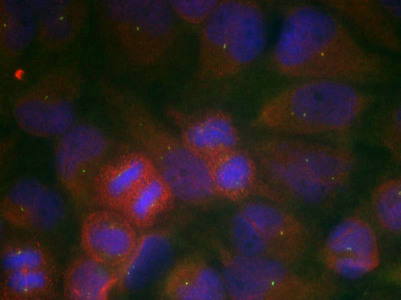
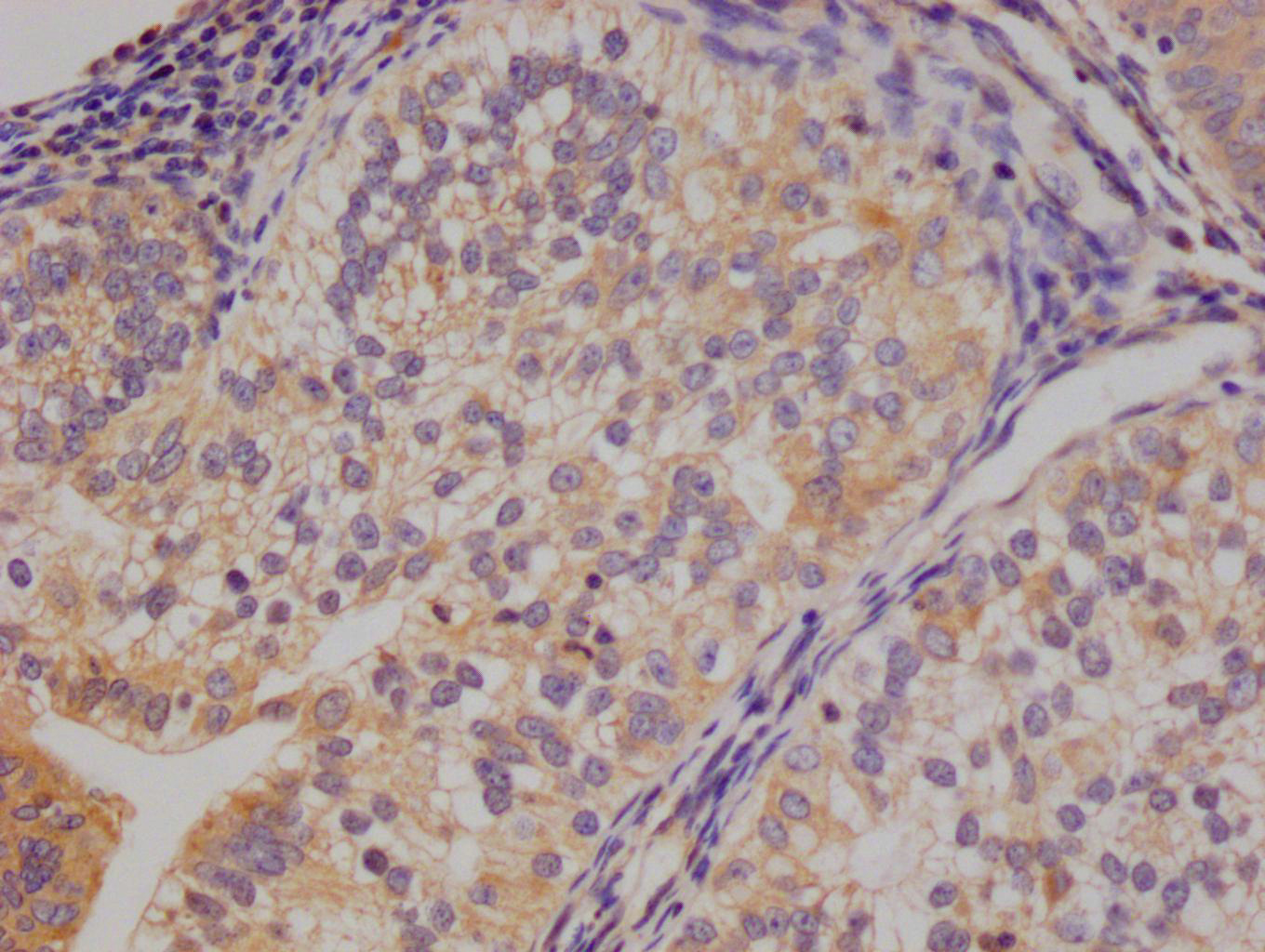
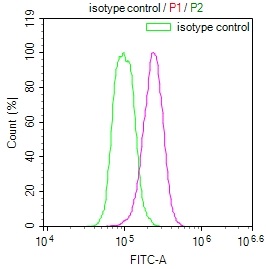
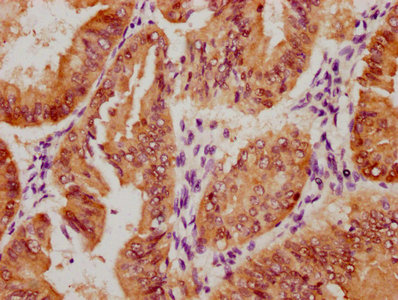
GRIA1 (Ab-863) Antibody
-
中文名稱:GRIA1 (Ab-863)兔多克隆抗體
-
貨號:CSB-PA226902
-
規格:¥2024
-
圖片:
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
產品名稱:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) GRIA1 Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反應種屬:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Peptide sequence around aa.861~865 (R-N-S-G-A) derived from Human GluR1.
-
免疫原種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
克隆類型:Polyclonal
-
純化方式:Antibodies were produced by immunizing rabbits with synthetic peptide and KLH conjugates. Antibodies were purified by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific peptide.
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
產品提供形式:Liquid
-
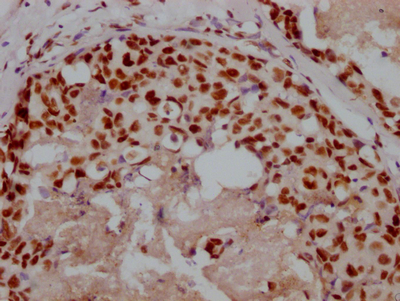
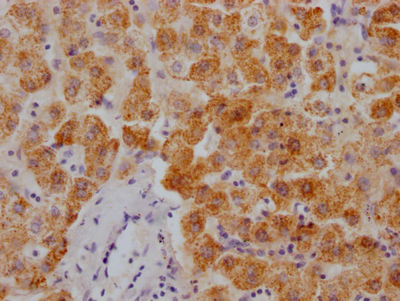
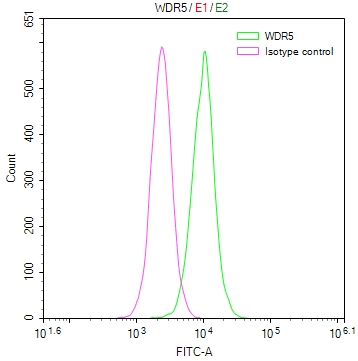
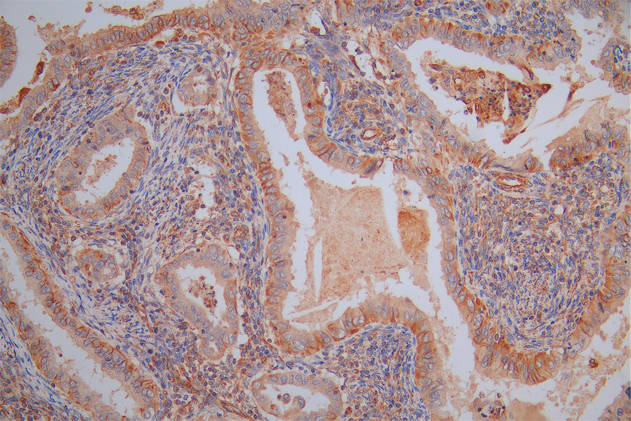
應用范圍:ELISA,IF
-
推薦稀釋比:
Application Recommended Dilution IF 1:100-1:200 -
Protocols:
-
儲存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
用途:For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Ionotropic glutamate receptor. L-glutamate acts as an excitatory neurotransmitter at many synapses in the central nervous system. Binding of the excitatory neurotransmitter L-glutamate induces a conformation change, leading to the opening of the cation channel, and thereby converts the chemical signal to an electrical impulse. The receptor then desensitizes rapidly and enters a transient inactive state, characterized by the presence of bound agonist. In the presence of CACNG4 or CACNG7 or CACNG8, shows resensitization which is characterized by a delayed accumulation of current flux upon continued application of glutamate.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- These findings indicate that the CaMKII-mediated GluA1 phosphorylation of S567 and S831 is critical for P2X2-mediated AMPAR internalization and ATP-driven synaptic depression. PMID: 27624155
- The reversible binding of kynurenic acid (KYNA) on human glutamate receptor (GluR1) polypeptide (GluR1270-300)-modified gold surface has been studied at various temperatures under physiological conditions by two-dimensional SPR experiments. The registered sensorgrams were fitted by using different kinetic models without application of any commercial software. Results suggested that the binding reaction was exothermic. PMID: 27459050
- Elevated GluA1 expression in spinal cord of the amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. PMID: 29367641
