Phospho-CTNNB1 (S33/S37) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
-
中文名稱:磷酸化-CTNNB1 (S33/S37)重組抗體
-
貨號:CSB-RA006169A33phHU
-
規格:¥1320
-
圖片:
-
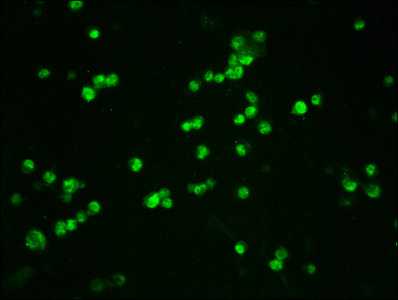
Immunofluorescence staining of 293T cells(treated with 50nM Calyculin A for 30min) with CSB-RA006169A33phHU at 1:100,counter-stained with DAPI. The cells were fixed in 4% formaldehyde, permeabilized using 0.2% Triton X-100 and blocked in 10% normal Goat Serum. The cells were then incubated with the antibody overnight at 4℃. The secondary antibody was Alexa Fluor 488-congugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L).
-
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
產品描述:Phospho-CTNNB1 (S33/S37) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody(Code: CSB-RA006169A33phHU)是一款高特異性抗體,靶向β-catenin蛋白在S33和S37位點的磷酸化修飾。β-catenin是Wnt信號通路的核心調控分子,其磷酸化狀態直接參與調控蛋白穩定性及核內信號轉導:S33/S37位點的磷酸化可促進β-catenin經泛素-蛋白酶體途徑降解,從而抑制下游靶基因激活。該抗體通過ELISA和免疫熒光(IF)嚴格驗證,推薦IF使用稀釋度為1:20-1:200,可在多種細胞模型中清晰檢測內源性磷酸化β-catenin的亞細胞定位變化,例如在Wnt通路激活條件下觀察到核內聚集減少,或經磷酸酶處理后信號強度顯著降低,證實其對目標表位的高度特異性識別。該產品適用于探究Wnt信號異常相關的分子機制研究,包括腫瘤發生、胚胎發育調控或細胞黏附功能分析等領域,為磷酸化依賴性蛋白互作、信號轉導動態及藥物干預研究提供可靠工具,僅限科研使用。
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:
-
別名:b-catenin antibody; Beta catenin antibody; Beta-catenin antibody; Cadherin associated protein antibody; Catenin (cadherin associated protein); beta 1; 88kDa antibody; Catenin beta 1 antibody; Catenin beta-1 antibody; CATNB antibody; CHBCAT antibody; CTNB1_HUMAN antibody; CTNNB antibody; CTNNB1 antibody; DKFZp686D02253 antibody; FLJ25606 antibody; FLJ37923 antibody; OTTHUMP00000162082 antibody; OTTHUMP00000165222 antibody; OTTHUMP00000165223 antibody; OTTHUMP00000209288 antibody; OTTHUMP00000209289 antibody
-
反應種屬:Human
-
免疫原:A synthesized peptide derived from Human Phospho-CTNNB1 (S33/S37)
-
免疫原種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
標記方式:Non-conjugated
-
克隆類型:Monoclonal
-
抗體亞型:Rabbit IgG
-
純化方式:Affinity-chromatography
-
克隆號:4C11
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:Rabbit IgG in 10mM phosphate buffered saline , pH 7.4, 150mM sodium chloride, 0.05% BSA, 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol.
-
產品提供形式:Liquid
-
應用范圍:ELISA, IF
-
推薦稀釋比:
Application Recommended Dilution IF 1:20-1:200 -
Protocols:
-
儲存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
用途:For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Key downstream component of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. In the absence of Wnt, forms a complex with AXIN1, AXIN2, APC, CSNK1A1 and GSK3B that promotes phosphorylation on N-terminal Ser and Thr residues and ubiquitination of CTNNB1 via BTRC and its subsequent degradation by the proteasome. In the presence of Wnt ligand, CTNNB1 is not ubiquitinated and accumulates in the nucleus, where it acts as a coactivator for transcription factors of the TCF/LEF family, leading to activate Wnt responsive genes. Involved in the regulation of cell adhesion, as component of an E-cadherin:catenin adhesion complex. Acts as a negative regulator of centrosome cohesion. Involved in the CDK2/PTPN6/CTNNB1/CEACAM1 pathway of insulin internalization. Blocks anoikis of malignant kidney and intestinal epithelial cells and promotes their anchorage-independent growth by down-regulating DAPK2. Disrupts PML function and PML-NB formation by inhibiting RANBP2-mediated sumoylation of PML. Promotes neurogenesis by maintaining sympathetic neuroblasts within the cell cycle. Involved in chondrocyte differentiation via interaction with SOX9: SOX9-binding competes with the binding sites of TCF/LEF within CTNNB1, thereby inhibiting the Wnt signaling.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- CXC chemokine ligand 9 promotes the progression of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in a beta-catenin-dependent manner. PMID: 30130730
- Results suggest that epigenetic regulation of CTNNB1 may serve as a novel avenue to block colon cancer cell migration and invasion. PMID: 29923144
- The results demonstrated that 2HF could inhibit EMT, and cell migration and invasion through the Wnt/bcatenin signaling pathway by suppressing GSK3b phosphorylation, betacatenin expression and transactivation. PMID: 30226607
- Collectively, these studies suggested the cellular transcription factor beta-catenin stimulates productive herpes simplex virus 1infection, in part because VP16 enhances beta-catenin dependent transcription. PMID: 30077727
- CTNNB1 mutations may be more related to tumorigenesis ( aldosterone-producing adenoma) rather than excessive aldosterone production PMID: 28102204
- CTNNB1 mutations were found in 60% of Basal cell adenoma but not in basal cell adenocarcinoma. None of the tested cases had PIK3CA mutations. CTNNB1 mutation trended to be more common in those cases having a predominant tubular or tubulotrabecular patterns. PMID: 29224720
- Data reveal that post-translational modifications of beta-catenin in the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway yield a truncated beta-catenin molecule containing a serine 552-phosphorylated core region without N and C termini. This proteolytic processing of beta-catenin is required for binding with TCF4 and subsequent transcriptional activation. PMID: 29330435
