Recombinant Human Nuclear mitotic apparatus protein 1 (NUMA1 NMP22 NUMA)
-
中文名稱:
-
貨號:CSB-YP016185HU
-
規格:
-
來源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:
-
貨號:CSB-EP016185HU
-
規格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:
-
貨號:CSB-EP016185HU-B
-
規格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:
-
貨號:CSB-BP016185HU
-
規格:
-
來源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:
-
貨號:CSB-MP016185HU
-
規格:
-
來源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
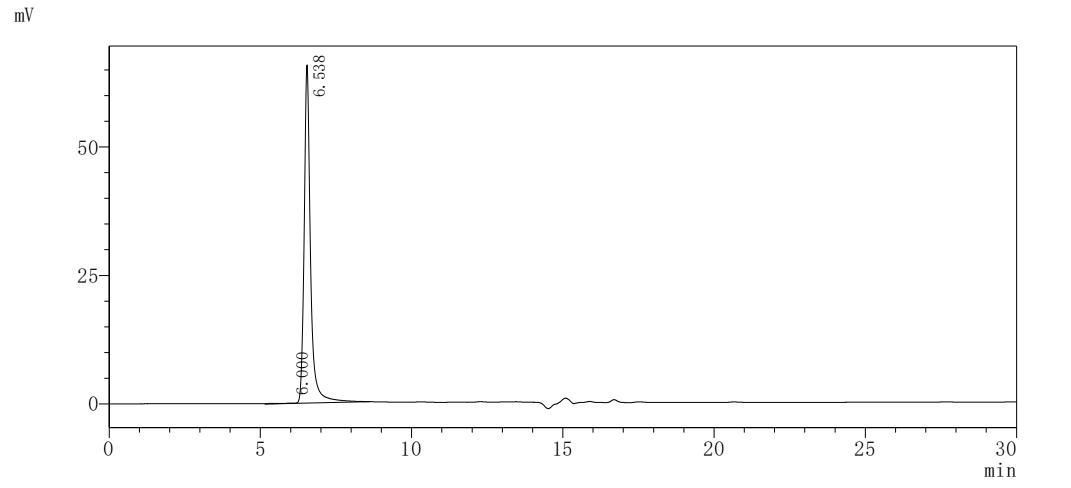
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:NUMA1
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:Nuclear mitotic apparatus protein 1; Nuclear matrix protein-22; NMP-22; Nuclear mitotic apparatus protein; NuMA protein; SP-H antigen; NUMA1 NMP22 NUMA
-
種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白標簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Microtubule (MT)-binding protein that plays a role in the formation and maintenance of the spindle poles and the alignement and the segregation of chromosomes during mitotic cell division. Functions to tether the minus ends of MTs at the spindle poles, which is critical for the establishment and maintenance of the spindle poles. Plays a role in the establishment of the mitotic spindle orientation during metaphase and elongation during anaphase in a dynein-dynactin-dependent manner. In metaphase, part of a ternary complex composed of GPSM2 and G(i) alpha proteins, that regulates the recruitment and anchorage of the dynein-dynactin complex in the mitotic cell cortex regions situated above the two spindle poles, and hence regulates the correct oritentation of the mitotic spindle. During anaphase, mediates the recruitment and accumulation of the dynein-dynactin complex at the cell membrane of the polar cortical region through direct association with phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PI(4,5)P2), and hence participates in the regulation of the spindle elongation and chromosome segregation. Binds also to other polyanionic phosphoinositides, such as phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate (PIP), lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) and phosphatidylinositol triphosphate (PIP3), in vitro. Also required for proper orientation of the mitotic spindle during asymmetric cell divisions. Plays a role in mitotic MT aster assembly. Involved in anastral spindle assembly. Positively regulates TNKS protein localization to spindle poles in mitosis. Highly abundant component of the nuclear matrix where it may serve a non-mitotic structural role, occupies the majority of the nuclear volume. Required for epidermal differentiation and hair follicle morphogenesis.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- It has been reported that the Galectin-3/NuMA interaction is functionally important for the spindle pole organization; spindle pole cohesion requires glycosylation-mediated localization of NuMA. PMID: 28469279
- The p37 negatively regulates this function of PP1, resulting in lower cortical NuMA levels and correct spindle orientation. PMID: 29222185
- The results show how E-cadherin instructs the assembly of the LGN/NuMA complex at cell-cell contacts, and define a mechanism that couples cell division orientation to intercellular adhesion. PMID: 28045117
- Here, the authors use quantitative imaging and laser ablation to show that NuMA targets dynactin to spindle microtubule minus-ends, localizing dynein activity there. PMID: 29185983
- All urine samples were analyzed by voided urine and bladder washing cytology, NMP22 and UBC rapid test (qualitatively and quantitatively). The best cutoff (highest Youden index; >/=6.7 ng/ml) for the quantitative UBC was determined by receiver operating characteristic curves. PMID: 28824318
- Short isoform of NuMA might be functioned as a putative role of tumor suppressor. Further studies should be made to illuminate the relationship between ACTN4, MYBL2, and tumor progression. PMID: 28748856
