Recombinant Human Calmodulin-2 (CALM2 CAM2 CAMB)
-
中文名稱:
-
貨號:CSB-YP270276HU
-
規格:
-
來源:Yeast
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:
-
貨號:CSB-EP270276HU
-
規格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:
-
貨號:CSB-EP270276HU-B
-
規格:
-
來源:E.coli
-
共軛:Avi-tag Biotinylated
E. coli biotin ligase (BirA) is highly specific in covalently attaching biotin to the 15 amino acid AviTag peptide. This recombinant protein was biotinylated in vivo by AviTag-BirA technology, which method is BriA catalyzes amide linkage between the biotin and the specific lysine of the AviTag.
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:
-
貨號:CSB-BP270276HU
-
規格:
-
來源:Baculovirus
-
其他:
-
中文名稱:
-
貨號:CSB-MP270276HU
-
規格:
-
來源:Mammalian cell
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
純度:>85% (SDS-PAGE)
-
基因名:CALM2
-
Uniprot No.:
-
別名:Calmodulin-2 CALM2 CAM2 CAMB
-
種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
蛋白標簽:Tag?type?will?be?determined?during?the?manufacturing?process.
The tag type will be determined during production process. If you have specified tag type, please tell us and we will develop the specified tag preferentially. -
產品提供形式:Liquid or Lyophilized powder
Note: We will preferentially ship the format that we have in stock, however, if you have any special requirement for the format, please remark your requirement when placing the order, we will prepare according to your demand. -
復溶:We recommend that this vial be briefly centrifuged prior to opening to bring the contents to the bottom. Please reconstitute protein in deionized sterile water to a concentration of 0.1-1.0 mg/mL.We recommend to add 5-50% of glycerol (final concentration) and aliquot for long-term storage at -20℃/-80℃. Our default final concentration of glycerol is 50%. Customers could use it as reference.
-
儲存條件:Store at -20°C/-80°C upon receipt, aliquoting is necessary for mutiple use. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
-
保質期:The shelf life is related to many factors, storage state, buffer ingredients, storage temperature and the stability of the protein itself.
Generally, the shelf life of liquid form is 6 months at -20°C/-80°C. The shelf life of lyophilized form is 12 months at -20°C/-80°C. -
貨期:Delivery time may differ from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.Note: All of our proteins are default shipped with normal blue ice packs, if you request to ship with dry ice, please communicate with us in advance and extra fees will be charged.
-
注意事項:Repeated freezing and thawing is not recommended. Store working aliquots at 4°C for up to one week.
-
Datasheet :Please contact us to get it.
靶點詳情
-
功能:Calmodulin mediates the control of a large number of enzymes, ion channels, aquaporins and other proteins through calcium-binding. Among the enzymes to be stimulated by the calmodulin-calcium complex are a number of protein kinases and phosphatases. Together with CCP110 and centrin, is involved in a genetic pathway that regulates the centrosome cycle and progression through cytokinesis. Mediates calcium-dependent inactivation of CACNA1C. Positively regulates calcium-activated potassium channel activity of KCNN2.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- Data suggest that TRPM4 exhibits binding sites for calmodulin (CaM) and S100 calcium-binding protein A1 (S100A1) located in very distal part of TRPM4 N-terminus. (TRPM4 = transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M member 4) PMID: 29240297
- The effect of Ca(2+), domain-specificity, and CaMKII on CaM binding to NaV1.1 has been reported. PMID: 30142967
- Our FRET-based HTS detects RyR binding of accessory proteins calmodulin (CaM) or FKBP12.6...One compound increased FRET and inhibited RyR1, which was only significant at nM [Ca(2+)], and accentuated without CaM present. PMID: 27760856
- Systematic review and meta-analysis of 5 case-control studies involving 2183 osteoarthritis patients 2654 healthy control subjects did not find association between the disease and the rs12885713 polymorphism of CALM1. PMID: 30200150
- We demonstrate that under these conditions the TRPV5 C-terminus is exclusively bound to the CaM C-lobe only, while it confers conformational freedom to the CaM N-lobe. We also show that at elevated calcium levels, additional interactions between the TRPV5 C-terminus and CaM N-lobe occur, resulting in formation of a tight 1:1 complex, effectively making the N-lobe the calcium sensor. PMID: 29584409
- we present a model for TRPV6 CaM-dependent inactivation, which involves a novel so-called "two-tail" mechanism whereby CaM bridges two TRPV6 monomers resulting in closure of the channel pore. PMID: 29505720