- This study demonstrated that a significant decrease in the protein level of GluA1 in major depression disorder. PMID: 27661418
- The findings do not support the association of GRIA1 SNPs with schizophrenia in the Chinese Han population. PMID: 26862833
- Our data of this study confirmed the association of GRIA1 (rs2195450) to female migraine susceptibility in the Chinese Han population. PMID: 26800698
- Polymorphisms in GRIA1 gene are a risk factor for asparaginase hypersensitivity during the treatment of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia PMID: 25697915
- The level of phosphorylated GluA1 at S831 and S845, two major sites implicated in AMPAR regulation, is almost negligible. Results impel us to reconsider the mechanisms underlying synaptic plasticity. PMID: 25533481
- This study failed to replicate previously reported association between GRIA1 rs548294 and migraine without aura, either as single marker or when analyzed in haplotype combination with rs2195450. PMID: 24030684
- the levels were comparable for complexes containing GluR2, GluR3 and GluR4 as well as 5-HT1A. Moreover, the levels of complexes containing muscarinic AChR M1, NR1 and GluR1 were significantly increased in male patients with AD. PMID: 24292102
- The N-terminal domain modulates alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptor desensitization. PMID: 24652293
- insight into the structure and function of the C-terminal domain of GluA1, which controls AMPA receptor function and trafficking during synaptic plasticity in the central nervous system. PMID: 24452473
- Inhibition of CREB function is associated with a specific reduction of AMPA receptor subunit GluA1. PMID: 23504989
- Studies indicate that AMPAR trafficking is a key mechanism that drives nascent synapse development, and is the main determinant of both Hebbian and homeostatic plasticity in mature synapses. PMID: 23475111
- human hippocampal samples from neonatal seizure autopsy cases also showed an increase in GluR1 S831 and S845. PMID: 23223299
- These results suggest that GRIA1 polymorphism may have influence upon the risk of developing schizophrenia. PMID: 23053966
- Glioblastoma brain tumor initiating cells express high concentrations of functional calcium-permeable AMPA receptors, raising the possibility that glutamate secretion in the GBM tumor microenvironment may stimulate brain tumor derived cancer stem cells. PMID: 23110111
- Did not observed any significant association between GRIA1 polymorphisms and clinical improvement in patients with Major depressive disorder. PMID: 22057216
- SNPs within GRIA1 may not be associated with the development and treatment outcomes in BD PMID: 22122651