- The function of nuclear mitotic apparatus protein (NuMA) in rDNA transcription and p53-independent nucleolar stress response suggests a central role for NuMA in cellular homeostasis. PMID: 28981686
- Importin-alpha/-beta regulates the NuMA functioning required for assembly of higher-order microtubule structures including the mitotic spindle. PMID: 28939615
- Low post translational modifications of NuMA protein is associated with neoplasms. PMID: 28209915
- Seven NuMA isoforms generated by alternative splicing were categorized into 3 groups: long, middle and short. Both exons 15 and 16 in long NuMA were "hotspot" for alternative splicing. Lower expression of short NuMA was observed in cancer cells compared with nonneoplastic controls. PMID: 25451259
- Chimeric proteins constructed by fusion of LANA of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus with the NuMA could bind with ori-P and enhance replication of an ori-P-containing plasmid. PMID: 27829174
- findings reveal a direct physical link between two important regulators of mitotic progression and demonstrate the critical role of the NuMA-Astrin interaction for accurate cell division. PMID: 27462074
- Aurora-A governs the dynamic exchange between the cytoplasmic and the spindle pole-localized pools of NuMA. Aurora-A phosphorylates directly the C terminus of NuMA on three Ser residues, of which Ser1969 determines the dynamic behavior and the spindle orientation functions of NuMA. PMID: 26832443
- Suppressor APC domain containing 2 negatively regulates the localization of LGN at the cell cortex, likely by competing with NuMA for its binding PMID: 26766442
- Letter: risk factors for false positive results when using urinary NMP22 as biomarker for early detection of bladder cancer. PMID: 24976592
- Results show that at low grade of disease, NMP22 test provided a significantly higher sensitivity for the detection of recurrent urothelial carcinoma of the bladder compared to voided urine cytology specimens. PMID: 25488052
- NuMA interacts with phosphoinositides and links the mitotic spindle with the plasma membrane.During anaphase correct NuMA localization is mediated by direct membrane phospholipid binding. PMID: 24996901
- Retinoblastoma protein (pRB) have a novel function in regulating the mitotic function of NuMA and spindle organization, which are required for proper cell cycle progression. PMID: 24350565
- Study finds that frictional forces increase nonlinearly with microtubule-associated proteins (MAP) velocity across microtubules and depend on filament polarity, with NuMA's friction being lower when moving toward minus ends, EB1's lower toward plus ends, and PRC1's exhibiting no directional preference. PMID: 24725408
- The mitosis-dependent dynamic SUMO-1 modification of NuMA might contribute to NuMA-mediated formation and maintenance of mitotic spindle poles during mitosis. PMID: 24309115
- ectopic expression of NuMA can manipulate endogenous p53 and p21 transcriptional expression during interphase. PMID: 23828576
- ectopic expression of BRAP2 inhibits nuclear localization of HMG20A and NuMA1, and prevents nuclear envelope accumulation of SYNE2. PMID: 23707952
- Hepatocyte Par1b defines lumen position in concert with the position of the astral microtubule anchoring complex LGN-NuMA to yield the distinct epithelial division phenotypes. PMID: 24165937
- NuMA phosphorylation by CDK1 couples mitotic progression with cortical dynein function. PMID: 23921553
- Phosphorylation of NuMA by aurora-A is important for cell survival. PMID: 23097092
- Data indicate that dynein- and astral microtubule-mediated transport of Galphai/LGN/nuclear mitotic apparatus (NuMA) complex from cell cortex to spindle poles. PMID: 23389635
- nuclear matrix protein 22 (nuclear mitotic apparatus protein, NuMA) has a role in upper tract urothelial tumors. PMID: 21865670
