TMEM173 Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
-
中文名稱:TMEM173重組抗體
-
貨號:CSB-RA843206A0HU
-
規格:¥1320
-
圖片:
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
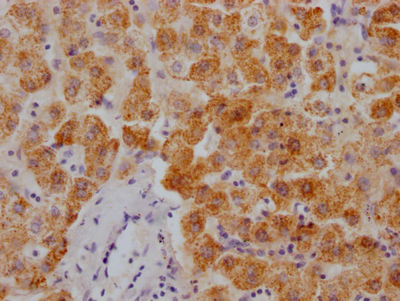
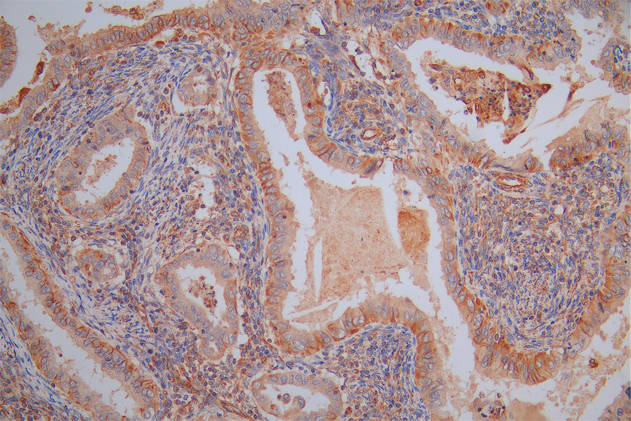
產品描述:TMEM173重組單克隆抗體(CUSABIO貨號:CSB-RA843206A0HU)是針對TMEM173蛋白(又稱STING)開發的高特異性科研工具,適用于ELISA和免疫印跡(WB)等實驗。TMEM173作為先天免疫信號通路的核心調控因子,在胞質DNA識別及I型干擾素應答中發揮關鍵作用,其功能涉及病毒感染防御、腫瘤免疫調控和自身免疫性疾病機制研究。本抗體經嚴格驗證,在WB實驗中展現出優異的檢測性能,推薦使用稀釋度范圍為1:500至1:5000,可高效識別內源性TMEM173蛋白,顯影條帶清晰且背景低。在應用場景中,該抗體適用于探索TMEM173在免疫信號轉導、DNA損傷應答及炎癥反應中的分子機制,為研究病毒感染模型、腫瘤微環境調控或自身免疫相關疾病提供可靠工具。產品采用重組單克隆技術生產,具備高批次一致性和穩定性,滿足蛋白質表達水平分析、通路互作研究等基礎科研需求,嚴格限定于體外實驗及非診斷性研究領域。
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:
-
別名:STING1; ERIS; MITA; TMEM173; Stimulator of interferon genes protein; hSTING; Endoplasmic reticulum interferon stimulator; Mediator of IRF3 activation; hMITA; Transmembrane protein 173
-
反應種屬:Human
-
免疫原:A synthesized peptide derived from human TMEM173
-
免疫原種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
標記方式:Non-conjugated
-
克隆類型:Monoclonal
-
抗體亞型:Rabbit IgG
-
純化方式:Affinity-chromatography
-
克隆號:7C7
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:Rabbit IgG in 10mM phosphate buffered saline , pH 7.4, 150mM sodium chloride, 0.05% BSA, 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol.
