Recombinant Semliki forest virus Structural polyprotein
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Semliki forest virus Structural polyprotein
-
貨號:CSB-CF356012SET
-
規格:
-
來源:in vitro E.coli expression system
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
基因名:N/A
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:Structural polyprotein; p130
-
種屬:Semliki forest virus (SFV)
-
蛋白長度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
表達區域:816-1253
-
氨基酸序列YEHSTVMPNVVGFPYKAHIERPGYSPLTLQMQVVETSLEPTLNLEYITCEYKTVVPSPYV KCCGASECSTKEKPDYQCKVYTGVYPFMWGGAYCFCDSENTQLSEAYVDRSDVCRHDHAS AYKAHTASLKAKVRVMYGNVNQTVDVYVNGDHAVTIGGTQFIFGPLSSAWTPFDNKIVVY KDEVFNQDFPPYGSGQPGRFGDIQSRTVESNDLYANTALKLARPSPGMVHVPYTQTPSGF KYWLKEKGTALNTKAPFGCQIKTNPVRAMNCAVGNIPVSMNLPDSAFTRIVEAPTIIDLT CTVATCTHSSDFGGVLTLTYKTNKNGDCSVHSHSNVATLQEATAKVKTAGKVTLHFSTAS ASPSFVVSLCSARATCSASCEPPKDHIVPYAASHSNVVFPDMSGTALSWVQKISGGLGAF AIGAILVLVVVTCIGLRR
Note: The complete sequence may include tag sequence, target protein sequence, linker sequence and extra sequence that is translated with the protein sequence for the purpose(s) of secretion, stability, solubility, etc.
If the exact amino acid sequence of this recombinant protein is critical to your application, please explicitly request the full and complete sequence of this protein before ordering. -
蛋白標簽:N-terminal 10xHis-tagged
-
產品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
緩沖液:Lyophilized from Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose, pH 8.0
-
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Forms an icosahedral capsid with a T=4 symmetry composed of 240 copies of the capsid protein surrounded by a lipid membrane through which penetrate 80 spikes composed of trimers of E1-E2 heterodimers. The capsid protein binds to the viral RNA genome at a site adjacent to a ribosome binding site for viral genome translation following genome release. Possesses a protease activity that results in its autocatalytic cleavage from the nascent structural protein. Following its self-cleavage, the capsid protein transiently associates with ribosomes, and within several minutes the protein binds to viral RNA and rapidly assembles into icosahedric core particles. The resulting nucleocapsid eventually associates with the cytoplasmic domain of the spike glycoprotein E2 at the cell membrane, leading to budding and formation of mature virions. In case of infection, new virions attach to target cells and after clathrin-mediated endocytosis their membrane fuses with the host endosomal membrane. This leads to the release of the nucleocapsid into the cytoplasm, followed by an uncoating event necessary for the genomic RNA to become accessible. The uncoating might be triggered by the interaction of capsid proteins with ribosomes. Binding of ribosomes would release the genomic RNA since the same region is genomic RNA-binding and ribosome-binding. Specifically inhibits interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1/IRAK1-dependent signaling during viral entry, representing a means by which the alphaviruses may evade innate immune detection and activation prior to viral gene expression.; Provides the signal sequence for the translocation of the precursor of protein E3/E2 to the host endoplasmic reticulum. Furin-cleaved E3 remains associated with spike glycoprotein E1 and mediates pH protection of the latter during the transport via the secretory pathway. After virion release from the host cell, the assembly protein E3 is gradually released in the extracellular space.; Plays a role in viral attachment to target host cell, by binding to the cell receptor. Synthesized as a p62 precursor which is processed by furin at the cell membrane just before virion budding, giving rise to E2-E1 heterodimer. The p62-E1 heterodimer is stable, whereas E2-E1 is unstable and dissociate at low pH. p62 is processed at the last step, presumably to avoid E1 fusion activation before its final export to cell surface. E2 C-terminus contains a transitory transmembrane that would be disrupted by palmitoylation, resulting in reorientation of the C-terminal tail from lumenal to cytoplasmic side. This step is critical since E2 C-terminus is involved in budding by interacting with capsid proteins. This release of E2 C-terminus in cytoplasm occurs lately in protein export, and precludes premature assembly of particles at the endoplasmic reticulum membrane.; Constitutive membrane protein involved in virus glycoprotein processing, cell permeabilization, and the budding of viral particles. Disrupts the calcium homeostasis of the cell, probably