Recombinant Rat Cryptochrome-1 (Cry1)
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Rat Cryptochrome-1(Cry1)
-
貨號:CSB-YP655597RA
-
規格:
-
來源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Rat Cryptochrome-1(Cry1)
-
貨號:CSB-EP655597RA
-
規格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Rat Cryptochrome-1(Cry1)
-
貨號:CSB-EP655597RA-B
-
規格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Rat Cryptochrome-1(Cry1)
-
貨號:CSB-BP655597RA
-
規格:
-
來源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Rat Cryptochrome-1(Cry1)
-
貨號:CSB-MP655597RA
-
規格:
-
來源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:Cry1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:Cry1Cryptochrome-1
-
種屬:Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
蛋白長度:full length protein
-
表達區域:1-588
-
氨基酸序列MGVNAVHWFR KGLRLHDNPA LKECIQGADT IRCVYILDPW FAGSSNVGIN RWRFLLQCLE DLDANLRKLN SRLFVIRGQP ADVFPRLFKE WNITKLSIEY DSEPFGKERD AAIKKLATEA GVEVIVRISH TLYDLDKIIE LNGGQPPLTY KRFQTLVSKM EPLEMPADTI TSDVIGKCTT PLSDDHDEKY GVPSLEELGF DTDGLSSAVW PGGETEALTR LERHLERKAW VANFERPRMN ANSLLASPTG LSPYLRFGCL SCRLFYFKLT DLYKKVKKNS SPPLSLYGQL LWREFFYTAA TNNPRFDKME GNPICVQIPW DKNPEALAKW AEGRTGFPWI DAIMTQLRQE GWIHHLARHA VACFLTRGDL WISWEEGMKV FEELLLDADW SINAGSWMWL SCSSFFQQFF HCYCPVGFGR RTDPNGDYIR RYLPVLRGFP AKYIYDPWNA PEGIQKVAKC LIGVNYPKPM VNHAEASRLN IERMKQIYQQ LSRYRGLGLL ASVPSNPNGN GGLMGYAPGE NVPSGGSGGG NCSQGSGILH YAHGDSQQTN PLKQGRSSMG TGLSSGKRPS QEEDAQSVGP KVQRQSSN
-
蛋白標簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶點詳情
-
功能:Transcriptional repressor which forms a core component of the circadian clock. The circadian clock, an internal time-keeping system, regulates various physiological processes through the generation of approximately 24 hour circadian rhythms in gene expression, which are translated into rhythms in metabolism and behavior. It is derived from the Latin roots 'circa' (about) and 'diem' (day) and acts as an important regulator of a wide array of physiological functions including metabolism, sleep, body temperature, blood pressure, endocrine, immune, cardiovascular, and renal function. Consists of two major components: the central clock, residing in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the brain, and the peripheral clocks that are present in nearly every tissue and organ system. Both the central and peripheral clocks can be reset by environmental cues, also known as Zeitgebers (German for 'timegivers'). The predominant Zeitgeber for the central clock is light, which is sensed by retina and signals directly to the SCN. The central clock entrains the peripheral clocks through neuronal and hormonal signals, body temperature and