-
產品提供形式:Liquid
-
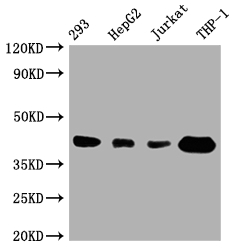
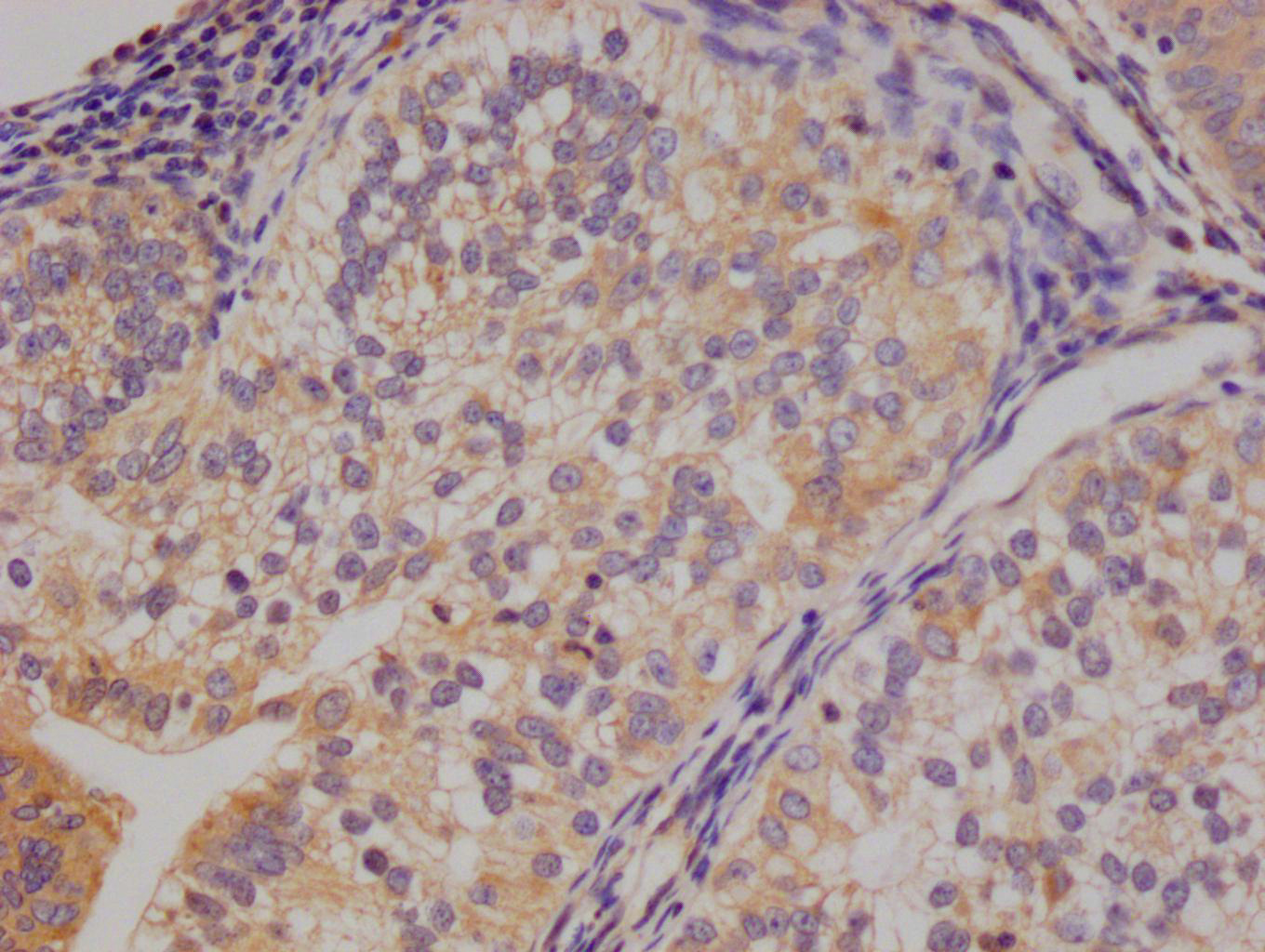
應用范圍:ELISA, WB
-
推薦稀釋比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:5000 -
Protocols:
-
儲存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
用途:For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Facilitator of innate immune signaling that acts as a sensor of cytosolic DNA from bacteria and viruses and promotes the production of type I interferon (IFN-alpha and IFN-beta). Innate immune response is triggered in response to non-CpG double-stranded DNA from viruses and bacteria delivered to the cytoplasm. Acts by binding cyclic dinucleotides: recognizes and binds cyclic di-GMP (c-di-GMP), a second messenger produced by bacteria, and cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP), a messenger produced by CGAS in response to DNA virus in the cytosol. Upon binding of c-di-GMP or cGAMP, STING1 oligomerizes, translocates from the endoplasmic reticulum and is phosphorylated by TBK1 on the pLxIS motif, leading to recruitment and subsequent activation of the transcription factor IRF3 to induce expression of type I interferon and exert a potent anti-viral state. In addition to promote the production of type I interferons, plays a direct role in autophagy. Following cGAMP-binding, STING1 buds from the endoplasmic reticulum into COPII vesicles, which then form the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC). The ERGIC serves as the membrane source for WIPI2 recruitment and LC3 lipidation, leading to formation of autophagosomes that target cytosolic DNA or DNA viruses for degradation by the lysosome. The autophagy- and interferon-inducing activities can be uncoupled and autophagy induction is independent of TBK1 phosphorylation. Autophagy is also triggered upon infection by bacteria: following c-di-GMP-binding, which is produced by live Gram-positive bacteria, promotes reticulophagy. Exhibits 2',3' phosphodiester linkage-specific ligand recognition: can bind both 2'-3' linked cGAMP (2'-3'-cGAMP) and 3'-3' linked cGAMP but is preferentially activated by 2'-3' linked cGAMP. The preference for 2'-3'-cGAMP, compared to other linkage isomers is probably due to the ligand itself, whichs adopts an organized free-ligand conformation that resembles the STING1-bound conformation and pays low energy costs in changing into the active conformation. May be involved in translocon function, the translocon possibly being able to influence the induction of type I interferons. May be involved in transduction of apoptotic signals via its association with the major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II).; (Microbial infection) Antiviral activity is antagonized by oncoproteins, such as papillomavirus (HPV) protein E7 and adenovirus early E1A protein. Such oncoproteins prevent the ability to sense cytosolic DNA.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- We present physiological evidence that UBXN3B positively regulates stimulator-of-interferon genes (STING) signaling. Mechanistic studies demonstrate that UBXN3B interacts with both STING and its E3 ligase TRIM56, and facilitates STING ubiquitination, dimerization, trafficking, and consequent recruitment and phosphorylation of TBK1. PMID: 29899553
- STAG2 deficiency induces interferon responses via cGAS-STING pathway and restricts virus infection. PMID: 29662124
- STING-IRF3 pathway promotes hepatocyte injury and dysfunction by inducing inflammation and apoptosis and by disturbing glucose and lipid metabolism. PMID: 29106945
