Recombinant Mouse Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte protein 4 (Ctla4),Partial
In Stock-
中文名稱:Recombinant Mouse Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte protein 4(Ctla4),Partial
-
貨號:CSB-EP006163MO1
-
規格:¥1836
-
圖片:
-
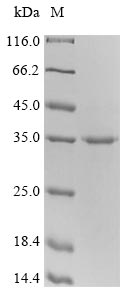
(Tris-Glycine gel) Discontinuous SDS-PAGE (reduced) with 5% enrichment gel and 15% separation gel.
-
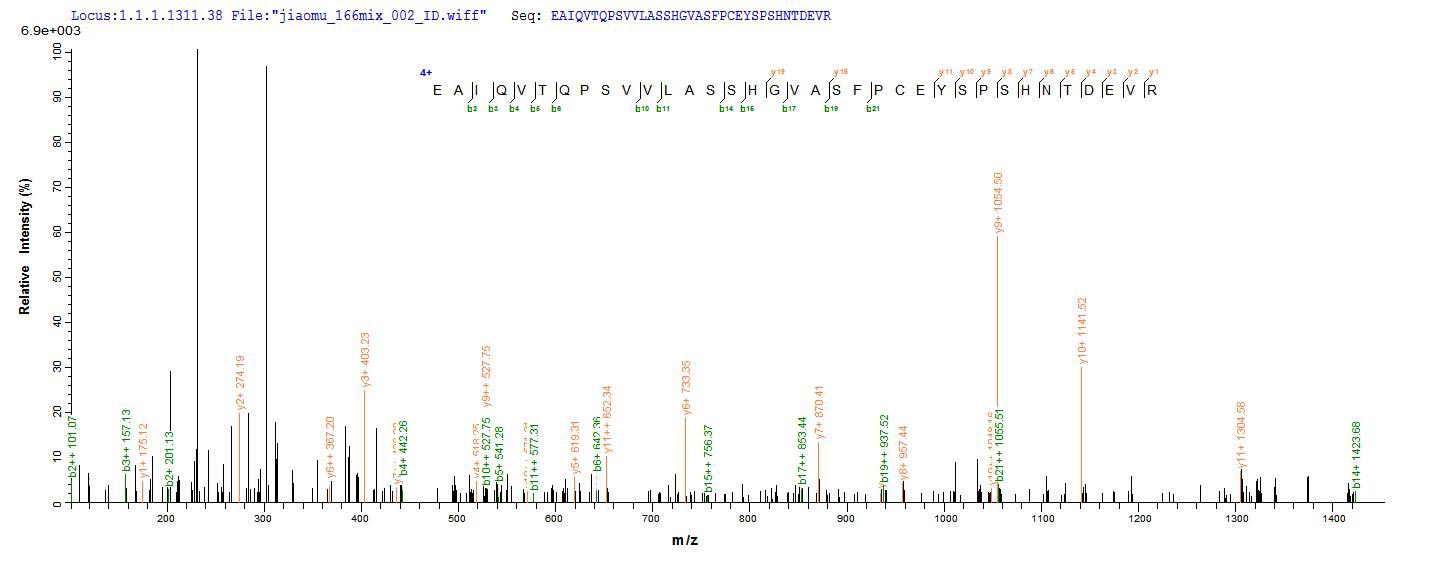
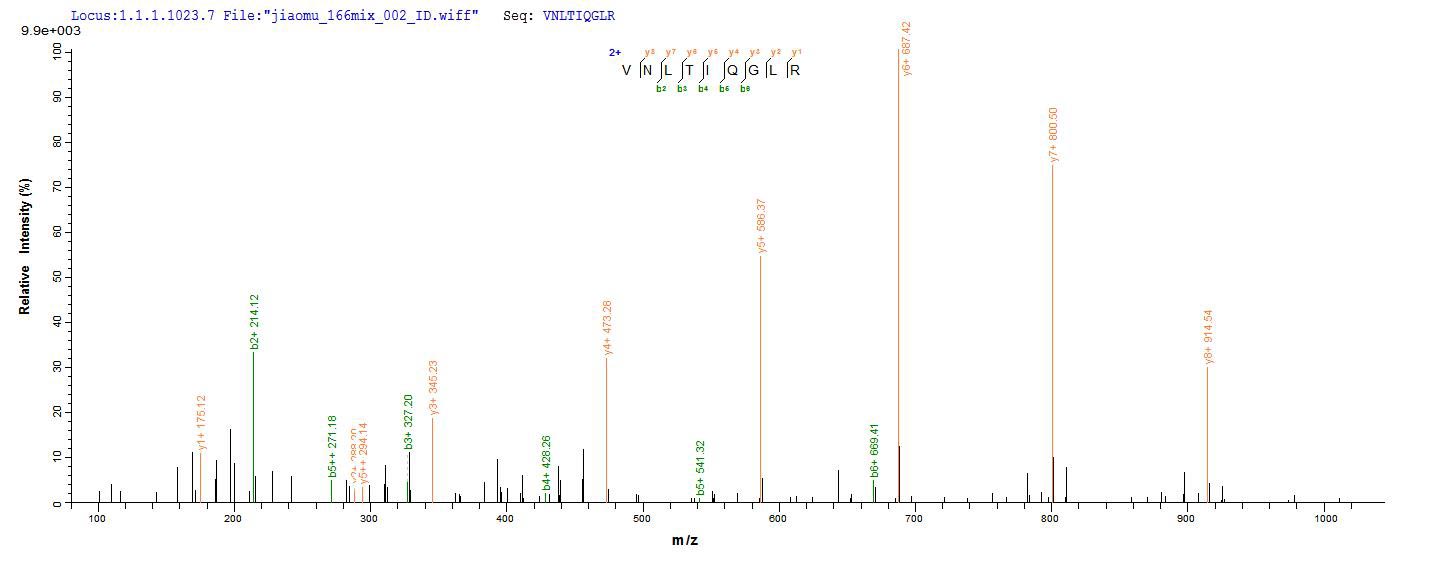
Based on the SEQUEST from database of E.coli host and target protein, the LC-MS/MS Analysis result of CSB-EP006163MO1 could indicate that this peptide derived from E.coli-expressed Mus musculus (Mouse) Ctla4.
-
Based on the SEQUEST from database of E.coli host and target protein, the LC-MS/MS Analysis result of CSB-EP006163MO1 could indicate that this peptide derived from E.coli-expressed Mus musculus (Mouse) Ctla4.
-
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
純度:Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:Ctla4; Cd152; Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte protein 4; Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4; CTLA-4; CD antigen CD152
-
種屬:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白長度:Extracellular Domain
-
來源:E.coli
-
分子量:33.9kDa
-
表達區域:36-161aa
-
氨基酸序列EAIQVTQPSVVLASSHGVASFPCEYSPSHNTDEVRVTVLRQTNDQMTEVCATTFTEKNTVGFLDYPFCSGTFNESRVNLTIQGLRAVDTGLYLCKVELMYPPPYFVGMGNGTQIYVIDPEPCPDSD
Note: The complete sequence may include tag sequence, target protein sequence, linker sequence and extra sequence that is translated with the protein sequence for the purpose(s) of secretion, stability, solubility, etc.