- The conservation of homologous residues in helix B of other Kv7 subtypes confer similar competition of Ca(2+)-calmodulin (CaM) with PIP2 binding to their proximal C-termini and suggest that PIP2-CaM interactions converge to Kv7 helix B to modulates channel activity in a Kv7 subtype-dependent manner. PMID: 28976808
- This review provides an overview over our present knowledge concerning the structural and functional aspects of the role of CaM as an adaptor protein and as a regulator of known adaptor/scaffold proteins PMID: 29247668
- Our up-to-date review discusses CaM's role in PI3K signaling at the membrane in KRAS-driven cancers. This is significant since it may help development of K-Ras-specific pharmacology. PMID: 28462395
- Calmodulin is up-regulated and can serve as the potential serum biomarker for predicting the recurrence of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PMID: 28849027
- cSH2 domain of p85alpha engages its two CaM-binding motifs in the interaction with the N- and C-lobes of CaM as well as the flexible central linker, and our nuclear magnetic resonance experiments provide structural details. PMID: 29494137
- The dynamics of calmodulin interactions with neurogranin and Ca(2+) /CAMKII alpha proteins has been reported. PMID: 28449373
- our work reveals a novel model by which CaM promotes cell migration through inhibiting the ubiquitination and degradation of TBC1D3. PMID: 28422741
- These in vivo and in vitro studies have been complementary with each other, representing the changes in the CN-dependent pathway affected by overexpression of alpha-syn. PMID: 29409956
- Human arrhythmogenic calmodulin mutations impede the activation of SK2 channels in human embryonic kidney 293 cells. PMID: 27165696
- The results demonstrated CaM binding to DR5-mediated DISC in a calcium dependent manner and may identify CaM as a key regulator of DR5-mediated DISC formation for apoptosis in breast cancer. PMID: 28092099
- Insights from structural proteomics can be used to generate CaM-insensitive mutants of CaM targets for functional studies in vitro or ideally in vivo. PMID: 28222617
- The unique C terminus of the calcineurin isoform CNAbeta1 confers non-canonical regulation of enzyme activity by Ca(2+) and calmodulin PMID: 28842480
- The main functional derangement in CALM1-F142L was prolonged repolarization with altered rate-dependency and sensitivity to beta-adrenergic stimulation. PMID: 28158429
- These results reveal that mTOR is a new type of calmodulin-dependent kinase, and TRPML1, lysosomal calcium and calmodulin play essential regulatory roles in the mTORC1 signaling pathway. PMID: 27787197
- The structural basis for the recognition of EEF2K by calmodulin has been presented. PMID: 27499441
- irradiated tumor cells were observed to significantly up-regulate the expression of calcium-binding proteins CALM1, CALU, and RCN1, suggesting important roles for these mediators in promoting irradiated tumor cell survival during hypoxia PMID: 27790916
- Calcium modulates calmodulin-ACTN1 interaction with and agonist-dependent internalization of the adenosine A2A receptor. PMID: 28130124
- Data suggest that GRB10 and GRB14 are both Ca2+-dependent CaM-binding proteins; more than one CaM-binding site and/or accessory CaM-binding sites appear to exist in GRB10 and GRB14, as compared to a single one present in GRB7. (GRB10 = growth factor receptor-bound protein 10; GRB14 = growth factor receptor-bound protein 14; CaM = calmodulin; GRB7 = growth factor receptor-bound protein 7) PMID: 28295264
- studies demonstrate that UBE3B is an E3 ubiquitin ligase and reveal that the enzyme is regulated by calmodulin. Furthermore, the modulation of UBE3B via calmodulin and calcium implicates a role for calcium signaling in mitochondrial protein ubiquitylation, protein turnover, and disease PMID: 28003368
- Up-regulation of miR-335 suppressed CaM protein expression in patients with acute ischemic stroke, and CaM was confirmed as a direct target of miR-335. PMID: 27856935
- The unique properties of the CaM-F142L mutation may provide novel clues on how to suppress excessive RyR2 Ca(2+) release by manipulating the CaM-RyR2 interaction. PMID: 27927985
- CaM is required for the regulation of lysosome/vacuole size by TRPML1, suggesting that TRPML1 may promote lysosome fission by activating CaM. PMID: 28360104
- Calmodulin-induced dimerization of ER-alpha is required for estrogen-stimulated transcriptional activation by the receptor. PMID: 28174300
