Recombinant Rat Cholecystokinin receptor type A (Cckar), partial
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Rat Cholecystokinin receptor type A(Cckar),partial
-
貨號:CSB-YP004772RA1
-
規格:
-
來源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Rat Cholecystokinin receptor type A(Cckar),partial
-
貨號:CSB-EP004772RA1
-
規格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Rat Cholecystokinin receptor type A(Cckar),partial
-
貨號:CSB-EP004772RA1-B
-
規格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Rat Cholecystokinin receptor type A(Cckar),partial
-
貨號:CSB-BP004772RA1
-
規格:
-
來源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Rat Cholecystokinin receptor type A(Cckar),partial
-
貨號:CSB-MP004772RA1
-
規格:
-
來源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:Cckar; Cholecystokinin receptor type A; CCK-A receptor; CCK-AR; Cholecystokinin-1 receptor; CCK1-R
-
種屬:Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
蛋白長度:Partial
-
蛋白標簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產品提供形式:Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Receptor for cholecystokinin. Mediates pancreatic growth and enzyme secretion, smooth muscle contraction of the gall bladder and stomach. Has a 1000-fold higher affinity for CCK rather than for gastrin. It modulates feeding and dopamine-induced behavior in the central and peripheral nervous system. This receptor mediates its action by association with G proteins that activate a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- This study demonistrated that Cckar and Melanin-concentrating hormone colization in neuron in the lateral hypothalamus (LH) and zona incerta (ZI), but MCHR1 mRNA is widely expressed throughout the brain. PMID: 24978951
- Data suggest that Apo AIV (apolipoprotein AIV) in NTS (nucleus of the solitary tract) or/and peripheral Cck (cholecystokinin) require vagal Cck1r/Cckar signaling to elicit satiation; high-fat diet reduces satiating capacity of these signals. PMID: 24564397
- factors secondary to obesity and/or diabetes rather than impaired CCK-1 receptor signaling may contribute to altered CART expression PMID: 23545074
- CCK-A receptors are located on the cell bodies of cholinergic interneurons in the corpus striatum. PMID: 22981453
- Activation of duodenal PKC-delta leads to the stimulation of CCK release and activation of the CCK-A receptor signaling axis to lower glucose production in normal rats. PMID: 21984583
- Data indicate that the Homo-Phe derivative 2 (VL-0797) enhanced 12-fold the affinity for the rat CCK(1)-R affinity and 15-fold for the human CCK(1)-R relative to the reference compound 12 (VL-0395). PMID: 21728335
- Data suggest L-364,718 potentiates electroacupuncture analgesia through the CCK-A receptor of pain-excited and pain-inhibited neurons in the nucleus parafascicularis. PMID: 20953702
- CCK1 and CCK2 receptors are expressed on pancreatic stellate cells and induce collagen production PMID: 20843811
- our results demonstrate for the first time, that CCK-1 receptor plays a crucial role in both meal-induced and fasting insulin sensitization PMID: 20624386
- Present study examined the contribution of genetics, sex and early maternal environment to anxiety-like behaviors and locomotion in CCK1 knockout rats, suggesting that the mutation may predispose (rather than induce) the animals to an anxious phenotype. PMID: 20347877
- The results of this study showed that increased oil intake in cck-1 receptor deficient rats is driven by both peripheral deficits to satiation and altered orosensory sensitivity. PMID: 19887078
- Gastric leptin may exert acute sympathoinhibitory and cardiovascular effects via vagal transmission and CCK(1) receptor activation and may play a separate role to adipose leptin in short-term cardiovascular regulation. PMID: 19940076
- Activation of high-affinity CCK(A) receptors elicits Ca(2+) oscillations, whereas stimulation of low-affinity CCK(A) receptors evokes a sustained Ca(2+) plateau; these modes are mediated through L-type Ca(2+) channel and involve G(q) protein. PMID: 12016125
- These results indicate that CCKB, but not CCKA receptors are involved in anxiety, as tested by microinjection of cholecystokinin agonists. PMID: 12373548
- endogenous CCK appears to act in part by a paracrine or neurocrine mechanism at CCKARs peripheral to the blood-brain barrier to inhibit gastric emptying PMID: 12388446
- Endogenous CCK appears to act in part at CCKARs peripheral to the blood-brain barrier to inhibit food intake PMID: 12414437