- Data show that both cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) and interferon-gamma inducible protein 16 (IFI16) are required for the activation of membrane protein STING (STING) and an innate immune response to exogenous DNA and DNA viruses. PMID: 28194029
- PUMA promotes the cytosolic release of mitochondrial DNA and activation of the DNA sensors DAI/Zbp1 and STING, leading to enhanced RIP3 and MLKL phosphorylation in a positive feedback loop. PMID: 29581256
- identified nitro-fatty acids as endogenously formed inhibitors of STING signaling and propose for these lipids to be considered in the treatment of STING-dependent inflammatory diseases. PMID: 30061387
- Cells of human individuals carrying HAQ TMEM173, which encodes a common hypomorphic variant of STING, were largely or partly defective in inducing type I IFNs and proinflammatory cytokines upon infection. PMID: 29263110
- Our studies indicate that the (extracellular vesicles) EVs released by HSV-1-infected cells carry innate immune components such as STING and other host and viral factors; they can activate innate immune responses in recipient cells and inhibit HSV-1 replication. The implication of these data is that the EVs released by HSV-1-infected cells could control HSV-1 dissemination promoting its persistence in the host. PMID: 29976662
- data demonstrate that numerous RNA viruses evade cGAS/STING-dependent signaling and affirm the importance of this pathway in shaping the host range of ZIKV. PMID: 29915078
- Immune activation of STING requires palmitoylation at the Golgi. PMID: 27324217
- In the Title. PMID: 27554814
- This study demonstrated that HSV-1 tegument protein VP22 counteracts the cGAS/STING-mediated DNA-sensing antiviral innate immunity signaling pathway by inhibiting the enzymatic activity of cGAS. PMID: 29793952
- an electrophoretic mobility shift assay showed that signal transducers and activators of transcription 1 (STAT1) attach to the GAS motif on the human STING promoter region. This indicates that IFN-gamma/Janus kinases/STAT1 signaling is essential for the STING upregulation in human keratinocytes. PMID: 29143896
- The cGAS-STING cascade contributes to antibacterial defense against L. pneumophila in mice and men, and provides important insight into how the common HAQ TMEM173/STING variant affects antimicrobial immune responses and susceptibility to infection. PMID: 29298342
- pharmacological activation of STING in macrophages and hepatocytes induces host innate responses that can efficiently control hepatitis B virus replication. Hence, despite not playing a significant role in host innate immune response to HBV infection of hepatocytes, STING is potentially a valuable target for immunotherapy of chronic hepatitis B. PMID: 28717041
- summarize recent findings that have pointed towards the STING pathway as an innate immune sensing mechanism driving type I interferon production in the tumor context PMID: 28639100
- this review summarizes important features of the STING activation pathway and recent highlights about the role of STING in bacterial infections by Chlamydia, Listeria, Francisella, Brucella, Shigella, Salmonella, Streptococcus, and Neisseria genera, with a special focus on mycobacteria. PMID: 28625530