feeding-related cues, aligning all clocks with the external light/dark cycle. Circadian rhythms allow an organism to achieve temporal homeostasis with its environment at the molecular level by regulating gene expression to create a peak of protein expression once every 24 hours to control when a particular physiological process is most active with respect to the solar day. Transcription and translation of core clock components (CLOCK, NPAS2, ARNTL/BMAL1, ARNTL2/BMAL2, PER1, PER2, PER3, CRY1 and CRY2) plays a critical role in rhythm generation, whereas delays imposed by post-translational modifications (PTMs) are important for determining the period (tau) of the rhythms (tau refers to the period of a rhythm and is the length, in time, of one complete cycle). A diurnal rhythm is synchronized with the day/night cycle, while the ultradian and infradian rhythms have a period shorter and longer than 24 hours, respectively. Disruptions in the circadian rhythms contribute to the pathology of cardiovascular diseases, cancer, metabolic syndromes and aging. A transcription/translation feedback loop (TTFL) forms the core of the molecular circadian clock mechanism. Transcription factors, CLOCK or NPAS2 and ARNTL/BMAL1 or ARNTL2/BMAL2, form the positive limb of the feedback loop, act in the form of a heterodimer and activate the transcription of core clock genes and clock-controlled genes (involved in key metabolic processes), harboring E-box elements (5'-CACGTG-3') within their promoters. The core clock genes: PER1/2/3 and CRY1/2 which are transcriptional repressors form the negative limb of the feedback loop and interact with the CLOCK|NPAS2-ARNTL/BMAL1|ARNTL2/BMAL2 heterodimer inhibiting its activity and thereby negatively regulating their own expression. This heterodimer also activates nuclear receptors NR1D1/2 and RORA/B/G, which form a second feedback loop and which activate and repress ARNTL/BMAL1 transcription, respectively. CRY1 and CRY2 have redundant functions but also differential and selective contributions at least in defining the pace of the SCN circadian clock and its circadian transcriptional outputs. More potent transcriptional repressor in cerebellum and liver than CRY2, though more effective in lengthening the period of the SCN oscillator. On its side, CRY2 seems to play a critical role in tuning SCN circadian period by opposing the action of CRY1. With CRY2, is dispensable for circadian rhythm generation but necessary for the development of intercellular networks for rhythm synchrony. Capable of translocating circadian clock core proteins such as PER proteins to the nucleus. Interacts with CLOCK-ARNTL/BMAL1 independently