.coli expression system |
KLRC2 Proteins for Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)
| 產品貨號 | 產品名稱 | 來源 |
|---|---|---|
| CSB-YP865035MOW CSB-EP865035MOW CSB-BP865035MOW CSB-MP865035MOW CSB-EP865035MOW-B |
Recombinant Macaca mulatta NKG2-C type II integral membrane protein (KLRC2), partial | Yeast E.coli Baculovirus Mammalian cell In Vivo Biotinylation in E.coli |
KLRC2 Proteins for Pan troglodytes (Chimpanzee)
| 產品貨號 | 產品名稱 | 來源 |
|---|---|---|
| CSB-YP875612EQV CSB-EP875612EQV CSB-BP875612EQV CSB-MP875612EQV CSB-EP875612EQV-B |
Recombinant Pan troglodytes NKG2-C type II integral membrane protein (KLRC2), partial | Yeast E.coli Baculovirus Mammalian cell In Vivo Biotinylation in E.coli |