- STING serves to detect - and promote immune defense against - DNA viruses and intracellular bacteria, as described in its initial discovery. The role of STING has since been expanded to include tumor surveillance and immune responses to cancer; indeed, defective STING responses are associated with certain cancers. PMID: 28724326
- C11 depends on signaling through STING to produce antiviral type I interferon, which further supports its potential as a therapeutic drug or research tool. PMID: 29263267
- This study demonstrates that the HCMV tegument protein pp65 inhibits IFN-beta production by binding and inactivating cGAS early during infection. In addition, this inhibitory activity specifically targets cGAS, since it can be bypassed via the addition of exogenous cGAMP, even in the presence of pp65. Notably, STING proteasome-mediated degradation was observed in both the presence and absence of pp65. PMID: 29263269
- The DNA binding domain of Ku70 was essential for formation of the Ku70-STING complex. Knocking down STING in primary human macrophages inhibited their ability to produce IFN-lambda1 in response to transfection with DNA or infection with the DNA virus HSV-2 (herpes simplex virus-2); STING mediates the Ku70-mediated IFN-lambda1 innate immune response to exogenous DNA or DNA virus infection. PMID: 28720717
- Data show that human cytomegalovirus (HCMV; human betaherpesvirus 5) glycoprotein US9 inhibits the IFN-beta response by targeting the mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein (MAVS) and stimulator of interferon genes (STING)-mediated signaling pathways. PMID: 29317664
- In the current study, we studied the role of MITA (Mediator of IRF3 Activation), a regulator of innate immunity, in the regulation of autophagy and its implication in cell death of breast cancer cells. Here, we report that MITA inhibits the fusion of autophagosome with lysosome as evident from different autophagy flux assays PMID: 28366813
- these studies demonstrate that transcription factors CREB and c-Myc maintain the transcriptional activity of STING PMID: 27835584
- TheTREX1 and STING, which are opposing regulators of the cytosolic DNA-sensing pathway. PMID: 28475463
- STING-regulated pathways underlie the pathogenesis of many diseases including infectious diseases and cancers. It has also become evident from these studies that STING is a promising therapeutic target for the treatment of cancer. PMID: 26980676
- using a murine HNSCC model that does not express STING, we demonstrate that STING ligands are an effective therapy regardless of expression of STING by the cancer cells PMID: 29135982
- Human T-lymphotropic virus 1 Tax protein impairs K63-linked ubiquitination of STING and disrupted the interactions between STING and TBK1 to evade host innate immunity. PMID: 28119118
- STING activated an antiviral/type I interferon response with live but not killed S. aureus. PMID: 28704551
- study identifies the AIM2 inflammasome and cGAS/IFI16-STING-type I IFN pathway as a novel mechanism for host innate immunity to the ALVAC vaccine vector. PMID: 28947539
- NEMO was critically involved in the cGAS-STING pathway. PMID: 28939760
- Studied association of genetic variants of the MAVS, MITA and MFN2 genes with leprosy in Han Chinese from Southwest China; found no association between the variants and susceptibility to leprosy. PMID: 27553710
- both IL-6 and RIG-I are downstream molecules of STING along the DNA sensor pathway. PMID: 28806404
- our data provide an important insight into STING-mediated induction of type I and III IFNs and subsequent antiviral signaling pathways that regulate VZV replication in human dermal cells. PMID: 28647346
