Recombinant Human Medium-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial (ACADM)
In Stock-
中文名稱:Recombinant Human Medium-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, mitochondrial(ACADM)
-
貨號:CSB-EP001126HU
-
規格:¥1836
-
圖片:
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
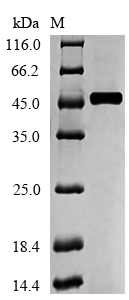
純度:Greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
-
基因名:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:ACAD 1; ACAD1; Acadm; ACADM_HUMAN; Acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase; Acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase C 4 to C 12 straight chain; FLJ18227; FLJ93013; FLJ99884; MCAD; MCADH; Medium chain acyl CoA dehydrogenase; Medium chain fatty acyl CoA dehydrogenase ; Medium chain specific acyl CoA dehydrogenase; Medium chain specific acyl CoA dehydrogenase mitochondrial; Medium-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; mitochondrial
-
種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白長度:Full Length of Mature Protein
-
來源:E.coli
-
分子量:47.6kDa
-
表達區域:26-421aa
-
氨基酸序列KANRQREPGLGFSFEFTEQQKEFQATARKFAREEIIPVAAEYDKTGEYPVPLIRRAWELGLMNTHIPENCGGLGLGTFDACLISEELAYGCTGVQTAIEGNSLGQMPIIIAGNDQQKKKYLGRMTEEPLMCAYCVTEPGAGSDVAGIKTKAEKKGDEYIINGQKMWITNGGKANWYFLLARSDPDPKAPANKAFTGFIVEADTPGIQIGRKELNMGQRCSDTRGIVFEDVKVPKENVLIGDGAGFKVAMGAFDKTRPVVAAGAVGLAQRALDEATKYALERKTFGKLLVEHQAISFMLAEMAMKVELARMSYQRAAWEVDSGRRNTYYASIAKAFAGDIANQLATDAVQILGGNGFNTEYPVEKLMRDAKIYQIYEGTSQIQRLIVAREHIDKYKN
Note: The complete sequence may include tag sequence, target protein sequence, linker sequence and extra sequence that is translated with the protein sequence for the purpose(s) of secretion, stability, solubility, etc.
If the exact amino acid sequence of this recombinant protein is critical to your application, please explicitly request the full and complete sequence of this protein before ordering. -
蛋白標簽:N-terminal 6xHis-tagged
-
產品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
緩沖液:If the delivery form is liquid, the default storage buffer is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 5%-50% glycerol.
Note: If you have any special requirement for the glycerol content, please remark when you place the order.
If the delivery form is lyophilized powder, the buffer before lyophilization is Tris/PBS-based buffer, 6% Trehalose. -
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:3-7 business days
-
注意事項:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet & COA:Please contact us to get it.
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Medium-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase is one of the acyl-CoA dehydrogenases that catalyze the first step of mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation, an aerobic process breaking down fatty acids into acetyl-CoA and allowing the production of energy from fats. The first step of fatty acid beta-oxidation consists in the removal of one hydrogen from C-2 and C-3 of the straight-chain fatty acyl-CoA thioester, resulting in the formation of trans-2-enoyl-CoA. Electron transfer flavoprotein (ETF) is the electron acceptor that transfers electrons to the main mitochondrial respiratory chain via ETF-ubiquinone oxidoreductase (ETF dehydrogenase). Among the different mitochondrial acyl-CoA dehydrogenases, medium-chain specific acyl-CoA dehydrogenase acts specifically on acyl-CoAs with saturated 6 to 12 carbons long primary chains.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- Our study has revealed the unique genetic backgrounds of MCAD deficiency among Japanese, based on the largest series of non-Caucasian cases. PMID: 27856190
- 17 VUS (37%; 7 in ACADM, 9 in GALT, and 1 in PAH) were reclassified from uncertain (6 to benign or likely benign and 11 to pathogenic or likely pathogenic). We identified common types of missing information that would have helped make a definitive classification and categorized this information by ease and cost to obtain PMID: 27308838
- Subjects with neonatal symptoms, or neonatal abnormal labs, or neonatal triggers were more likely to have at least one copy of the severe c.985A>G ACADM gene mutation PMID: 27477829
- Exclusively breastfed neonates with MCAD are at risk for early metabolic decompensation. As breastfeeding rates increase, close management of feeding difficulties is essential for all neonates awaiting newborn screening results PMID: 27148938
- The in silico structural changes in medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (hMCAD) p.K329E variant protein affect the disturbed oligomeric profile, thermal stability, and conformational flexibility, with respect to the wild-type. PMID: 27976856
- LCHAD and MCAD are differentially expressed in maternal and fetal tissues during normal late pregnancy, which may represent a metabolic adaptation in response to physiological maternal dyslipidemia during late pregnancy. PMID: 27871288
- Study determined three mutations (p.R53C, p.R281S and p.G362E) in MCAD protein predisposing for MCAD deficiency which seems to be unique to Japanese population. PMID: 26947917
- our study demonstrates that not all mutations identified in children with abnormal NBS profiles suggestive of MCAD deficiency result in a total loss in MCAD activity and function PMID: 24966162
- The c.600-18G > A variant activates a cryptic splice site, which competes with the natural splice site. PMID: 26223887