- NuMA is required for the recruitment of cyclin-dependent kinase 8, a component of the Mediator complex and a promoter of p53-mediated p21 gene function. PMID: 23589328
- Studies indicate that the Inscuteable (Insc)and NuMA are mutually exclusive interactors of LGN. PMID: 22977735
- Numa regulates spindle assemby in conjunction with Eg5. PMID: 23368718
- NuMA expression was upregulated in tumours, with a significant association with disease stage in mucinous EOC subtypes, lymph node involvement and patient age PMID: 22719996
- Low NUMA1 is associtated with glioblastoma. PMID: 22619067
- Without functional NuMA, microtubules lose connection to meiosis I spindle poles, resulting in highly disorganized early spindle assembly. PMID: 22552228
- During apoptotic rearrangement of interchromatin granule clusters, the nuclear matrix (NuMa rearrangement) and chromatin are closely associated. This process occurs in defined stages and depends on the activity of protein phosphatases, caspases and CAD. PMID: 22023725
- The levels of urinary NMP22 and CK18 in the patients with transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder were significantly higher than those in the non-transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. PMID: 19615282
- Accurate distribution of NuMA is important for oocyte maturation, zygote and embryo development in humans. Proper assembly of NuMA is likely necessary for bipolar spindle organization and human oocyte developmental competence. PMID: 21297155
- NuMA is expressed in interphase nuclei of fibroblasts and oocytes. PMID: 21406448
- Phenotype onset is correlated with NuMA-RARalpha copy number; mice with higher copy number developing disease later than those with lower copy number. PMID: 21255834
- These results suggest that NuMA may provide structural support in the interphase nucleus by contributing to the organization of chromatin. PMID: 20467816
- Ric-8A and Gi alpha recruit LGN, NuMA, and dynein to the cell cortex to help orient the mitotic spindle. PMID: 20479129
- Data suggest that pADPr provides a dynamic cross-linking function at spindle poles by extending from covalent modification sites on PARP-5a and NuMA and binding noncovalently to NuMA and that this function helps promote assembly of exactly two poles. PMID: 19759176
- A domain within the C-terminal tail of NuMA interacts with tubulin and induces bundling and stabilisation of microtubules and leads to formation of abnormal mitotic spindles. PMID: 11956313
- NuMA is cleaved differently in Jurkat T and HeLa cells, suggesting that different sets of caspases are activated in these cell lines. The normal diffuse intranuclear distribution of NuMA changed during apoptosis. PMID: 12508117
- role in development of myelodi leukemia with promyelocytic features PMID: 14737102
- Proteins and open reading frames with a NuMA C terminus distal portion like region were found in a diverse set of vertebrate species including mammals, birds, amphibia, and early teleost fish. PMID: 15388855
- Multiple mechanisms regulate NUMA1 dynamics at spindle poles. PMID: 15561764
- concluded that variations in the NuMA gene are likely responsible for the observed increased breast cancer risk PMID: 15684076
- NuMA plays diverse important roles in vertebrate cells [review] PMID: 16146802
- NuMA has a role in mammary epithelial differentiation by influencing the organization of chromatin. PMID: 17108325
- point to the Rae1-NuMA interaction as a critical element for normal spindle formation in mitosis PMID: 17172455
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:Nucleus. Nucleus, nucleoplasm. Nucleus matrix. Chromosome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle pole. Cytoplasm, cell cortex. Cell membrane; Lipid-anchor; Cytoplasmic side. Lateral cell membrane.; [Isoform 3]: Cytoplasm, cytosol. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle pole.; [Isoform 4]: Cytoplasm, cytosol. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle pole.