- STING, a critical innate sensor, also functions intrinsically in cells of the adaptive immune system to inhibit proliferation. PMID: 28484079
- We discuss three newly described monogenic autoinflammatory diseases [deficiency of adenosine deaminase 2 (DADA2), a subtype of macrophage activation syndrome (MAS), and stimulator of interferon genes (STING)-associated vasculopathy with onset in infancy (SAVI)], discuss the possibilities of somatic mosaicism and digenic inheritance, and give an update on new concepts in pathways involved in familial Mediterranean fever PMID: 27362340
- Human Cytomegalovirus tegument protein UL82 negatively regulates STING-mediated signaling. PMID: 28132838
- Structural analysis indicates that the 3 disease-associated mutations at positions 206, 281, and 284 of the STING protein define a novel cluster of amino acids with functional importance in the regulation of type I interferon signaling PMID: 28087229
- a critical role of p38-mediated USP21 phosphorylation in regulating STING-mediated antiviral functions and identifies p38-USP21 axis as an important pathway that DNA virus adopts to avoid innate immunity responses. PMID: 28254948
- We conclude that the R71H-G230A-R293Q (HAQ) of TMEM173 is a null TMEM173 allele. PMID: 27927967
- The authors found that the herpes simplex virus 1 UL46 protein interacts with and colocalizes with STING. PMID: 28592536
- Essential roles of the cGAS-cGAMP-STING pathway. [review] PMID: 27706894
- These results suggest that pDCs sense cytosolic DNA and cyclic dinucleotides via the cGAS-STING pathway and that targeting this pathway could be of therapeutic interest. PMID: 27125983
- Human herpesvirus 1 ICP27 interacted with TBK1 and STING in a manner that was dependent on TBK1 activity and the RGG motif in ICP27 and inhibited type I IFN induction through the cGAS-STING-TBK1 pathway in human macrophages. PMID: 27234299
- Multivariate analysis supported TMEM173 as an independent prognostic factor. PMID: 27814372
- The mitochondrial damage-cGAS-STING-IRF3 pathway is critically involved in metabolic stress-induced endothelial inflammation. PMID: 28302626
- These data uncover a promycobacterial role for STING-dependent OASL production during Mycobacterium leprae infection that directs the host immune response toward a niche that permits survival of the pathogen. PMID: 27190175
- A heterozygous gain-of-function mutation in STING can cause familial chilblain lupus. PMID: 27566796
- cGAs recognizes bacterial/viral DNA, and is a strong activator of STING that can further activate IRF3 and subsequent type I interferon production. (Review) PMID: 27696330
- In the present study, the authors found that herpes simplex virus 1 tegument protein UL41 was involved in counteracting the cGAS/STING-mediated DNA-sensing pathway. PMID: 28077645
顯示更多
收起更多
-
相關疾病:STING-associated vasculopathy, infantile-onset (SAVI)
-
亞細胞定位:Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cytoplasm, perinuclear region. Endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cytoplasmic vesicle, autophagosome membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Mitochondrion outer membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:TMEM173 family
-
組織特異性:Ubiquitously expressed. Expressed in skin endothelial cells, alveolar type 2 pneumocytes, bronchial epithelium and alveolar macrophages.
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
-
-
-
-
-