- Results identify CTNNB1 as a Girdin-interacting protein. Girdin-depleted skin cancer cells displayed scattering and impaired E-cadherin-specific cell-cell adhesion. PMID: 30194792
- the dysregulation of TET2/E-cadherin/beta-catenin regulatory loop is a critical oncogenic event in HCC progression PMID: 29331390
- High CTNNB1 expression is associated with bladder cancer progression. PMID: 30015971
- It has been found that miR-27a-3p modulated the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous carcinoma stem cells by down-regulating SFRP1. PMID: 28425477
- Beta-catenin pathway is activated by CBX8 in in hepatocellular carcinoma. PMID: 29066512
- our data provide a novel evidence for the biological and clinical significance of SPAG5 as a potential biomarker, and we demonstrate that SPAG5-b-catenin-SCARA5 might be a novel pathway involved in hepatocellular carcinoma progression. PMID: 30249289
- Results show that hypoxia enhanced nuclear accumulation and transcriptional activity of beta-catenin which promotes expression of EMT-related genes and eventually contributes to the metastatic process in lung cancer cells. PMID: 30396950
- This study demonstrates that FOXC1 induces cancer stem cells (CSCs)-like properties in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) by promoting beta-catenin expression. The findings indicate that FOXC1 is a potential molecular target for anti-CSC-based therapies in NSCLC PMID: 30189871
- High TBL1XR1 expression indicates poor disease-free survival of stage I-III colorectal cancer patients; beta-catenin signaling is critical for TBL1XR1-mediated colorectal cancer cells oncogenicity. PMID: 28295012
- Taking together, these results suggest that Wnt/beta-catenin signal pathway activation-dependent up-regulation of syncytin-1 contributes to the pro-inflammatory factor TNF-alpha-enhanced fusion between oral squamous cell carcinoma cells and endothelial cells. PMID: 28112190
- The disassociation of the beta-catenin/E-cadherin complex in the osteoblast membrane under stretch loading and the subsequent translocation of beta-catenin into the nucleus may be an intrinsic mechanical signal transduction mechanism. PMID: 29901167
- Aberrant CTNNB1 expression was seen in a substantial proportion of our hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cases. CTNNB1-positive HCC was associated with normal AFP levels, unicentric tumors, well-differentiated histology, and an unfavorable outcome. PMID: 30082549
- Long noncoding RNA AFAP1-AS1 enhances cell proliferation and invasion in osteosarcoma through regulating miR-4695-5p/TCF4-beta-catenin signaling. PMID: 29901121
- High CTNNB1 expression is associated with the recurrece of Adamantinomatous Craniopharyngiomas. PMID: 29625497
- High CTNNB1 expression is associated with uterine fibroids. PMID: 29066531
- The nucleus and/or cytoplasm expression of beta-catenin was associated with tumor progression and correlated overall survival of patients with ovarian cancer (OC). beta-catenin may be a possible potential prognostic biomarker for the patients with OC. [review] PMID: 30103006
- In the two wild type (WT) cases, two novel alterations were detected: a complex deletion of APC and a pathogenic mutation of LAMTOR2. Focusing on WT DT subtype, deep sequencing of CTNNB1, APC and LAMTOR2 was conducted on a retrospective series of 11 WT DT using a targeted approach PMID: 29901254
- DLX1 interacted with beta-catenin and enhanced the interaction between beta-catenin and TCF4 T-cell factor PMID: 29317218
- Nuclear beta-catenin immunoreactivity with appropriate criteria may be helpful to distinguish basal cell adenocarcinoma (BCAC) from histologically similar tumors. However, a minor subset of adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC) with nuclear beta-catenin expression require careful diagnosis. PMID: 29496310
- High CTNNB1 expression is associated with metastasis in cholangiocarcinoma. PMID: 30193944
- beta;-catenin directly interacts with the Cx43 carboxyl-terminal domain. PMID: 29882937
- This study showed that beta-catenin expression was the most evident in the nucleus rather than in cytoplasm. PMID: 29297710
- Nuclear beta-catenin accumulation in non-mitotic glioblastoma cells is due to a feed forward mechanism between DOCK4 and beta-catenin. PMID: 28925399
- Study found that HIF1alpha overexpression led to an enhanced betacatenin nuclear translocation, while betacatenin silencing inhibited betacatenin nuclear translocation. The enhanced betacatenin nuclear translocation induced resulted in an enhanced cell proliferation and cell invasion, an altered cell cycle distribution, decreased apoptosis, and improved nonhomologous end joining repair under normal and irradiation cond... PMID: 29658569
- our results demonstrated that miR-188 inhibits glioma cell proliferation by targeting beta-catenin PMID: 29268818