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
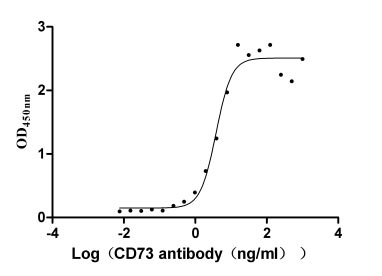
Recombinant Human 5'-nucleotidase (NT5E) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
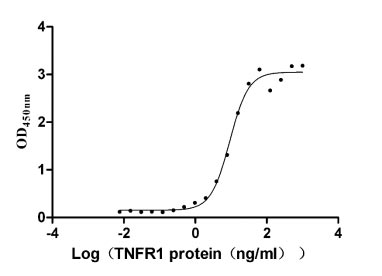
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1A (TNFRSF1A), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
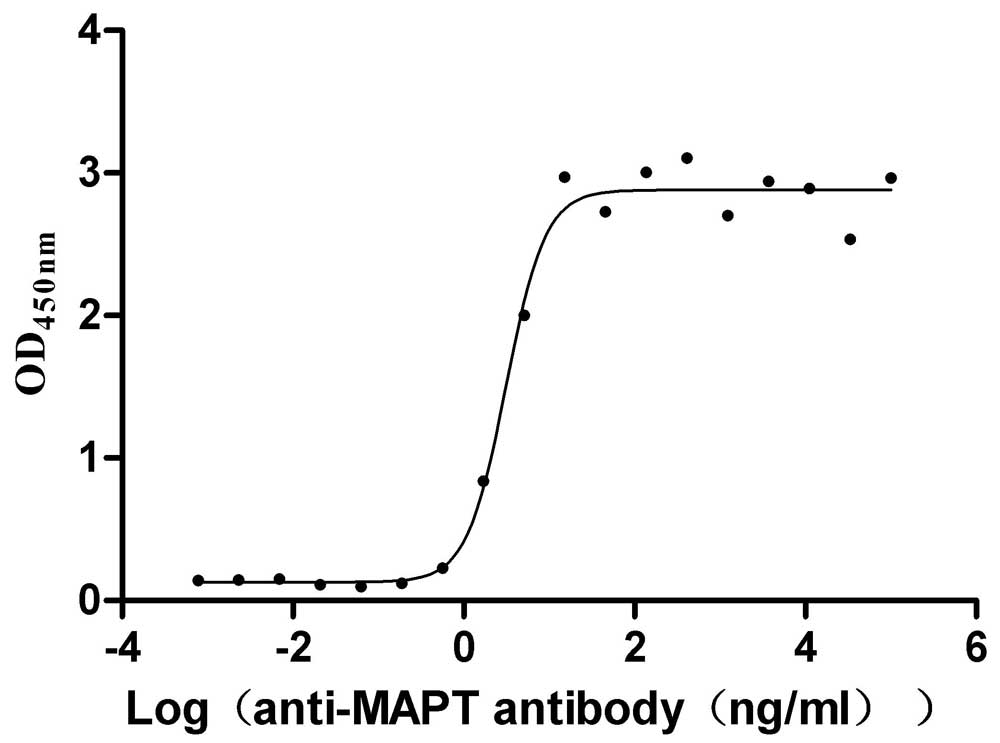
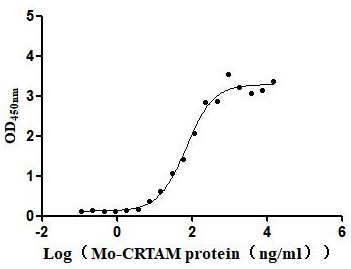
Recombinant Macaca mulatta Microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque)
-
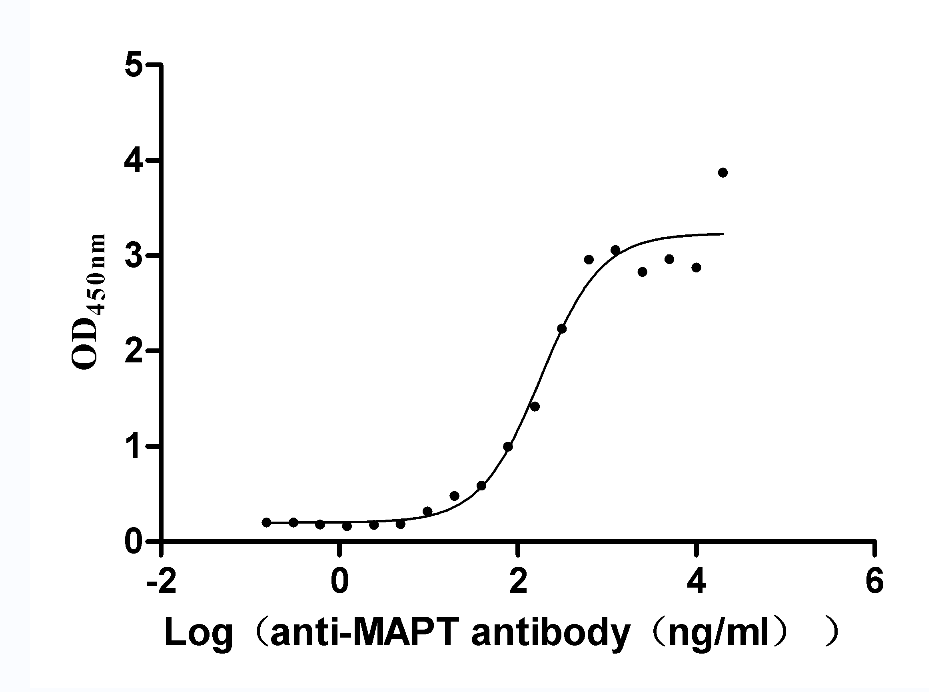