- None of the three known phases of the febrile response of rats to lipopolysaccharides requires the CCK-A receptor. PMID: 12562931
- results demonstrate that cholecystokinin stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of three sites in focal adhesion kinase and proline-rich kinase 2 but differs in participation of cholecystokinin receptor A and by protein kinase C and [Ca2+] PMID: 12651850
- CCK-AR and CCK-BR gene were present in pulmonary vascular endothelial cells, macrophages, bronchial epithelial cells and alveolar epithelial cells, which play an important role in mediating the regulatory actions of CCK-8 on these cells. PMID: 12800239
- peripheral and central responses to enterostatin are mediated through or dependent on peripheral and central CCK-A receptors PMID: 12855414
- CCK-A receptors play an important role in the regulation of central dopamine transmission, as revealed by studies of the CCK-A receptor-deficient Otsuka Long Evans Tokushima Fatty (OTLEF) rat strain. PMID: 12932815
- spatial memory was impaired in the OLETF rats with genetic abnormality in cck-a receptor PMID: 14607104
- the data identified CCK-A and CCK-B receptor mRNAs in the rat retina and demonstrated that they are functional, stimulating tyrosine phosphorylation pathways. PMID: 14698681
- involvement of type A CCK receptors in the mediation of the inhibitory effect of large doses of ethanol on the gastric emptying PMID: 14700745
- acute pancreatitis induced by bile-pancreatic duct ligation associates with a temporal increase in pancreatic cholecystokinin-A receptor protein expression, p38 mitogen activated protein kinase activation, and nuclear factor-kappaB activation PMID: 14988658
- apo A-IV released from the intestinal mucosa during lipid absorption stimulates the release of endogenous CCK that activates CCK(1) receptors on vagal afferent nerve terminals initiating feedback inhibition of gastric motility. PMID: 15117731
- Differential roles for cholecystokinin a receptors in energy balance in rats and mice. PMID: 15123537
- The OLETF rats showed a large hysteresis. PMID: 15178543
- Taste preference in Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima fatty (OLETF) rats with deficiency of this receptor. PMID: 15358606
- These findings demonstrate that compared with controls, OLETF rats differ in their gustatory functions with an overall augmented sensitivity for sweet that progresses during prediabetes. PMID: 16081877
- Lack of CCK-1 receptors, or other OLETF-related abnormalities, resulted in a satiation deficit, leading to increased meal size, hyperphagia, and increased weight gain as early as 2-4 postnatal days. PMID: 16099824
- Cholecystokinin-8 activates the brainstem and myenteric neurons through the CCK1 receptor. PMID: 16112401
- CCK1 receptors have a role in stress and pain responses in rats PMID: 16289472
- under 'basal' conditions, a portion of the glandular protein synthesis, as well as the whole increase in synthesis in response to administration of pentagastrin, engaged both types of CCK receptors. PMID: 16556659
- OLETF rats do not express deficits in controlling gastric emptying rates; however, they exhibit decreased behavioral and vagal responsiveness to gastric distension that may contribute to the increased meal size in these animals. PMID: 16728725
- REVIEW: hyperphagia and obesity in OLETF rats without CCK-1 receptors PMID: 16815799
- Report effects of cholecystokinin-58 on type 1 cholecystokinin receptor function and regulation. PMID: 18776046
- cholecystokinin CCK1 and serotonin 5-HT3 receptors are mediators of the excitatory effects of cholecystokinin and 5-HT, respectively, on pancreatic vagal afferent discharge PMID: 19026634
- Fischer 344 rats lacking the cholecystokinin-1 receptor gene show normal feeding and body weight. PMID: 19111529
- The findings suggest that in addition to previously described deficits in peripheral satiety signals and augmented orexigenic regulation, the anorectic effect of CART peptide may also be diminished in CCK-1 deficient rats. PMID: 19533109
- endogenous CCK-1 receptor signaling in infants is a potential pathway through which maternal-pup interactions regulate the development and functional organization of emotional circuits that control anxiety-like behavior in the offspring. PMID: 20001102
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:G-protein coupled receptor 1 family
-
組織特異性:Pancreas and brain. Also expressed in the gastrointestinal system and vagus nerve.