- No significant association GRIA1 polymorphisms was found with the diagnosis of schizophrenia. PMID: 22094384
- New insights in endosomal dynamics and AMPA receptor trafficking PMID: 21843653
- AMPA receptor regulation during synaptic plasticity in hippocampus and neocortex PMID: 21856433
- These results do not support a significant role of GRIA1 or CLINT1 in the development of schizophrenia in the German population. PMID: 21116212
- analysis of how the AMPA receptor is activated by partial agonists PMID: 21846932
- These results provide critical new insights into the agonist dependence of both AMPA receptor activation and desensitization and the mechanism of the effects of stargazin on responses of partial agonists. PMID: 21697386
- by favoring apoCaM binding to AKAP79, KN-62 and KN-93 derail the ability of AKAP79 to efficiently recruit PKC for regulation of GluA1. Thus, AKAP79 endows PKC with a pharmacological profile that overlaps with CaMKII. PMID: 21156788
- Findings reveal the ligand-binding domain as the critical quality control target in AMPAR biogenesis. PMID: 20837486
- In transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans, glutamate receptor 1 is required for nose-touch avoidance behavior. PMID: 21037582
- single-nucleotide polymorphisms annotated to GRIA1 were also significantly associated with allergy to asparaginase PMID: 20592726
- Two variants in the regulative regions of GRIA1 (rs2195450) and GRIA3 (rs3761555) genes resulted strongly associated with MA (P = 0.00002 and P = 0.0001, respectively), but not associated with MO. PMID: 20579352
- Increase in GluR1 trafficking by leptin is associated with an increase in phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate (PtdIns(3,4,5)P3) levels. PMID: 20237279
- Modeling of the pore domain of the GLUR1 channel: homology with K+ channel and binding of channel blockers PMID: 11916847
- Flip and flop splice variants of AMPA receptor subunits in the spinal cord of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PMID: 12125045
- a short sequence present in the N-terminal domain has a role in controlling anterograde trafficking of ionotropic glutamate receptors PMID: 12368290
- kinetics for the opening of the GluR1Qflip channel PMID: 14610080
- This study investigated whether the AMPA receptor subunit content (GluR1, GluR2, GluR2/3) within "vulnerable" vs. "resistant" sectors of the hippocampus is quantitatively altered with increasing Alzheimer Disease neuropathology PMID: 15144856
- cell loss and up-regulation of glutamate receptor subunits appear early in temporal lobe epilepsy and contribute to the synaptic plasticity that may facilitate the subsequent sprouting of mossy fiber collaterals PMID: 15145077
