Phospho-MLKL (S358) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
-
中文名稱:磷酸化-MLKL (S358)重組抗體
-
貨號:CSB-RA850851A358phHU
-
規格:¥1320
-
圖片:
-
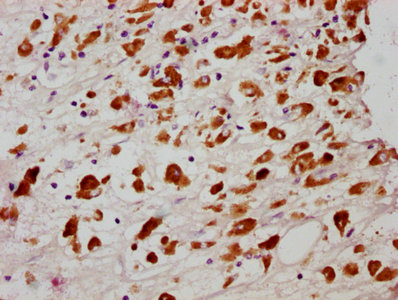
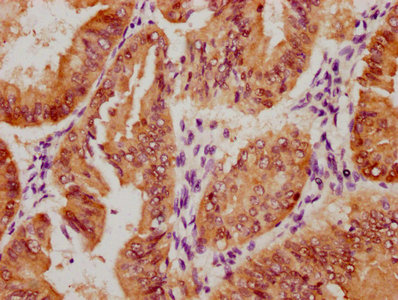
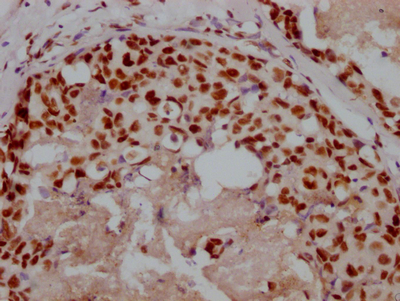
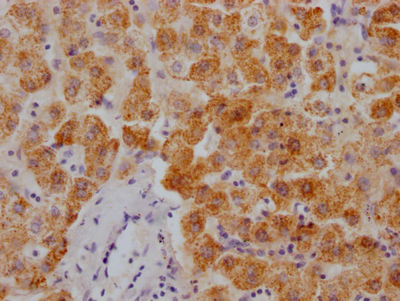
IHC image of CSB-RA850851A358phHU diluted at 1:100 and staining in paraffin-embedded human melanoma cancer performed on a Leica BondTM system. After dewaxing and hydration, antigen retrieval was mediated by high pressure in a citrate buffer (pH 6.0). Section was blocked with 10% normal goat serum 30min at RT. Then primary antibody (1% BSA) was incubated at 4℃ overnight. The primary is detected by a biotinylated secondary antibody and visualized using an HRP conjugated SP system.
-
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
產品描述:CSB-RA850851A358phHU 磷酸化MLKL (S358)重組單克隆抗體是針對壞死性凋亡關鍵調控蛋白MLKL的磷酸化特異性抗體,可特異性識別MLKL第358位絲氨酸磷酸化修飾位點。該抗體經ELISA和免疫組化(IHC)嚴格驗證,推薦IHC實驗使用1:50-1:200的稀釋比例,具有高親和力和低交叉反應性,能清晰定位組織中磷酸化MLKL的時空表達特征。MLKL作為程序性壞死的終末效應蛋白,其S358位點的磷酸化是激活壞死性凋亡通路的重要分子事件,該抗體可應用于研究缺血再灌注損傷、神經退行性疾病及炎癥性疾病中壞死性凋亡的分子機制,支持石蠟切片、冰凍切片等樣本的定位分析,以及通過ELISA技術進行定量檢測,為探索細胞死亡調控網絡提供可靠工具,適用于基礎科研領域的信號通路研究與病理模型分析。
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:
-
別名:9130019I15Rik antibody; FLJ34389 antibody; hMLKL antibody; Mixed lineage kinase domain like antibody; Mixed lineage kinase domain like protein antibody; Mixed lineage kinase domain like pseudokinase antibody; Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein antibody; Mlkl antibody; MLKL_HUMAN antibody
-
反應種屬:Human
-
免疫原:A synthesized peptide derived from Human Phospho-MLKL (S358)
-
免疫原種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
標記方式:Non-conjugated
-
克隆類型:Monoclonal
-
抗體亞型:Rabbit IgG
-
純化方式:Affinity-chromatography
-
克隆號:4A6
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:Rabbit IgG in 10mM phosphate buffered saline , pH 7.4, 150mM sodium chloride, 0.05% BSA, 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol.
