Recombinant Mouse C-type lectin domain family 4 member E (Clec4e), partial
-
中文名稱:Recombinant Mouse C-type lectin domain family 4 member E(Clec4e) ,partial
-
貨號:CSB-EP870809MO
-
規格:¥2328
-
圖片:
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
純度:Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:Clec4e; Clecsf9; Mincle; C-type lectin domain family 4 member E; C-type lectin superfamily member 9; Macrophage-inducible C-type lectin; Mincle
-
種屬:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
蛋白長度:Extracellular Domain
-
來源:E.coli
-
分子量:23.6kDa
-
表達區域:46-214aa
-
氨基酸序列TYRSSQISGQNLQPHRNIKELSCYSEASGSVKNCCPLNWKHYQSSCYFFSTTTLTWSSSLKNCSDMGAHLVVIDTQEEQEFLFRTKPKRKEFYIGLTDQVVEGQWQWVDDTPFTESLSFWDAGEPNNIVLVEDCATIRDSSNSRKNWNDIPCFYSMPWICEMPEISPLD
Note: The complete sequence may include tag sequence, target protein sequence, linker sequence and extra sequence that is translated with the protein sequence for the purpose(s) of secretion, stability, solubility, etc.
If the exact amino acid sequence of this recombinant protein is critical to your application, please explicitly request the full and complete sequence of this protein before ordering. -
蛋白標簽:N-terminal 6xHis-tagged
-
產品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
緩沖液:If the delivery form is liquid, the default storage buffer is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 5%-50% glycerol.
Note: If you have any special requirement for the glycerol content, please remark when you place the order.
If the delivery form is lyophilized powder, the buffer before lyophilization is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose. -
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Calcium-dependent lectin that acts as a pattern recognition receptor (PRR) of the innate immune system: recognizes damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) of abnormal self and pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) of bacteria and fungi. The PAMPs notably include mycobacterial trehalose 6,6'-dimycolate (TDM), a cell wall glycolipid with potent adjuvant immunomodulatory functions. Interacts with signaling adapter Fc receptor gamma chain/FCER1G to form a functional complex in myeloid cells. Binding of mycobacterial trehalose 6,6'-dimycolate (TDM) to this receptor complex leads to phosphorylation of the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) of FCER1G, triggering activation of SYK, CARD9 and NF-kappa-B, consequently driving maturation of antigen-presenting cells and shaping antigen-specific priming of T-cells toward effector T-helper 1 (Th1) and T-helper 17 (Th17) cell subtypes. Also recognizes alpha-mannose residues on pathogenic fungi of the genus Malassezia and mediates macrophage activation. Through recognition of DAMPs released upon nonhomeostatic cell death, enables immune sensing of damaged self and promotes inflammatory cell infiltration into the damaged tissue.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- our results indicate that Mincle plays an important role in neutrophil infiltration and suggest that Mincle signaling may provide a therapeutic target for treating sepsis PMID: 28112221
- Mincle activation by cholesterol sulfate causes the secretion of a range of proinflammatory mediators in response to skin damage. PMID: 28292894
- this study shows that mincle inhibits neutrophils and macrophages apoptosis in Aspergillus fumigatus keratitis PMID: 28888778
- Mincle is induced specifically on M1 macrophages, where Mincle-Syk signaling promotes and maintains inflammatory phenotypes of M1 macrophages in acute renal inflammation. PMID: 28017324
- work implicates a novel innate immune driver of Con A hepatitis and, more broadly, suggests a potential role for Mincle in diseases governed by sterile inflammation. PMID: 27559045
- Mincle deletion results in TLR4-mediated inflammation. PMID: 26747838
- Priming by Mincle-deficient dendritic cells (DCs). PMID: 27742545
- this study shows that immune activation in vitro and in vivo by trehalose esters of simple fatty acids requires two acyl chains of length and involves Mincle PMID: 27252171
- Attenuated neutrophil extracellular trap formation in Mincle-/- neutrophils correlates with impaired autophagy activation in vitro and in vivo, whereas reactive oxygen species formation in these neutrophils remained intact. PMID: 28186242
- We here show that Mincle gene expression was induced in alveolar macrophages and neutrophils in bronchoalveolar lavage fluids of mice and patients with pneumococcal pneumonia PMID: 27923071
- this study shows a significant role for Mincle in Pneumocystis modulating host defense during infection PMID: 28298521