- Data indicate that the IQGAP1 N-terminal fragment spanning residues 1-191 (CHDF) binds to both F-actin and Ca(2+)/calmodulin. PMID: 27798963
- This study reports how phosphorylation of a regulatory site (Ser-500) integrates with Ca(2+) and CaM to influence eEF-2K activity. PMID: 27956550
- Findings show that calmodulin (CaM) stimulates phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K) lipid kinase activity by binding MARCKS and displacing it from phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) headgroups, thereby releasing free PIP2 that recruits active PI3K to the membrane and serves as the substrate for the generation of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3). PMID: 27933776
- CaM D129G mutation led to bradycardia in zebrafish and an arrhythmic phenotype. PMID: 27815504
- These findings suggest that ENT1 is regulated via receptor-dependent calcium-linked pathways resulting in an alteration of purine flux, which may modulate purinergic signaling and influence NA drug efficacy. PMID: 27009875
- Our results have demonstrated that capsaicin and resiniferatoxin form nanomolar complexes with calmodulin, and competitively inhibit TRPV1-calmodulin interaction. These interactions involve the protein recognition interface of calmodulin, which is responsible for all of the cell-regulatory calmodulin-protein interactions. PMID: 27339229
- The human EAG1 (hEAG1) channel is remarkably sensitive to inhibition by intracellular calcium (Ca(2+) i) through binding of Ca(2+)-calmodulin to three sites adjacent to the eagD and cNBHD. PMID: 27325704
- CaM and S100A1 can concurrently bind to and functionally modulate RyR1 and RyR2, but this does not involve direct competition at the RyR CaM binding site. PMID: 27226555
- the spectrum and prevalence of pathogenic CaM variants in a cohort of genetically elusive long QT syndrome, were determined. PMID: 26969752
- ERK1 and erk2 activation was dependent on the calcium/calmodulin/calmodulin kinase in Penicillium marneffei-infected human macrophages. PMID: 26828872
- identify six specific phospho-species of calmodulin (CaM). Phosphorylation of CaM at four sites by CK2 was found to follow a sequential order, with Ser81 as the first, Thr79 as the second, and Ser101 or Thr117 as the third. PMID: 26675311
- Results show that calmodulin (CaM) directly binds to death receptor-5 (DR5) in a calcium dependent manner in breast cancer cells. PMID: 27129269
- miR-26b targeted CALM1 and affected the expression of CaM at the post-transcriptional level, which likely contributed to the progression of acute cerebral infarction brain injury. PMID: 26001204
- inactivation regulation via Ca(2+)/calmodulin does not interfere with the beta subunit's enzymatic activity as an NADPH-dependent oxidoreductase, thus rendering the Kvb1.1 subunit a multifunctional receptor PMID: 26487174
- These findings suggest that lysoPC induces CaM phosphorylation at Tyr(99) by a Src family kinase and that phosphorylated CaM activates PI3K to produce PIP3, which promotes TRPC6 translocation to the cell membrane. PMID: 26858457
- Elevated calcium levels clinically observed in adenocarcinomas may explain calmodulin's involvement in recruiting and stimulating PI3Kalpha through interaction with its n/cSH2 domains as well as K-Ras4B; importantly, it also explains why K-Ras4B specifically is a key player in ductal carcinomas, such as pancreatic, colorectal, and lung cancers. [Review] PMID: 26085527
- Identification and Characterization of the Interaction Site between cFLIPL and Calmodulin. PMID: 26529318
- Our data indicate that the TW site is dispensable for function, contributes to the stabilization of the CaM-Kv7.2 complex and becomes essential when docking to either helix A or when helix B is perturbed. PMID: 26148514
- results demonstrate that CaM senses changes in [Ca2+]i and binds to the cytoplasmic loop of NCX1 to regulate exchange activity. PMID: 26421717
- The study characterized a calcium-mediated conformational transition whereby the coordination of Ca(2+) by just one oxygen of the bidentate ligand E140 triggers a concerted movement of the two EF-hands that exposes the target binding site of Calmodulin. PMID: 26618792
- Common variants in TRDN and CALM1 are associated with increased risk of sudden cardiac death in patients with chronic heart failure. PMID: 26196381
顯示更多
收起更多
-
相關疾病:Long QT syndrome 15 (LQT15)
-
亞細胞定位:Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle pole. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Note=Distributed throughout the cell during interphase, but during mitosis becomes dramatically localized to the spindle poles and the spindle microtubules.