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
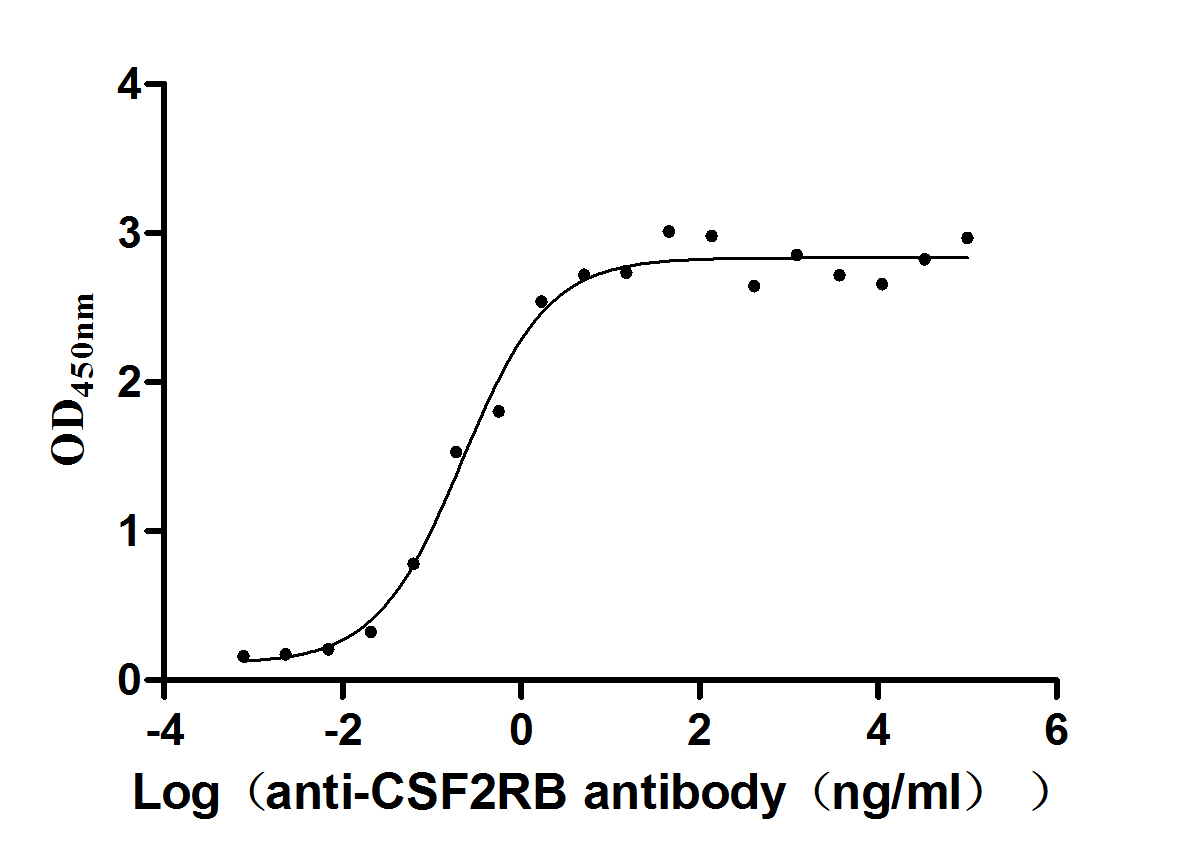
Recombinant Human Cytokine receptor common subunit beta (CSF2RB), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
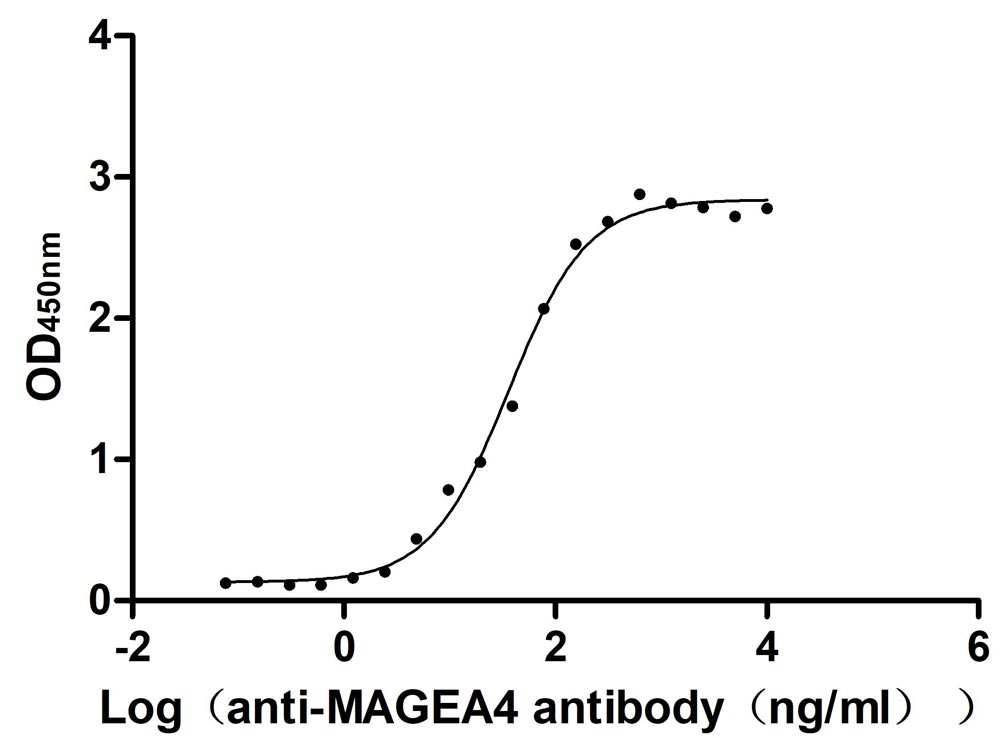
Recombinant Human Melanoma-associated antigen 4 (MAGEA4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