- According to receptor simulations, most differences can be explained if the C-terminal domain is assumed to stabilize the ligand-bound closed and open states. PMID: 15866042
- Data indicate that GRIA1 may be involved in susceptibility to DSM-IV-TR schizophrenia. PMID: 16526023
- Results indicate that CTZ and TCM target deactivation and agonist potency independently of desensitization, most likely by modifying agonist dissociation (koff). PMID: 17208968
- the Q/R site modulates the interaction of stargazin with the transmembrane domains of AMPA receptors via an allosteric mechanism and that this modulation leads to the observed differences in the electrophysiological properties of the receptor PMID: 17483093
- biochemical study of GLUR1 L497Y AMPA receptor PMID: 17545169
- AKAP79 provides a mechanism to overcome limitations in kinase abundance thereby ensuring faithful signal propagation and efficient modification of AMPA receptor-mediated responses PMID: 18305116
- These results suggest that AMPA receptors are abundantly expressed in high-grade gliomas and gene silencing of the GluR1 AMPA receptor subunit results in abrogation of AMPA-mediated signaling and tumor growth. PMID: 18317690
- combined analysis of all 60 families continued to support evidence for association of GRIA1 with psychotic BP; however, individual SNPs could not be replicated across datasets PMID: 18484081
- Overexpression of GluR1 positively correlated with glioma cell adhesion to type I and type IV collagen PMID: 18957620
- Attenuated AMPA receptor expression allows glioblastoma cell survival in glutamate-rich environment PMID: 19536293
- the intracellularly located CTD of GLUR1 is the origin of TARP-specific functional modulation and not merely a facilitator of trafficking PMID: 19773551
- Data show that S-nitrosylation of stargazin increases binding to the AMPAR subunit GluR1, causing increased surface expression of the AMPAR. PMID: 19805317
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell junction, synapse, postsynaptic cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell junction, synapse, postsynaptic density membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell projection, dendrite. Cell projection, dendritic spine. Early endosome membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Recycling endosome membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:Glutamate-gated ion channel (TC 1.A.10.1) family, GRIA1 subfamily
-
組織特異性:Widely expressed in brain.
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-