- Marked upregulation of beta-catenin and its downstream targets effectively enhanced hepatosphere formation, with an associated induction of CD133, OCT4 and Sox2 expression and also caused an significant enhancement of HCC proliferation PMID: 29792038
- Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway may play a significant role in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia by regulating the invasion and proliferation of trophoblast. PMID: 29603045
- Associations between environmental variants together with single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of beta-catenin (ctnnb1) and lung cancer risk were analyzed using a logistic regression model. PMID: 29562493
- that CTNNB1 is overexpressed and confers a poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia PMID: 29496308
- High CTNNB1 expression is associated with cisplatin-resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. PMID: 30009824
- beta-catenin immunopositivity is seen in majority of cases of sinonasal sarcoma PMID: 29566950
- For the first time, we demonstrated that rather than excluding lymphocytes infiltration as reported in mela-noma, high levels of TILs were associated with beta-catenin overexpression in BC. PMID: 29286921
- Study shows that apigenin-induced lysosomal degradation of beta-catenin in Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. PMID: 28337019
- Used CRISPR-Cas9 technology to study effect of knockout of catenin beta 1 (CTNNB1) on cell behavior and signal pathways in HEK293 cells. Results showed knockout of CTNNB1 effected Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway and suppressed adhesion and proliferation of HEK 293T cells. PMID: 29249062
- our results also revealed that lncRNA SNHG20 knockdown inhibited Wnt/b catenin signaling activity by suppressing beta-catenin expression and reversing the downstream target gene expression. Taken together, lncRNA SNHG20 plays an pivotal role in ovarian cancer progression by regulating Wnt/b-catenin signaling PMID: 29101241
- Wnt3A regulates the expression of 1,136 genes, of which 662 are upregulated and 474 are downregulated in CCD-18Co cells. A set of genes encoding inhibitors of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway stand out among those induced by Wnt3A, which suggests that there is a feedback inhibitory mechanism. PMID: 29044515
- The aim of our study was to analyze the immunohistochemical expression of beta-catenin, E-cadherin and Snail, depending on clinico-morphological aspects of the laryngeal squamous cell carcinomas. Results revealed variable E-cadherin, beta-catenin and Snail expression, depending on differentiation degree and tumor stage. PMID: 29250652
- In this study we showed that the activation of Wnt/beta-catenin pathway culminates in the upregulation of MGAT1 enzyme both at transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels. We also showed that overexpression of the beta-catenin gene (CTNNB1) increased the promoter activity of MGAT1. PMID: 29310626
- CTNNB1 mutation is associated with acquired resistance to KIT inhibitor in metastatic melanoma. PMID: 28421416
- three CTNNB1 SNPs were suggested to have the potential to be novel biomarkers for risk prediction of cancer in overall population or some specific subgroups. [Review] PMID: 28963373
- A CTNNB1 exon 3 mutation restricted to the areas exhibiting both positive glutamine synthetase (GS) and C-reactive protein (CRP) expression, whereas wild-type CTNNB1 was found in areas showing only CRP staining. These two cases illustrate focal beta-catenin activation that can occur within Inflammatory hepatocellular adenoma (IHCAs). PMID: 28618047
- Results show that E-cadherin/beta-catenin complex is disrupted by ICAT promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cervical cancer cells. PMID: 29048651
- Toosendanin administration inhibited growth and liver metastasis of orthotopically implanted SGC7901 tumors in vivo through miR200amediated beta-catenin pathway. Our data suggest that Toosendanin may suppress oncogenic phenotypes of human GC cells partly via miR200a/beta-catenin axis. Hence, Toosendanin may have a promising chemotherapeutic activity for GC therapy. PMID: 29048657
顯示更多
收起更多
-
相關疾病:Colorectal cancer (CRC); Pilomatrixoma (PTR); Medulloblastoma (MDB); Ovarian cancer (OC); Mesothelioma, malignant (MESOM); Mental retardation, autosomal dominant 19 (MRD19); Vitreoretinopathy, exudative 7 (EVR7)
-
亞細胞定位:Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Cell junction, adherens junction. Cell junction. Cell membrane. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle pole. Cell junction, synapse. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, cilium basal body.
-
蛋白家族:Beta-catenin family
-
組織特異性:Expressed in several hair follicle cell types: basal and peripheral matrix cells, and cells of the outer and inner root sheaths. Expressed in colon. Present in cortical neurons (at protein level). Expressed in breast cancer tissues (at protein level).
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-
-