of PER proteins and is found at CLOCK-ARNTL/BMAL1-bound sites, suggesting that CRY may act as a molecular gatekeeper to maintain CLOCK-ARNTL/BMAL1 in a poised and repressed state until the proper time for transcriptional activation. Represses the CLOCK-ARNTL/BMAL1 induced transcription of BHLHE40/DEC1, ATF4, MTA1, KLF10 and NAMPT. May repress circadian target genes expression in collaboration with HDAC1 and HDAC2 through histone deacetylation. Mediates the clock-control activation of ATR and modulates ATR-mediated DNA damage checkpoint. In liver, mediates circadian regulation of cAMP signaling and gluconeogenesis by binding to membrane-coupled G proteins and blocking glucagon-mediated increases in intracellular cAMP concentrations and CREB1 phosphorylation. Inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis by decreasing nuclear FOXO1 levels that downregulates gluconeogenic gene expression. Besides its role in the maintenance of the circadian clock, is also involved in the regulation of other processes. Represses glucocorticoid receptor NR3C1/GR-induced transcriptional activity by binding to glucocorticoid response elements (GREs). Plays a key role in glucose and lipid metabolism modulation, in part, through the transcriptional regulation of genes involved in these pathways, such as LEP or ACSL4. Represses PPARD and its target genes in the skeletal muscle and limits exercise capacity. Plays an essential role in the generation of circadian rhythms in the retina. Represses the transcriptional activity of NR1I2.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- N-nitroso-N-methylurea disrupted the expression of Cry1 in mammary glands of Fischer 344 rats PMID: 20424134
- Circadian expression of Cry1 and Cry2 mRNA in the suprachiasma nucleus displayed a circadian rhythm with a peak at the day/night transition, and there was a slightly different circadian pattern of expression of Cry1 and Cry2 in the eye. PMID: 15529004
-
亞細胞定位:Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:DNA photolyase class-1 family
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Pro-neuregulin-1, membrane-bound isoform (NRG1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
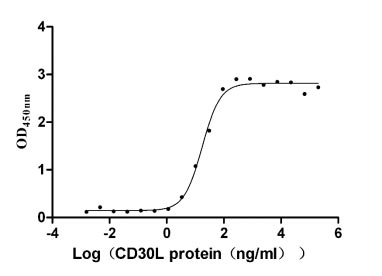
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 8 (TNFRSF8), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
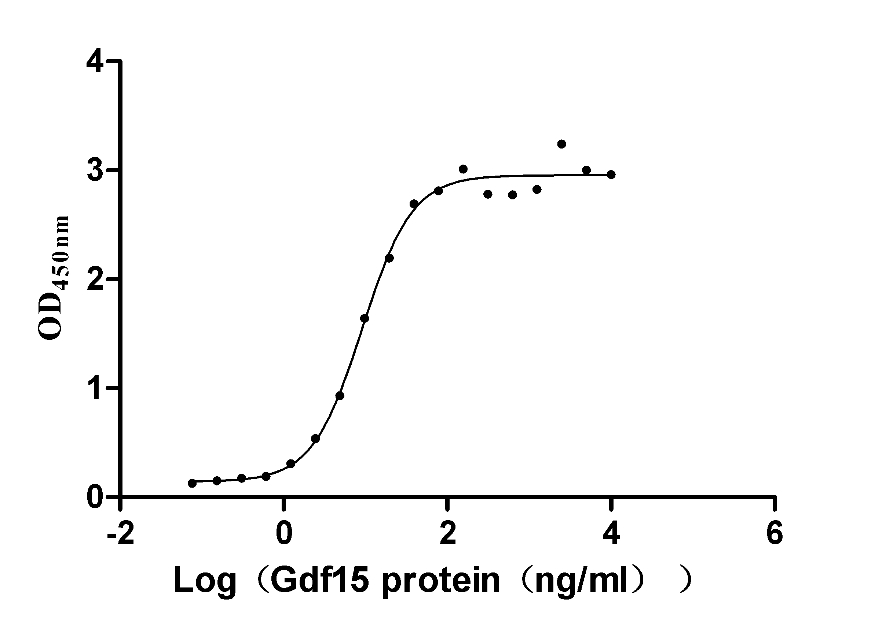
Recombinant Mouse GDNF family receptor alpha-like (Gfral), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
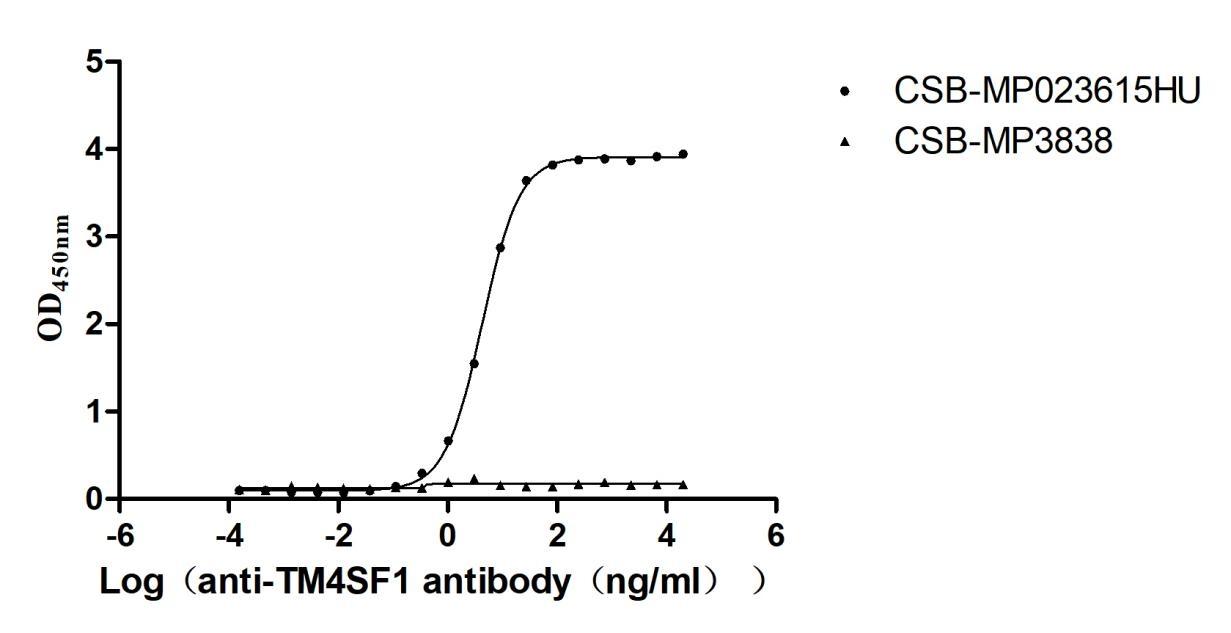
Recombinant Human Transmembrane 4 L6 family member 1(TM4SF1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)