- mutations in the ACADM gene lower the temperature threshold at which medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency loss-of-function occurs. PMID: 24718418
- Segregation studies in the Gypsy families showed that 93/123 relatives were carriers of the acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase G985 allele, suggesting its high prevalence in this ethnic group. PMID: 23829193
- Identify an ACADM founder mutation for MCADD in Saudi Arabian population. PMID: 20567907
- This supports that c.1161A>G is a functional SNP, which leads to higher MCAD expression, perhaps due to improved splicing. This study is a proof of principle that synonymous SNPs are not neutral. PMID: 23810226
- medium chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase involve in the metabolism of phenylbutyrate. PMID: 23141465
- Subjects with variant ACADM genotypes and residual MCAD enzyme activities <10% should be considered to have the same risks as patients with classical ACADM genotypes PMID: 22630369
- The octanoyl-CoA oxidation rate, therefore, allows a risk assessment at birth and the identification of new ACADM genotypes associated with asymptomatic disease variants. PMID: 23028790
- A novel variant in the Medium-Chain Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase (MCAD) gene was identified in a Greek cohort of neonates with suspected MCAD deficiency. PMID: 22683754
- physiological concentrations of flavin adenine dinucleotide resulted in a spectacular enhancement of the thermal stabilities of MCADH and prevented enzymatic activity loss PMID: 21968293
- The mutation in Medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency is the first report of the c.461T>G mutation in the acyl-CoA dehydrogenase gene. PMID: 21239873
- classification of genotypes with at least one variant of unknown significance in individuals who are carriers of, or affected with, MCAD deficiency of the following genotypes: c.985A>G/wildtype, c.199T>C/c.985A>G and c.985A>G/c.985A>G PMID: 20434380
- MCAD is induced by PGC-1 in an ERRalpha-dependent manner PMID: 12522104
- Interference between PPARA and ERRalpha and RXRA complex heterodimer and the nuclear receptor site of MCAD PMID: 12914524
- single arginine residue is essential for the binding of electron transferring flavoprotein to MCAD, but the single histidine residue, although involved, is not PMID: 14692513
- first molecular identification of MCADD in an Arab patient and the first reported splice mutation in the MCAD gene that has been functionally characterized PMID: 15171999
- Two novel rare mutations, R256T and K364R, have been investigated to assess how far the biochemical properties of the mutant proteins correlate with the clinical phenotype of medium chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. PMID: 16128823
- analysis of MCAD deficiency (homozygous at c.985A>G (K329E)) complicated by acute liver failure in pregnancy [case report] PMID: 17186412
- Measurement of MCAD activity in leukocytes or lymphocytes using phenylpropionyl-CoA as a substrate can be regarded as the gold standard to diagnose MCAD deficiency upon initial positive screening test results. PMID: 18188679
- Six novel and seven previously reported medium chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase mutations were detected in newborns with medium chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. PMID: 18241067
- Ethnic-specific homozygous adenin/guanine substitution in an ACADM birth prevalence from a large-scale United Kingdom newborn screening study. PMID: 18927092
- study indicates that c.449-452delCTGA represents a common mutation in Japanese patients with medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (MCADD) PMID: 19064330
- Protein misfolding of MCAD protein is the molecular basis in medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. PMID: 19224950
- In the medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, the 985G mutant and 985A normal alleles had allelic frequencies of 0.0020 and 0.9980, respectively. PMID: 19551636
- Meta-analysis and HuGE review of genotype prevalence, gene-disease association, gene-gene interaction, and healthcare-related. (HuGE Navigator) PMID: 11263545
顯示更多
收起更多
-
相關疾病:Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase medium-chain deficiency (ACADMD)
-
亞細胞定位:Mitochondrion matrix.
-
蛋白家族:Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase family
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human C5a anaphylatoxin chemotactic receptor 1 (C5AR1)-VLPs (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Epithelial discoidin domain-containing receptor 1 (DDR1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis lymphocyte antigen 6 family member G6D (LY6G6D) (Active)
Express system: Yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Human Tumor-associated calcium signal transducer 2 (TACSTD2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Mouse Cell adhesion molecule 1 (Cadm1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 8(CEACAM8) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor (GIPR), partial (Active)
Express system: yeast
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)
-
Recombinant Macaca fascicularis Interleukin 1 receptor accessory protein(IL1RAP), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Macaca fascicularis (Crab-eating macaque) (Cynomolgus monkey)