- The authors report that microbial stimulation triggers Mincle (Clec4e) expression through the myeloid differentiation primary response gene 88 (MyD88) pathway; a process that does not require MCL (Clecsf8, Clec4d). Conversely, they show that MCL is constitutively expressed but retained intracellularly until Mincle is induced, whereupon the receptors form heterodimers which are translocated to the cell surface. PMID: 27005451
- a nonredundant role for Clec4e in coordinating major biological pathways involved in atherosclerosis PMID: 27587433
- this paper shows that mycobacterial cell envelope glycolipid TDM modulates TLR2-mediated IL-10 and IL-12p40 responses in macrophages through Mincle, which is, in turn, up-regulated by Mycobacterium bovis BCG PMID: 26939595
- Data show that Mincle, the inducible receptor for mycobacterial cord factor, is the key switch for the transition of macrophages from cytokine expression to high nitric oxide production. PMID: 27089465
- work shows parallel networks of necroptosis-induced CXCL1 and Mincle signalling that promote macrophage-induced adaptive immune suppression and thereby enable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression PMID: 27049944
- The results indicate differential roles for Dectin-2 and Mincle in the generation of adaptive immune responses to F. pedrosoi fungal infection in mice. PMID: 26140582
- Mincle is essential for the activation of macrophages by trehalose glycolipids, the receptor does not play a role in the uptake of these glycolipids or of glycolipid-coated particles. PMID: 25645884
- These results suggest that MCL positively regulates Mincle expression through protein-protein interaction via its stalk region, thereby magnifying Mincle-mediated signaling. PMID: 25888641
- Collectively, authors show that expression of Mincle, particularly by classical dendritic cells, contributes to the control of splenic Mycobacterium bovis BCG infection in mice. PMID: 25332121
- Trehalose 6,6'-dimycolate-induced Mincle expression is dependent on Dectin-3-mediated NF-kappaB activation through the CARD9-BCL10-MALT1 complex. PMID: 25202022
- identify C/EBPbeta as central hub in Mincle expression and inflammatory gene induction, whereas HIF1alpha controls Nos2 expression. PMID: 25156364
- These results demonstrated that GroMM is a unique ligand for human Mincle that is not recognized by mouse Mincle. PMID: 24733387
- These results demonstrate protective role of Mincle in host defense against K. pneumoniae pneumonia by coordinating bacterial clearance mechanisms of neutrophils. PMID: 24353272
- Solvent-based fractionation revealed that Mincle and Dectin-2 recognize lipophilic and hydrophilic components of Malassezia. PMID: 23601109
- that absence of the innate receptor Mincle can be fully compensated for in vivo in terms of sensing Mtb and mounting a protective inflammatory immune response. PMID: 22784441
- The expression profile of Mincle is studied on resident alveolar macrophages as well as inflammatory elicited lung exudate macrophages and neutrophils and its role in protective immunity against Mycobacterium bovis BCG challenge in mice. PMID: 22869905
- silencing of renal DNaseI gene expression initiates a cascade of inflammatory signals including activation of Toll like receptors and Clec4e, leading to progression of both murine and human lupus nephritis PMID: 22479529
- The physiological relevance of the Mincle-mediated anti-TDM immune response was confirmed by defective immune responses in Mincle/ mice upon aerosol infections with Mtb. PMID: 22496642
- Mincle is a key C-type lectin receptor for mycobacterial cord factor and controls T helper cell type (Th)1/Th cell type (Th)17 adjuvanticity of cord factor trehalose-6,6-dimycolate (TDM) and trehalose-6,6-dibehenate (TDB). PMID: 20164423
- findings show that Mincle plays a novel and nonredundant role in the induction of inflammatory signaling in response to C. albicans infection PMID: 18490740
- Mincle is a receptor that senses nonhomeostatic cell death and thereby induces the production of inflammatory cytokines to drive the infiltration of neutrophils into damaged tissue. PMID: 18776906
- Mincle may recognize specific geometry of alpha-mannosyl residues on Malassezia species and use this to distinguish them from other fungi. PMID: 19171887
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:Cell membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein. Cell projection, phagocytic cup.
-
組織特異性:Highly expressed in macrophages in response to stimulation with bacterial glycolipids and proinflammatory cytokines. Expressed in dendritic cells (at protein level) in response to stimulation with mycobacterial trehalose 6,6'-dimycolate (TDM).