If the exact amino acid sequence of this recombinant protein is critical to your application, please explicitly request the full and complete sequence of this protein before ordering. -
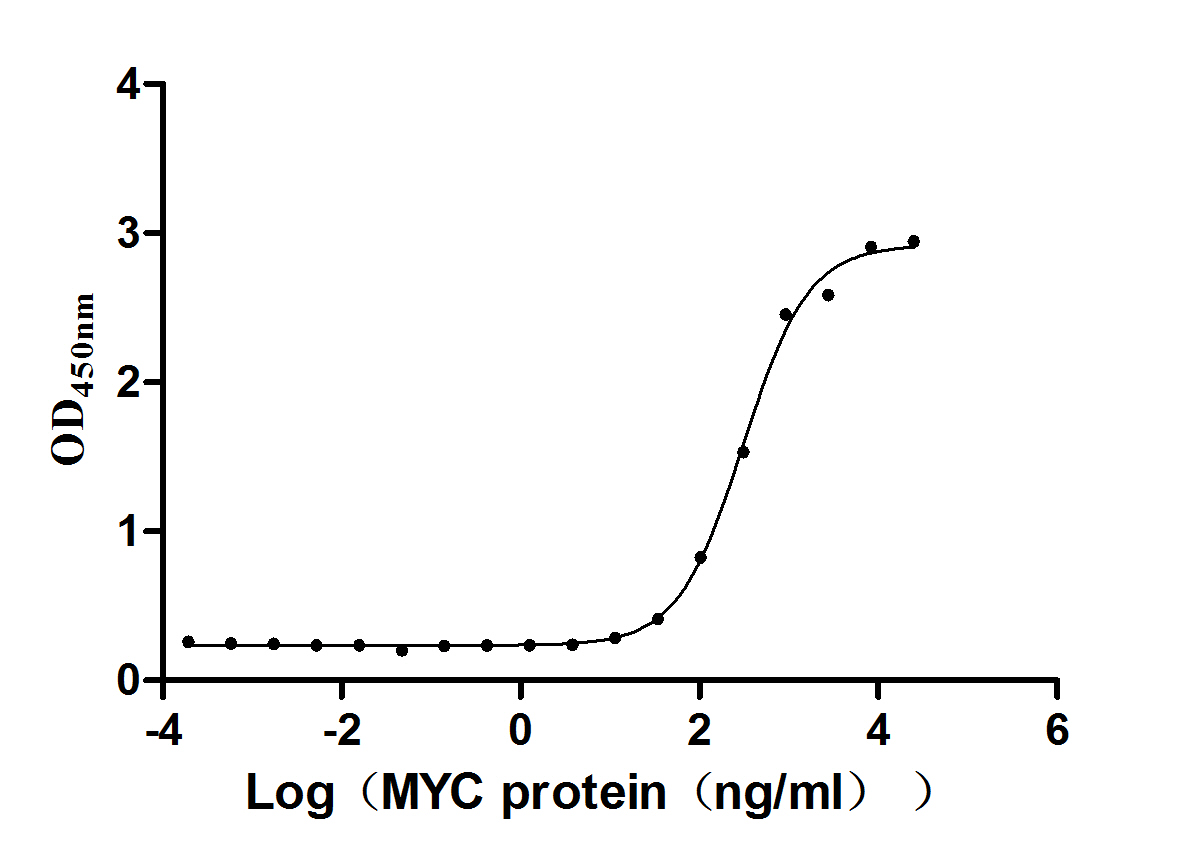
蛋白標簽:N-terminal 10xHis-SUMO-tagged and C-terminal Myc-tagged
-
產品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
緩沖液:If the delivery form is liquid, the default storage buffer is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 5%-50% glycerol.
Note: If you have any special requirement for the glycerol content, please remark when you place the order.