at the endoplasmic reticulum level. This leads to cytoplasmic calcium elevation. Because of its lipophilic properties, the 6K protein is postulated to influence the selection of lipids that interact with the transmembrane domains of the glycoproteins, which, in turn, affects the deformability of the bilayer required for the extreme curvature that occurs as budding proceeds. Present in low amount in virions, about 3% compared to viral glycoproteins.; Class II viral fusion protein. Fusion activity is inactive as long as E1 is bound to E2 in mature virion. After virus attachment to target cell and endocytosis, acidification of the endosome would induce dissociation of E1/E2 heterodimer and concomitant trimerization of the E1 subunits. This E1 trimer is fusion active, and promotes release of viral nucleocapsid in cytoplasm after endosome and viral membrane fusion. Efficient fusion requires the presence of cholesterol and sphingolipid in the target membrane. Fusion is optimal at levels of about 1 molecule of cholesterol per 2 molecules of phospholipids, and is specific for sterols containing a 3-beta-hydroxyl group.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- results suggest that the E2 D-loop interacts with the E1 protein to promote Alphavirus budding PMID: 29114027
- Lysine or glutamic acid residues at position 162 or 247 in the SFV E2 glycoprotein affects the level of viremia and the efficiency of neuroinvasion. PMID: 25972559
- Thus, E3 mediates pH protection of E1 during virus biogenesis via interactions strongly dependent on Y47 at the E3-E2 interface. PMID: 23864626
- Our results suggest a critical and previously unidentified role for the DI-DIII linker region during the low-pH-dependent refolding of E1 that drives membrane fusion. PMID: 21543498
- The results suggest that furin-cleaved E3 continues to protect the spike from premature activation in acidic compartments of the cell and that its release in the neutral extracellular space primes the spike for low-pH activation. PMID: 21430054
- D188K mutation of E1 blocks E1 trimerization and inhibits virus entry and infection. PMID: 20826687
- results indicate that the E1 ij loop and the conserved H230 residue play a critical role in alphavirus-membrane fusion and suggest the presence of a previously undescribed late intermediate in the fusion reaction PMID: 15564465
- concluded that the SFV E1 fusion protein, after acid-induced dissociation from E2, rapidly adopts an intermediate, nontrimeric conformation in which it is no longer able to interact with target membrane lipids PMID: 15919953
- second-site mutations in E1 that rescue the H230A mutant were located in a cluster within the hinge region, at the membrane-interacting tip, and within the groove where the E1 stem is believed to pack. PMID: 16731950
- findings demonstrated that there was a strong requirement for the E1 stem in virus assembly and budding, probably reflecting its importance in lateral interactions of the envelope proteins PMID: 16971447
- transformation into a fusogenic stage is modeled; while the fusion loop is available for external interaction and the shell and stalk domains of the spike begin to deteriorate, the E1 and E2 remain in close contact in the spike head PMID: 17192272
- Cells expressing low pH-triggered class II viral fusion protein E1 of SFV were fused to target cells. It is proposed that the trans-negative voltage across the endosomal membrane facilitates fusion after low-pH-induced conformational changes of SFV E1. PMID: 17686870
- SFV E1 is the first virus fusion protein demonstrated to directly bind cholesterol. PMID: 18632857
- findings showed the E1 H3A mutation produced impaired virus growth & a more acidic pH requirement for virus-membrane fusion; results & location of H3 suggest this residue acts to regulate the low-pH-dependent refolding of E1 during membrane fusion PMID: 19244325
- Results indicate that the D188K mutation of Semliki Forest virus E1 protein block SFV fusion and infection. PMID: 19692469
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:[Capsid protein]: Virion. Host cytoplasm. Host cell membrane. Host nucleus.; [Spike glycoprotein E2]: Virion membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Host cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.; [6K protein]: Host cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Virion membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.; [Spike glycoprotein E1]: Virion membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Host cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.