-
蛋白家族:Calmodulin family
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Recombinant Human Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 5 (CD40), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
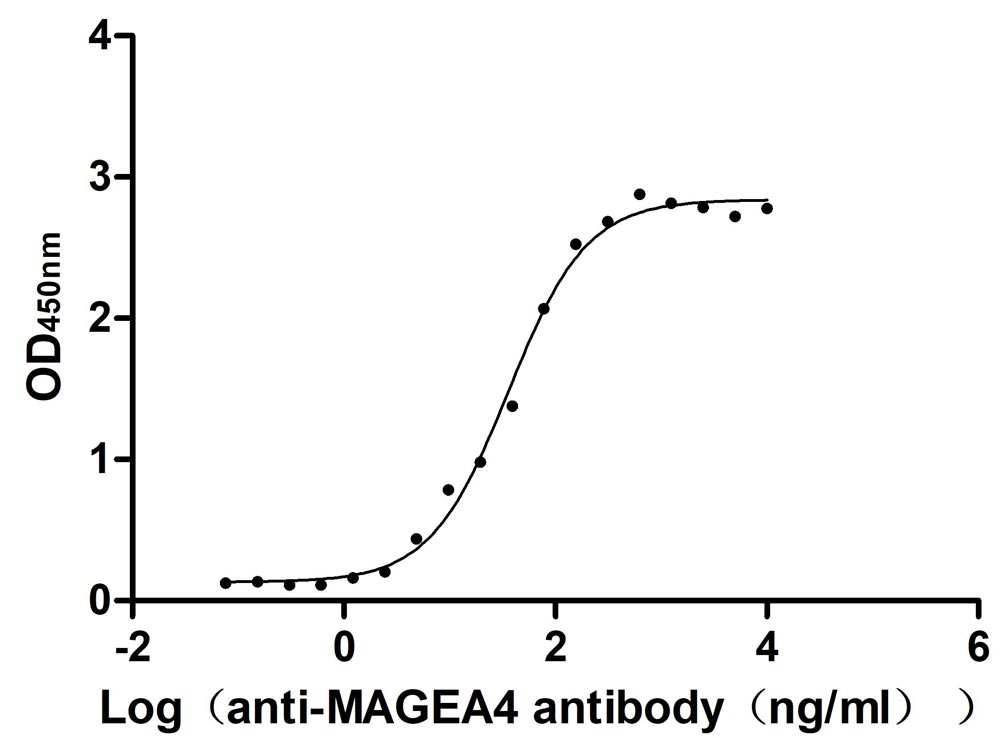
Recombinant Human Melanoma-associated antigen 4 (MAGEA4) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
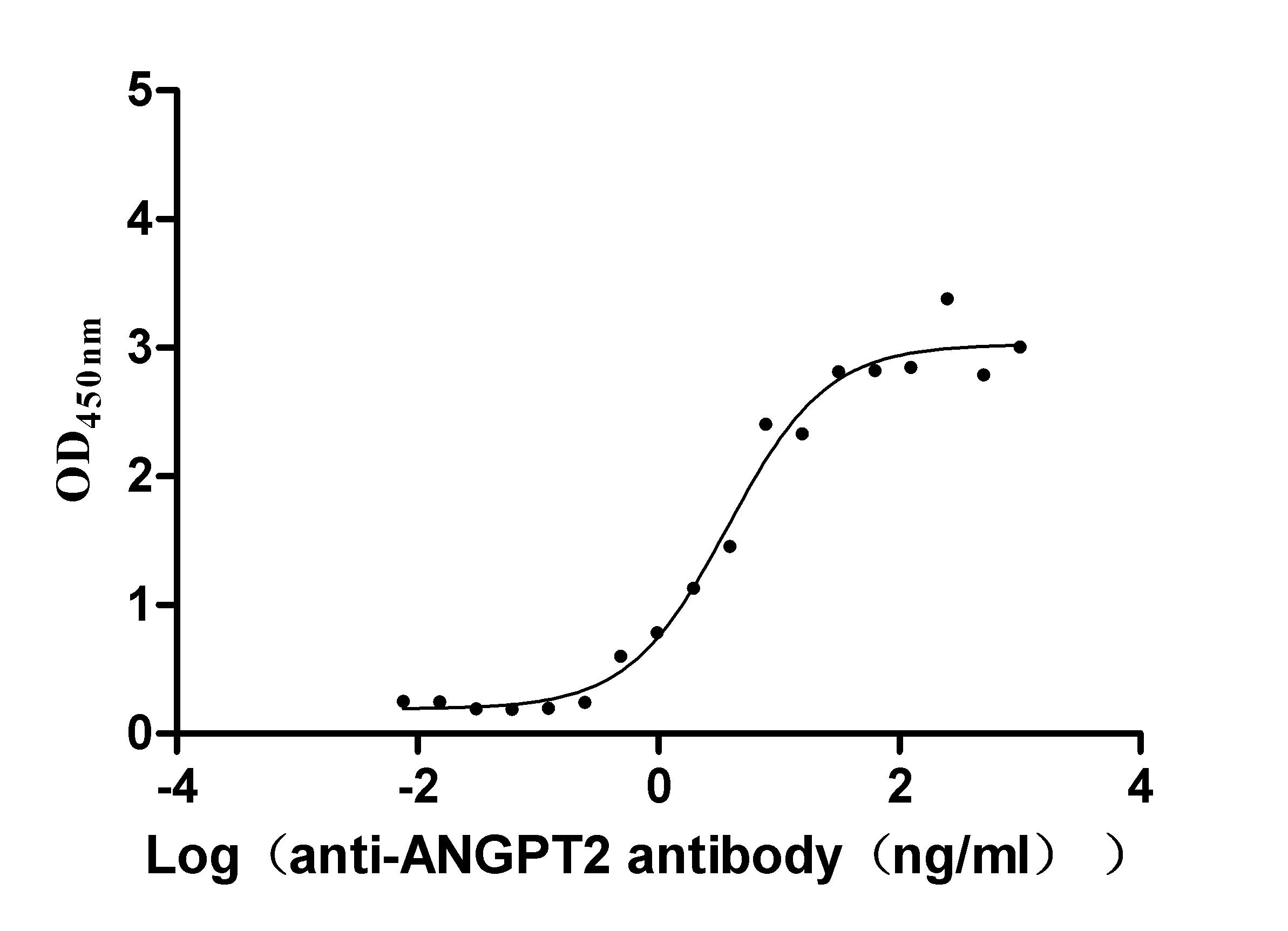
Recombinant Dog Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris)
-
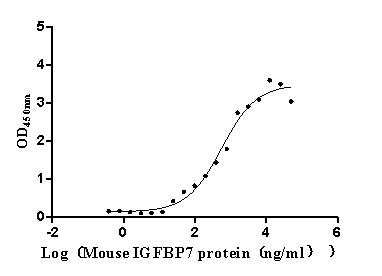
Recombinant Mouse Complement component C1q receptor (Cd93), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