If the delivery form is lyophilized powder, the buffer before lyophilization is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose. -
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:3-7 business days
-
注意事項:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Inhibitory receptor acting as a major negative regulator of T-cell responses. The affinity of CTLA4 for its natural B7 family ligands, CD80 and CD86, is considerably stronger than the affinity of their cognate stimulatory coreceptor CD28.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- Immunogenic mouse neuroblastoma acquires adaptive immune resistance by up-regulating PD-L1 expression, whereas PD-L1 is of lesser consequence in nonimmunogenic neuroblastoma tumors. Combining PD-L1 checkpoint inhibition with whole tumor cell/anti-CTLA-4 vaccination enhanced tumor cell killing, cured mice with established tumors, and induced long-term immune memory (6 months). PMID: 29377881
- the investigation of RANK and RANKL as possible novel immunotherapy targets in cancer is a rational approach. Here we have defined the mechanism of action of RANKL-RANK blockade in combination with anti-CTLA4, and provide insight into the combination efficacy observed in the case reports. PMID: 28634284
- reveal a novel CTLA-4-mediated pathway to attenuate cytotoxic T-lymphocytes and indicate the importance of post-transcriptional mechanisms in the regulation of anti-tumor immune responses PMID: 28644433
- The potential of the CTLA4 and G250 co-expression DNA vaccine. PMID: 28351777
- Tregs were observed to regulate CD4(+), but not CD8(+), T cell infiltration into tumors through a CTLA-4/CD80 dependent mechanism. Disrupting CTLA-4 interaction with CD80 was sufficient to induce CD4 T cell infiltration into tumors. PMID: 28856392
- These results suggest that CD44(+)CD117(+) T cells are stem cells and a specific T-cell phenotype that initially develops in the thymus, but they do not progress through DN3 and DN4 stages, lack a DP stage, and potently suppress T-cell proliferation and modulate the CTLA-4 pathway. PMID: 28279199
- data suggest that increased expression of checkpoint blockade molecules PD-1 and CTLA-4 on donor T cells is not sufficient to prevent GvHD, and that cooperation between checkpoint blockade signaling by host cells and donor Tregs is necessary to limit GvHD in allo-HSCT recipients PMID: 28953925
- Treg cells expand in both humans and mice in blood-stage malaria and interfere with conventional T helper cell responses and follicular T helper (TFH)-B cell interactions in germinal centers. Mechanistically, Treg cells function in a critical temporal window to impede protective immunity through cytotoxic-T-lymphocyte-associated protein-4 (CTLA-4). PMID: 28892065
- CTLA-4 expressed by FOXP3(+) regulatory T cells prevents inflammatory tissue attack and not T-cell priming in arthritis. PMID: 28497863
- results are consistent with a complex pathway in which CD28 is the primary driver of Treg proliferation and CTLA-4 functions as the main brake but is also dependent on TCR signals and interactions with CD80/CD86 PMID: 28053234
- CTLA-4(+) microvesicles can competitively bind B7 costimulatory molecules on bystander dendritic cells, resulting in downregulation of B7 surface expression. PMID: 26979751
- this study shows that miR-155 is modulated by a major dust mite allergen, Dermatophagoides farinae (Df1), and increases CD4+ T cell proliferation through the downregulation of cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) expression PMID: 28110885
- CTLA-4 regulates atherosclerosis by suppressing proatherogenic immune responses. PMID: 27055906
- Data suggest enhanced clinical benefit from combining CTLA-4 antigen blockade with poxvirus-based active immunotherapy. PMID: 26961085
- up-regulated expression correlates with the tolerogenic effect of syngeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation PMID: 26311302
- Induced Treg Cells Augment the Th17-Mediated Intestinal Inflammatory Response in a CTLA4-Dependent Manner PMID: 26950218
- CTLA-4 has a regulatory T cell-intrinsic role in limiting peripheral regulatory T cell expansion and activation, and in their capacity to control conventional T cells. PMID: 26371185
- The Ctla4 SNP (e2_77A/G) does not alter diabetes susceptibility, but does control mRNA alternative splicing. PMID: 26450994
- Sorafenib suppressed the expression of immunosuppressive factors in MDSCs. These data indicate that combination therapy of sorafenib and anti-CTLA-4 Ab may be effective in advanced kidney cancer patients. PMID: 25845968
- The co-stimulatory molecule CTLA-4 mediates in vitro differentiation of iTreg cells. PMID: 25238105
- The bullseye immunological synapse formation is mediated by CTLA4, and may negatively control T-cell activation as a suppressive synapse. PMID: 25287444
- this study reports that regulatory T (Treg) cells orchestrate memory T cell quiescence by suppressing effector and proliferation programs through inhibitory receptor, cytotoxic- T-lymphocyte-associated protein-4 (CTLA-4). PMID: 26084026