-
產品提供形式:Liquid
-
應用范圍:ELISA, IHC
-
推薦稀釋比:
Application Recommended Dilution IHC 1:50-1:200 -
Protocols:
-
儲存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
用途:For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Pseudokinase that plays a key role in TNF-induced necroptosis, a programmed cell death process. Does not have protein kinase activity. Activated following phosphorylation by RIPK3, leading to homotrimerization, localization to the plasma membrane and execution of programmed necrosis characterized by calcium influx and plasma membrane damage. In addition to TNF-induced necroptosis, necroptosis can also take place in the nucleus in response to orthomyxoviruses infection: following activation by ZBP1, MLKL is phosphorylated by RIPK3 in the nucleus, triggering disruption of the nuclear envelope and leakage of cellular DNA into the cytosol.following ZBP1 activation, which senses double-stranded Z-RNA structures, nuclear RIPK3 catalyzes phosphorylation and activation of MLKL, promoting disruption of the nuclear envelope and leakage of cellular DNA into the cytosol. Binds to highly phosphorylated inositol phosphates such as inositolhexakisphosphate (InsP6) which is essential for its necroptotic function.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- Following activation, toggling within the MLKL pseudokinase domain promotes 4HB domain disengagement from the pseudokinase domain alphaC helix and pseudocatalytic loop, to enable formation of a necroptosis-inducing tetramer. PMID: 29930286
- Data show that phosphatidylinositol transfer protein alpha (PITPalpha) is involved in the function of mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein (MLKL) in necroptosis. PMID: 29104146
- MLKL expression alters APP metabolism and loss-of-function mutation might contribute to late-onset ApoE varepsilon4-negative AD in the Hong Kong Chinese population. PMID: 29656768
- Results demonstrate that MLKL concentrations measured after three days of ICU treatment in critically ill patients predict prognosis during intensive care unit treatment. These data not only suggest a previously unrecognized function of MLKL as a biomarker in critical illness and sepsis but also highlight the clinical relevance of MLKL in the pathophysiology of inflammatory and infectious diseases. PMID: 29606984
- Thus, activation of MLKL determines cell lysis with release of proinflammatory mediators. We found that pMLKL, the activated form of MLKL, is significantly increased in intestinal epithelial cells expressing RIP3 as well as in bioptic inflamed ileal and colonic tissues from CD and UC patients. PMID: 28844856
- Biological events and molecular signaling following MLKL activation during necroptosis have been reported. PMID: 28854080
- Low expression of mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein was associated with decreased overall survival in all patient-group with resected colon cancer. PMID: 27432118
- Phosphorylated MLKL leads to a conformational change, exposure of the N-terminal domain, results in MLKL membrane localization, oligomerization and membrane permeabilization. PMID: 26868910
- adhesion-induced eosinophil cytolysis takes place through RIPK3-MLKL-dependent necroptosis, which can be counterregulated by autophagy PMID: 28412393
- MLKL forms cation channels that are permeable preferentially to Mg(2+) rather than Ca(2+) in the presence of Na(+) and K(+). PMID: 27033670
- RIPK3 is a key factor in protection against OLs death and abnormal myelin development via its interaction with MLKL. PMID: 28230861
- these findings demonstrate that Trx1 is a critical regulator of necroptosis that suppresses cell death by maintaining MLKL in a reduced inactive state. PMID: 28878015
- this study shows that release of phosphorylated MLKL within extracellular vesicles serves as a mechanism for self-restricting the necroptotic activity of this protein PMID: 28666573
- this study shows that MLKL is an endogenous activator of the NLRP3 inflammasome, and that MLKL activation provides a mechanism for concurrent processing and release of IL-1beta independently of gasdermin-D PMID: 28130493
- Data suggest that necroptotic cells externalize phosphatidylserine (PS) after translocation of phosphorylated MLKL to cell membrane; necroptotic cells with exposed PS release extracellular vesicles containing MLKL; inhibition of MLKL after PS exposure can reverse process of necroptosis and restore cell viability. PMID: 28650960