Recombinant Human Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
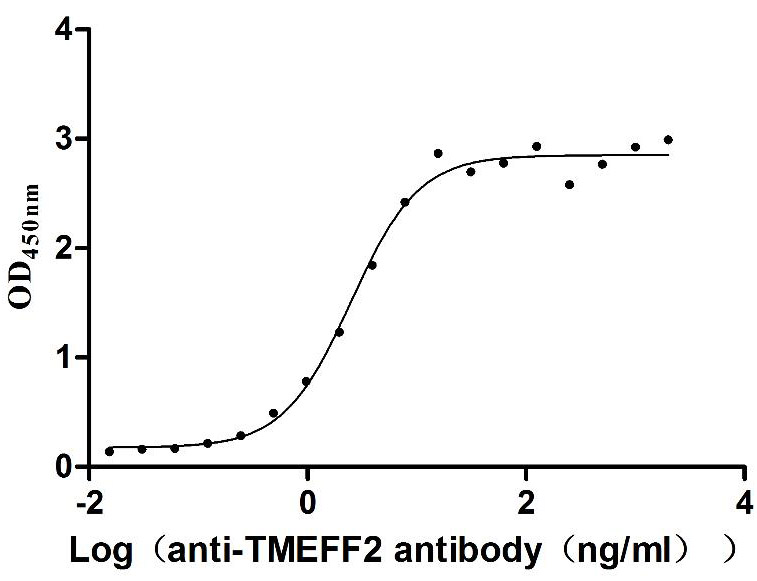
Recombinant Human Tomoregulin-2 (TMEFF2), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Recombinant Human Cell adhesion molecule 1 (CADM1), partial (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)
-
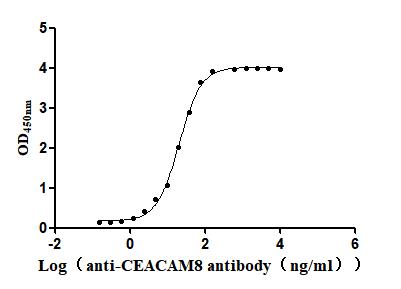
Recombinant Human Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 8(CEACAM8) (Active)
Express system: Mammalian cell
Species: Homo sapiens (Human)


-AC1.jpg)