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
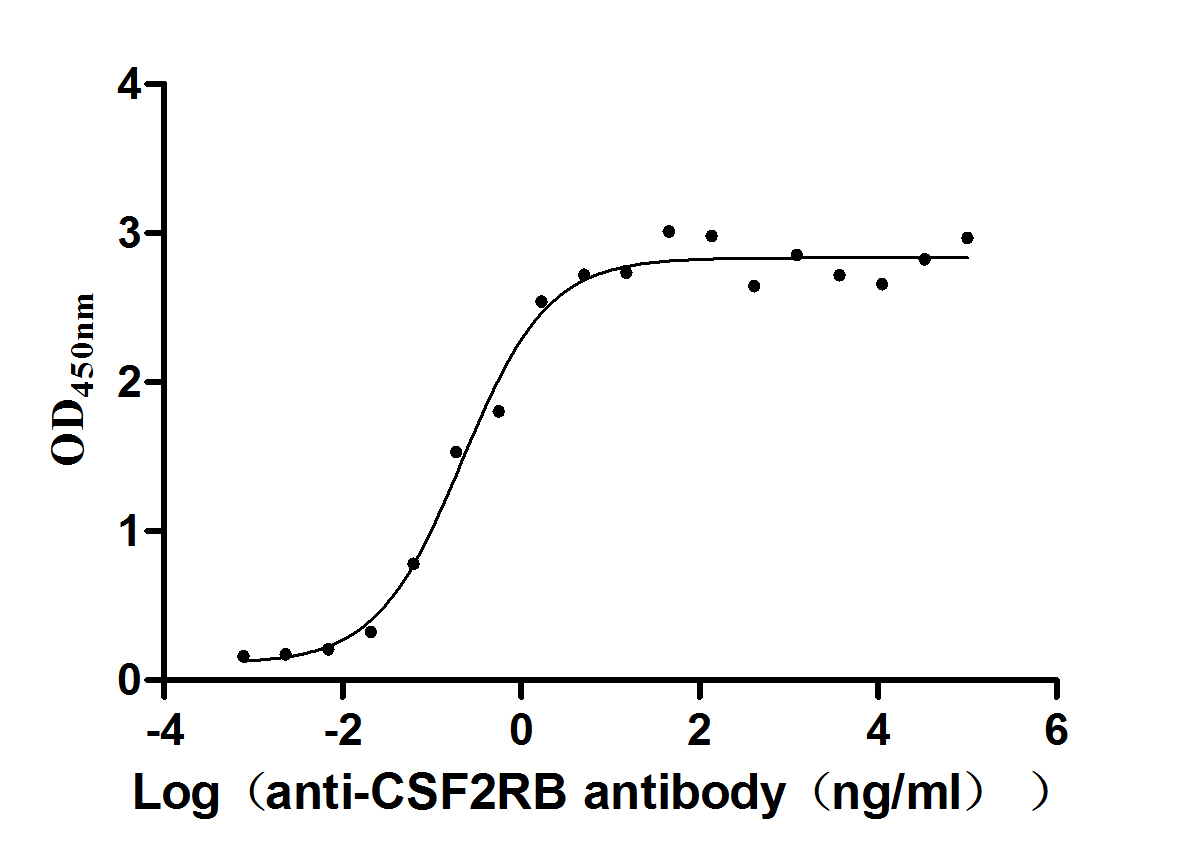
Recombinant Human Cytokine receptor common subunit beta (CSF2RB), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
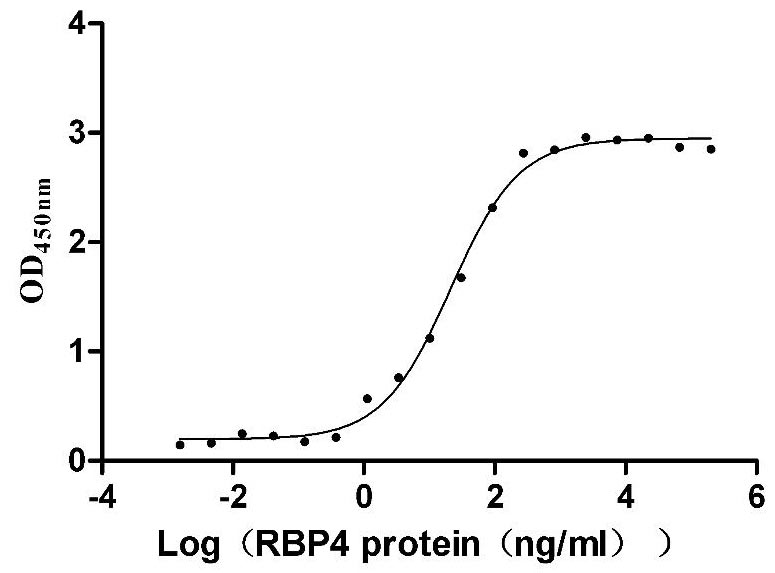
Recombinant Mouse Transthyretin (Ttr) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
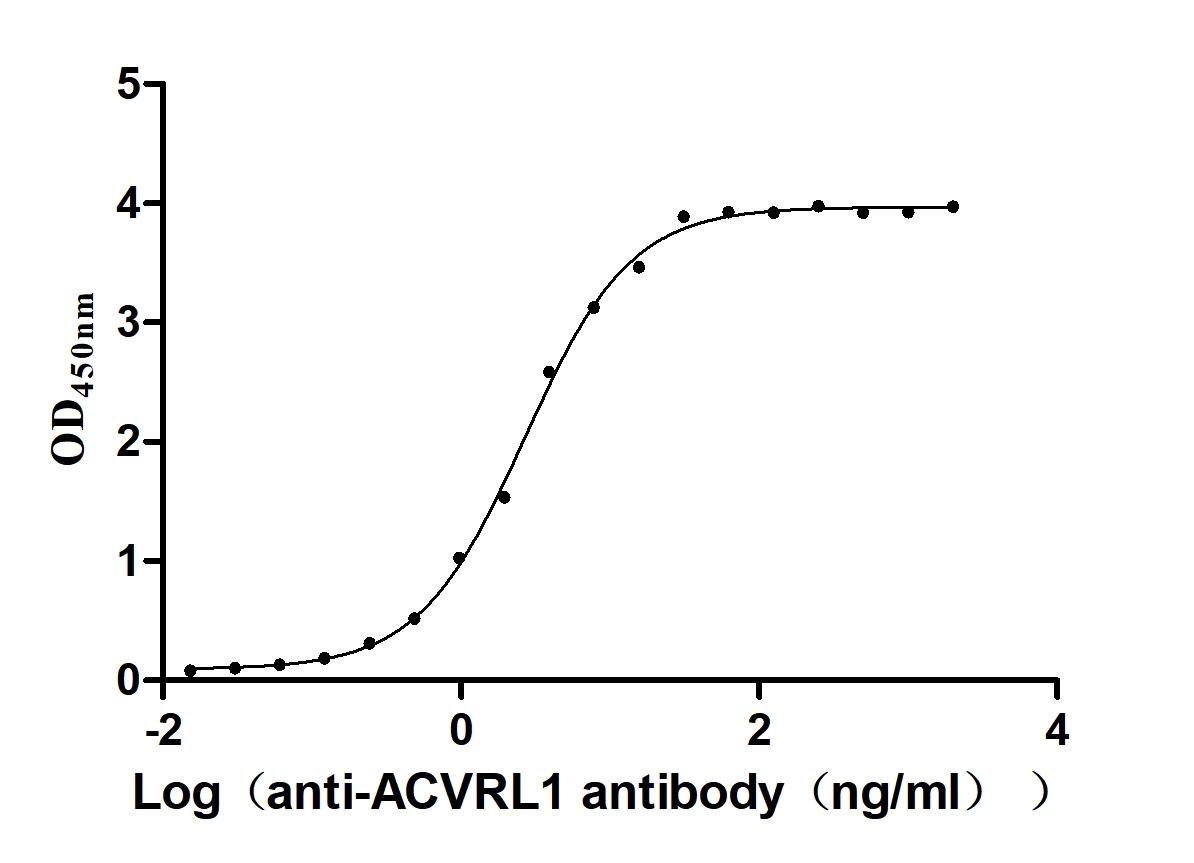
Recombinant Human Serine/threonine-protein kinase receptor R3 (ACVRL1), partial (Active)
Express system: Baculovirus
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human CD81 antigen (CD81), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Interleukin-2 (IL2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (GIPR), partial (Active)
Express system: yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 15(TNFSF15) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)



-AC1.jpg)