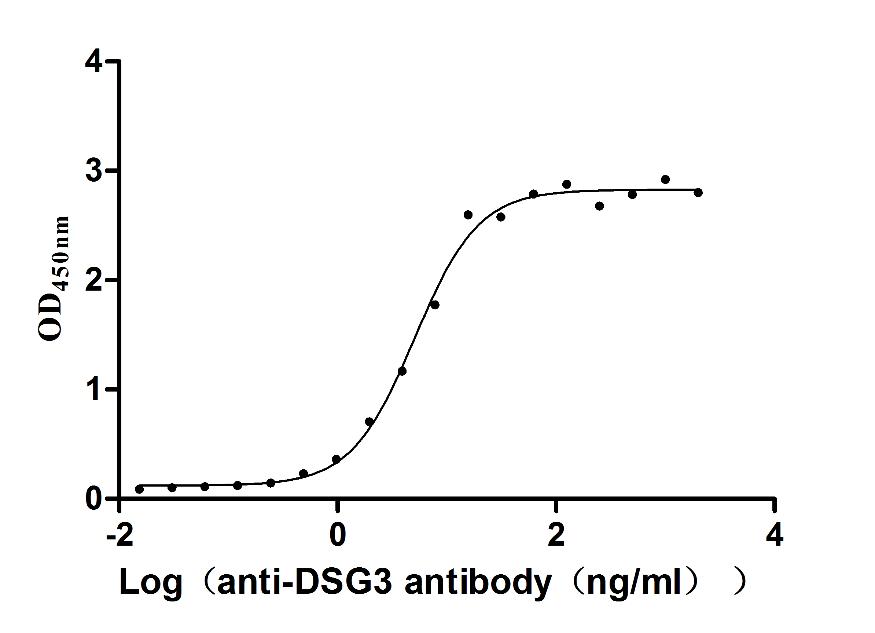
Recombinant Human Desmoglein-3 (DSG3), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
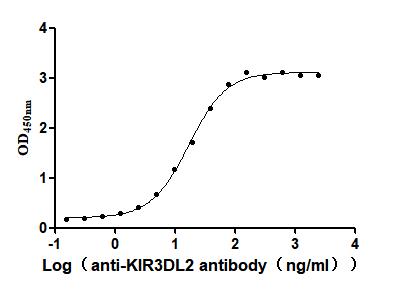
Recombinant Human Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DL2 (KIR3DL2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 15(TNFSF15) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)