-
數據庫鏈接:
KEGG: vg:922351
Most popular with customers
-
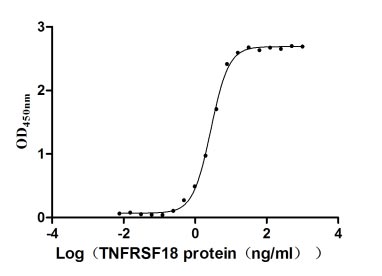
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 18 (TNFRSF18), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
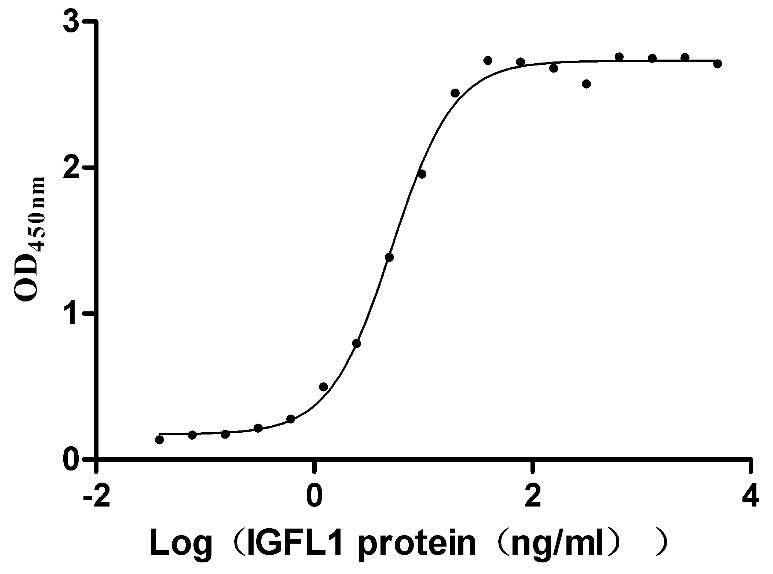
Recombinant Human IGF-like family receptor 1 (IGFLR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
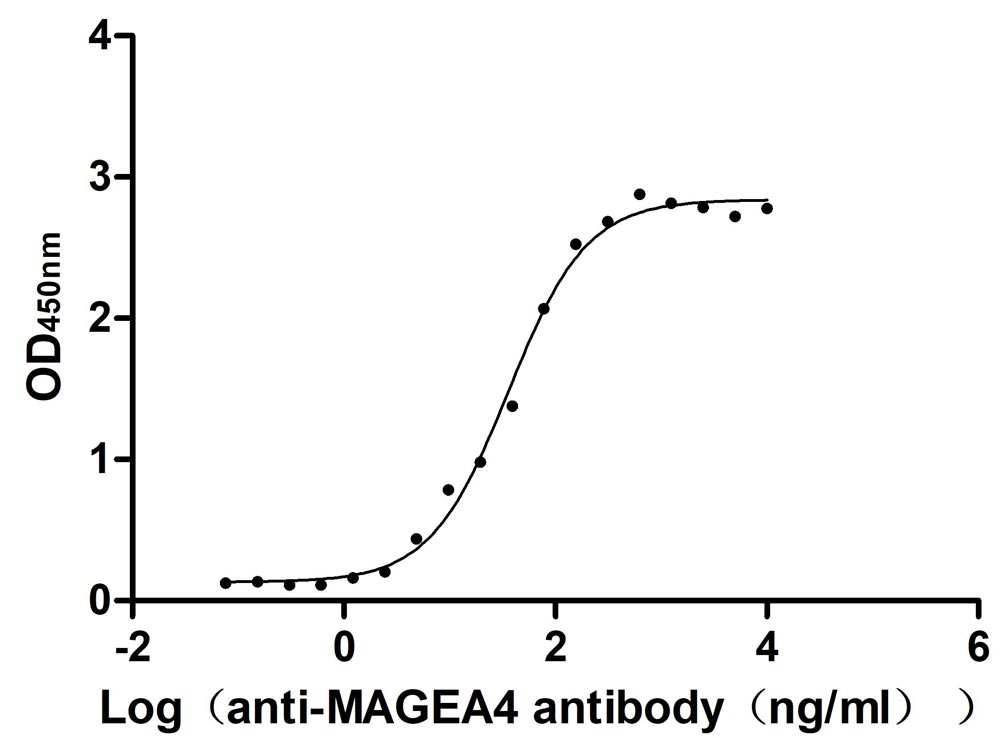
Recombinant Human Melanoma-associated antigen 4 (MAGEA4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