- results reveal a pathway for MLKL-dependent programmed necrosis that is executed in the absence of RIPK3 and potentially drives the pathogenesis of severe liver diseases. PMID: 27756058
- MLKL octamer formation depends on alpha-helices 4 and 5. PMID: 27920255
- Necroptosis signaling is modulated by the kinase RIPK1 and requires the kinase RIPK3 and the pseudokinase MLKL. (Review) PMID: 26865533
- In AML, MLKL expression is reduced in specific subsets. This is linked to its function in activating the ASC inflammasome. PMID: 27411587
- Downregulated expression of MLKL is associated with gastric caner. PMID: 27473085
- Results from interaction proteomics identified MLKL as a novel HSP90 client protein in HT-29 cells. PMID: 26933192
- coexpression of Hsp90 increases MLKL oligomerization and plasma membrane translocation and enhances MLKL-mediated necroptosis. Findings demonstrate that an efficient necrotic response requires a functional Hsp90. PMID: 26866270
- MLKL was a prognostic biomarker for cervical squamous cell carcinoma PMID: 26823841
- Modelling predicts that a C-terminal helix constrains the activity of MLKL1, but not MLKL2 PMID: 26704887
- Results show that upon activation, MLKL undergoes oligomerization mediated by the brace domain, being recruited to the plasma membrane through avidity of N-terminal helix bundle for phosphatidylinositol phosphate (PIP). PMID: 26853145
- MLKL structure determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy reveals how different structural elements of the MLKL N-terminal region contribute to MLKL function and membrane permeation. PMID: 25220470
- MLKL upregulation in SPARC overexpressed cells treated with Ara-C, indicates necrosis as a possible cell death process for the SKM-1 cells under these stringent conditions PMID: 26165695
- in the absence of caspase-8 activity, 24(S)-Hydroxycholesterol induces a necroptosis-like cell death which is RIPK1-dependent but MLKL-independent. PMID: 25697054
- These data reveal a potential role for RIPK3 as a suppressor of MLKL activation and indicate that phosphorylation can fine-tune the ability of MLKL to induce necroptosis. PMID: 26283547
- a novel non-enzymatic function of AChE-R is to stimulate RIPK1/MLKL-dependent regulated necrosis (necroptosis). The latter complements a cholinergic system in the ovary, which determines life and death of ovarian cells. PMID: 25766324
- High expression of RIP3 in keratinocytes from toxic epidermal necrolysis patients potentiates MLKL phosphorylation/activation and necrotic cell death. PMID: 25748555
- Authors demonstrate that the full four-helical bundle domain (4HBD) in the N-terminal region of MLKL is required and sufficient to induce its oligomerization and trigger cell death. PMID: 24813885
- MLKL binding to phosphatidylinositol phosphates is required for plasma membrane rupture PMID: 24813885
- Report role of MLKL/RIP3 pathway in necrotic membrane disruption. PMID: 24703947
- MLKL protein expression is significantly upregulated in children, diagnosed with inflammatory bowel disease. PMID: 24322838
- Data suggest that nucleotide- (ATP-) binding residues of human MLKL have divergently evolved from mouse Mlkl and conventional protein kinases; studies include small-angle X-ray scattering, thermal shift of nucleotide binding, and sequence alignment. PMID: 24219132
- This study reveals a crucial mechanism of MLKL-mediated TNF-induced necroptosis. PMID: 24316671
- Low expression of MLKL is associated with decreased OS in patients with resected PAC and decreased RFS and OS in the subset of patients with resected PAC who receive adjuvant chemotherapy. PMID: 23720157
- the importance of the RIP3-MLKL interaction in the formation of functional necrosomes and suggest that translocation of necrosomes to mitochondria-associated membranes is essential for necroptosis signaling. PMID: 23612963
- study suggests that MLKL is a key RIP3 downstream component of TNF-induced necrotic cell death PMID: 22421439
- Findings implicate MLKL as a key mediator of necrosis signaling downstream of the kinase RIP3. PMID: 22265413
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:Cytoplasm. Cell membrane. Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:Protein kinase superfamily
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-
-