Recombinant Rat Microtubule-associated protein tau (Mapt) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
Recombinant Mouse Cell adhesion molecule 1 (Cadm1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
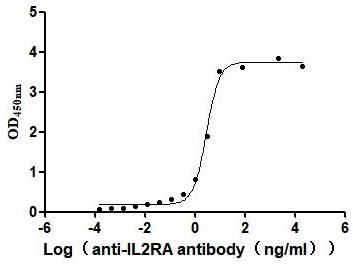
Recombinant Human Interleukin-2 receptor subunit alpha (IL2RA), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
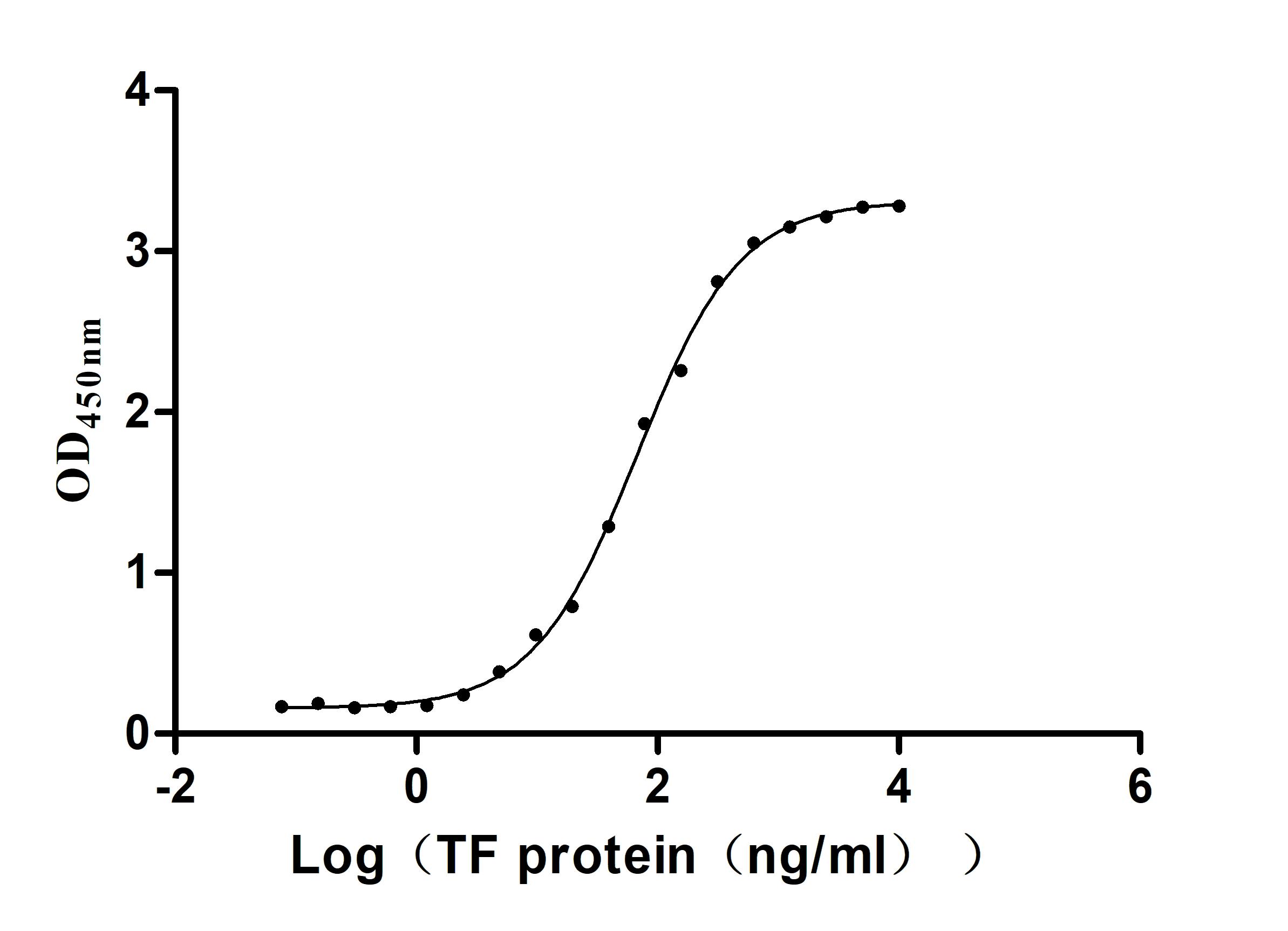
Recombinant Human Serotransferrin(TF) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human C-C chemokine receptor type 9 (CCR9)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)