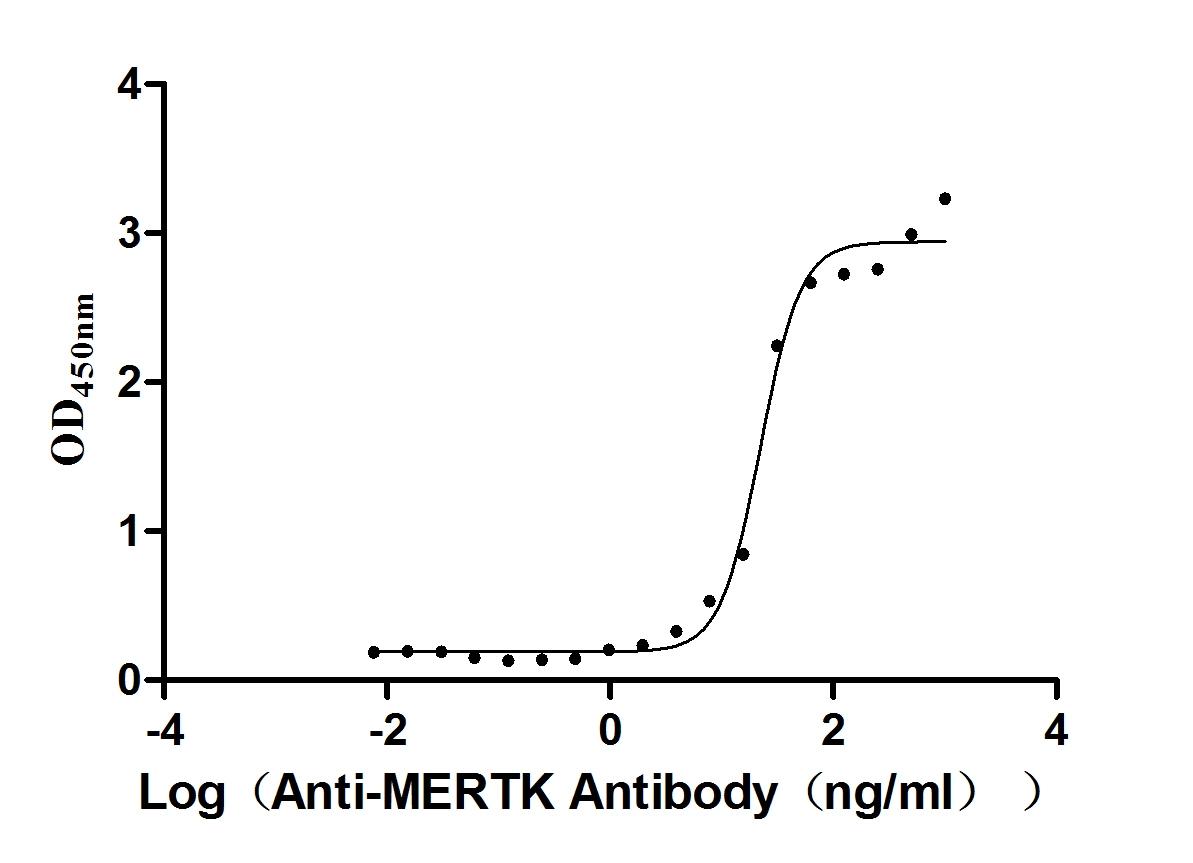
Recombinant Mouse Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer (Mertk), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Pancreatic adenocarcinoma up-regulated factor (ZG16B) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-2 receptor subunit alpha (IL2RA), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DL2 (KIR3DL2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator(BTLA), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)