- Short-term blockade with anti-CTLA-4 antibody in wild-type mice is sufficient to elicit follicular helper T cell generation and germinal center development. The latter occurs in a CD28-dependent manner. PMID: 25548162
- CTLA-4 and mTOR down-regulation cooperate during CD8+ T cell priming to promote memory formation and metabolic readiness. PMID: 25624453
- role in Treg cell-mediated control of T follicular regulatory cell proliferation, germinal center formation,and of humoral immune responses PMID: 25526312
- The study concludes that although the presence of CTLA4 plays a critical role in controlling homeostasis of T cells, its quantitative variation may impose diverse or even opposing effects on distinct lineages of T cells, an optimal sum of which is necessary for preservation of T cell immunity while suppressing tissue damage. PMID: 25246499
- cardiomyocytes can express CD80; this expression pattern can resist CTL-mediated lysis through CTLA-4 pathway PMID: 24507064
- Alternative splice forms of CTLA-4 induced by antisense mediated splice-switching influences autoimmune diabetes susceptibility in NOD mice. PMID: 24494586
- CTLA4(apt) fused to a STAT3-targeting siRNA (CTLA4(apt)-STAT3 siRNA) resulted in internalization into tumor-associated CD8 T cells and silencing of STAT3, which activated tumor antigen-specific T cells in tumor models. PMID: 24892807
- results show that CTLA-4 promotes Tc17 differentiation that results in robust Tc17 responses PMID: 24723371
- These data suggest that effects associated with and mediated through Tyr201 of CTLA-4s intracellular domain are critical for Treg-cell function. PMID: 24648182
- Our in vitro experiments revealed that IL-2 induced expression of CTLA-4 in mouse natural killer cells PMID: 24688023
- These novel insights into the differential regulation of CTLA-4 coinhibition on CD4(+) T cells have implications for the immunomodulation of pathologic T cell responses during transplantation and autoimmunity. PMID: 24493820
- SOCS3 interacts with CTLA-4 and negatively regulates CTLA-4 levels in T cells, providing a mechanistic explanation for the expansion of regulatory T cells in CD4-SOCS3 during experimental autoimmune uveitis. PMID: 24101549
- This novel mechanism of CTLA-4lg immunotherapy may lead to an ideal anti-obesity/inflammation/insulin resistance agent. PMID: 23872146
- Data show coexpression of PD-1 and CTLA-4 correlates with more severe dysfunction of tumor-specific CD8+ T cells. PMID: 23633484
- Our results identify CTLA-4 as a key factor that regulates the composition of the Foxp3+ T-cell population in the intestine. PMID: 22910217
- The soluble isoform of CTLA-4 is a regulator of T-cell responses. PMID: 23400950
- The presence of the alternatively spliced 1/4 CTLA-4 isoform can further promote autoimmunity and autoimmune pathology in lupus-prone mice and suggests that altered splicing of CTLA4 contributes to the expression of autoimmune disease. PMID: 23203389
- Li-CTLA-4 expressed at physiologic levels in the CTLA-4-sufficient NOD background suppresses autoimmunity; but, the functionality of the li-CTLA-4 isoform depends on the presence of the full-length molecule to alter effector T cell signaling. PMID: 23293354
- CTLA-4 is expressed in the corticomedullary region of the thymus. Its absence alters the response of CD4(+)CD8(-) thymocytes to self-antigen recognition, which affects the quantity of the Treg cells and broadens the repertoire of peripheral T cells. PMID: 23267099
- pathways by which cAMP regulates CTLA4 expression, focusing on transcriptional activation PMID: 23024062
- Findings indicate that CTLA-4-negative regulation of conventional T cells (Tconvs) but not regulatory T cells (Tregs) in immune responses. PMID: 23047820
- direct evidence that CTLA4 inhibits spontaneous tumor development PMID: 22777737
- CTLA-4 on normal effector CD4-positive T cells completely abrogates the dramatically increased expansion normally experienced by their CTLA-4-deficient counterparts. PMID: 22753941
- a potential new role for CTLA-4 in Treg differentiation PMID: 22337882
- the importance of intracellular localization for CTLA-4 protein function and reveal that CTLA-4 protein externalization imparts suppressor function to both regulatory and conventional CD4(+) T cells. PMID: 22403258
- boosting CD152 or its down-stream signal transduction could aid therapies aimed at sensitizing T lymphocytes for optimal migration, thus contributing to a precise and effective immune response. PMID: 22412835
- The expression of CTLA-4 and PD-1 on T cells correlates with the extent of proinflammatory responses induced during Plasmodium berghei infection, being higher in C57BL/6 than in BALB/c mice. PMID: 22319445
- CTLA4-Ig may promote neuronal differentiation during the treatment of neurological diseases with cell replacement therapy PMID: 22155494
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.
