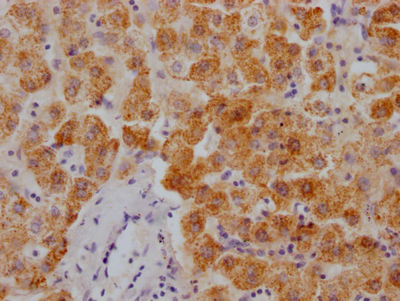
SLC39A4 Antibody
-
中文名稱(chēng):SLC39A4兔多克隆抗體
-
貨號(hào):CSB-PA021633GA01HU
-
規(guī)格:¥3,900
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:SLC39A4
-
別名:SLC39A4; ZIP4; Zinc transporter ZIP4; Solute carrier family 39 member 4; Zrt- and Irt-like protein 4; ZIP-4
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反應(yīng)種屬:Human
-
免疫原:Human SLC39A4
-
免疫原種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
抗體亞型:IgG
-
純化方式:Antigen Affinity purified
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:PBS with 0.1% Sodium Azide, 50% Glycerol, pH 7.3. -20°C, Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Liquid
-
應(yīng)用范圍:ELISA,WB
-
Protocols:
-
儲(chǔ)存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
用途:For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
相關(guān)產(chǎn)品
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
功能:Plays an important role in cellular zinc homeostasis as a zinc transporter. Regulated in response to zinc availability.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- Results showed decreased expression of Zn uptake transporters ZIP2 and ZIP4 on mRNA and protein level correlating with SHANK3 expression levels, and found reduced levels of ZIP4 protein co-localizing with SHANK3 at the plasma membrane. ZIP4 exists in a complex with SHANK3. Further results confirmed a link between enterocytic SHANK3, ZIP2 and ZIP4. PMID: 28345660
- Expression of zinc transporters ZIP4, ZIP14 and ZnT9 in hepatic carcinogenesis-An immunohistochemical study PMID: 29895370
- exosomal ZIP4 promotes cancer growth and is a novel diagnostic biomarker for pancreatic cancer. PMID: 30007115
- Structural insights of ZIP4 extracellular domain critical for optimal zinc transport have been uncovered. PMID: 27321477
- ZIP4 regulates human epidermal homeostasis in patients with acrodermatitis enteropathica. PMID: 27940220
- ZIP4 and intracellular zinc have essential roles in tumoral growth in oral squamous cell carcinoma PMID: 28017725
- Case Report: heterozygote mutation in SLC39A4 resulting in acrodermatitis enteropathica. PMID: 26351177
- Data sho that silencing of zinc transporter ZIP4 resulted in increased bone tissue mineral density, and restoration of bone strength. PMID: 26305676
- Studied the zinc binding properties of the large intracellular loop of hZIP4. PMID: 25882556
- The results described a previously uncharacterized role of ZIP4 in apoptosis resistance and elucidated a novel pathway through which ZIP4 regulates pancreatic cancer growth. PMID: 24553114
- In glioma tumors, high ZIP4 expression was significantly associated with higher grade. PMID: 25921144
- Developed is a structural model of ZIP4 by combining protein prediction methods with in situ experiments. Insight into the permeation pathway of ZIP4 is provided. PMID: 25971965
- SLC39A4 mutations have roles in zinc deficiency PMID: 25391167
- Both acrodermatitis mutations cause absence of the ZIP4 transporter cell surface expression and nearly absent zinc uptake. PMID: 24586184
- ZIP4 activates the zinc-dependent transcription factor CREB and requires this transcription factor to increase miR-373 expression through the regulation of its promoter. PMID: 23857777
- High ZIP4 expression is associated with glioma. PMID: 23595627
- resulkts indicate ZIP4 is the only zinc transporter that is significantly up-regulated in pancreatic cancer and might be the major zinc transporter that plays an important role in pancreatic cancer growth PMID: 23331012
- The results suggest that ZIP4 may be a tumor suppressor gene and down-regulation of ZIP4 may be a critical early event in the development of prostate carcinoma PMID: 21803616
- Expression of two Zn(2+) influx transporters, ZIP2 and ZIP4, is reduced as a function of retinal pigment epithelium age. PMID: 21603979
- Zinc, copper(II), and nickel can be transported by human ZIP4 when the cation concentration is in the micromolar range; nickel can bind to but is not transported by human ZIP4. PMID: 22242765
- The transporter ZIP4 is expressed along the entire gastrointestinal tract and acts as a major processor of dietary zinc PMID: 21462106
- GSPE and EGCG enhance the expression of cellular zinc importers ZIP4 (SLC39A4). PMID: 20471814
- Cell migration assays revealed that RNAi knockdown of Zip4 in Hepa cells depressed in vitro migration whereas forced over-expression in Hepa cells and MCF-7 cells enhanced in vitro migration PMID: 20957146
- Zinc can regulate the mRNA expression of ZIP4 in Caco2 cells. PMID: 16986515
- Overexpression of ZIP4 caused significantly increased expression of NRP-1, VEGF, MMP-2 and MMP-9 and is associated with angiogenesis, invasion and metastasis pathways in pancreatic cancer. PMID: 20023433
- ZIP4 overexpression causes increased IL-6 transcription through CREB, which in turn activates STAT3 and leads to increased cyclin D1 expression PMID: 20160059
- A novel member of a zinc transporter family, hZIP4, is defective in acrodermatitis enteropathica. PMID: 12032886
- SLC39A4 is centrally involved in the pathogenesis of acrodermatitis enteropathica. PMID: 12068297
- Three novel mutations, 1017ins53, which creates premature termination codon, and two mis-sense mutations, R95C and Q303H. PMID: 12787121
- temporal and spatial patterns of expression of the mouse ZIP1, 3, 4, and 5 genes in the developing intestine and the effects of maternal dietary zinc deficiency on these patterns of expression were examined PMID: 16682017
- ubiquitin-mediated degradation of the ZIP4 protein is critical for regulating zinc homeostasis in response to the upper tier of physiological zinc concentrations. PMID: 17202136
- therapeutic strategy whereby ZIP4 is targeted to control pancreatic cancer growth PMID: 18003899
- Acrodermatitis enteropathica is a rare autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in SLC39A4, which encodes the tissue-specific zinc transporter ZIP4. PMID: 18328205
- the clinical manifestations in three acrodermatitis enteropathica patients with a novel mutation PMID: 19416242
- results suggest that exon 9 in the SLC39A4 gene encompassing c.1438G should be screened first in the molecular diagnosis of Japanese patients with Acrodermatitis Enteropathic. PMID: 19416256
- Knocking down ZIP4 by short hairpin RNA might be a novel treatment strategy for pancreatic cancers with ZIP4 overexpression. PMID: 19755388
顯示更多
收起更多
-
相關(guān)疾病:Acrodermatitis enteropathica, zinc-deficiency type (AEZ)
-
亞細(xì)胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Recycling endosome membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Note=Colocalized with TFRC in the recycling endosomes. Cycles between endosomal compartments and the plasma membrane in response to zinc availability.
-
蛋白家族:ZIP transporter (TC 2.A.5) family
-
組織特異性:Highly expressed in kidney, small intestine, stomach, colon, jejunum and duodenum.
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-
-