-
組織特異性:Widely expressed with highest levels in lymphoid tissues.
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus Spike glycoprotein (S), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Human SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV) (Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus)
-
Recombinant Human Leukemia inhibitory factor receptor (LIFR), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human papillomavirus type 16 Protein E7 (E7) (Active)
Express system: E.coli
Species: Human papillomavirus type 16
-
Recombinant Human Melanoma-associated antigen 4 (MAGEA4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
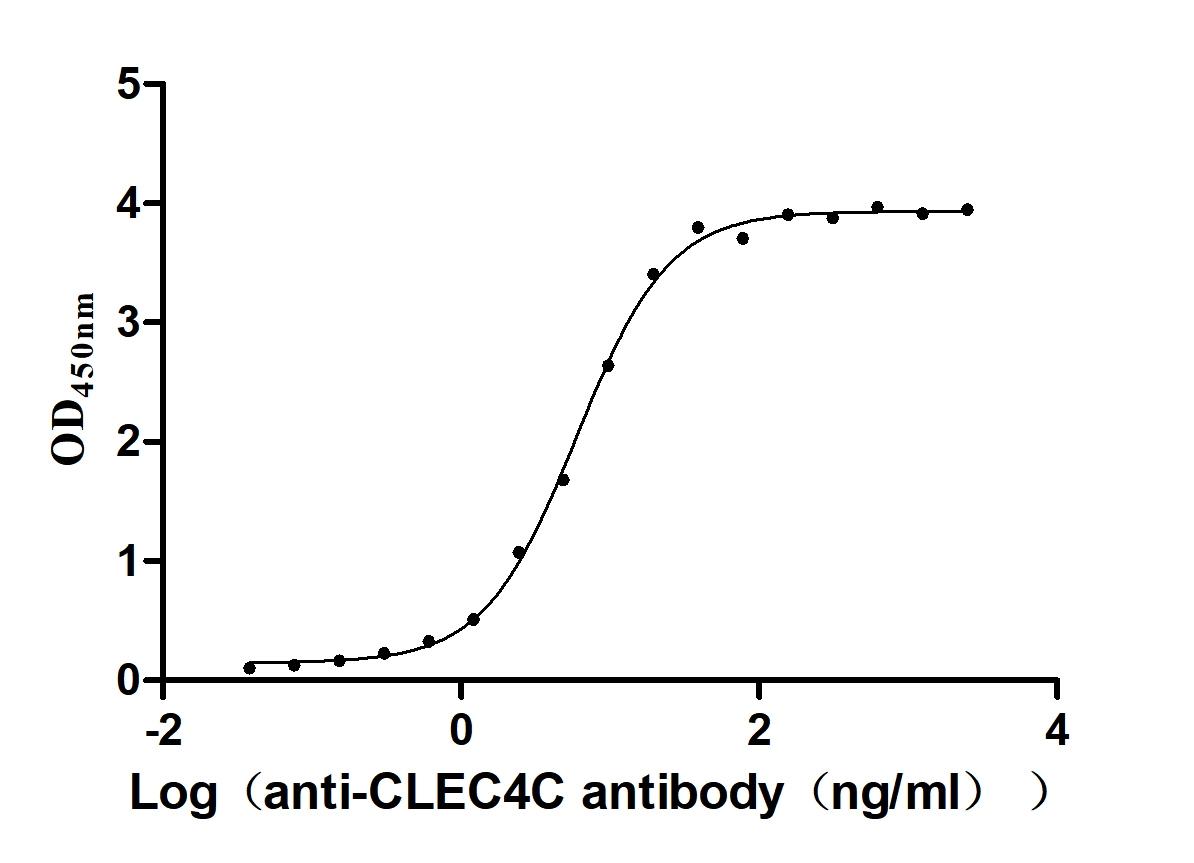
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis C-type lectin domain family 4 member C(CLEC4C), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
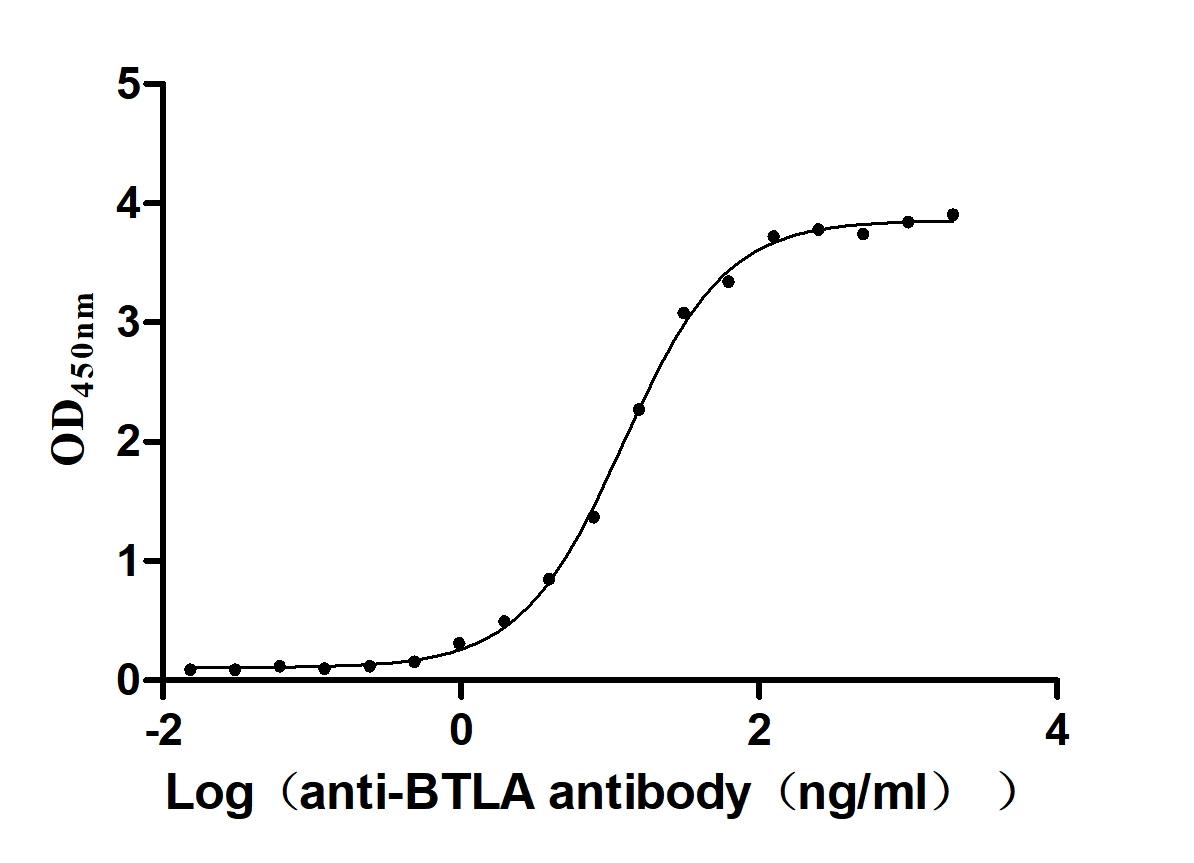
Recombinant Human B- and T-lymphocyte attenuator(BTLA), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-


-AC1.jpg)