Phospho-VAV1 (Y174) Antibody
-
中文名稱:磷酸化-VAV1 (Y174)兔多克隆抗體
-
貨號:CSB-PA060050
-
規(guī)格:¥1090
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:
-
別名:Oncogene vav antibody; p95Vav antibody; Proto-oncogene vav antibody; Protooncogene vav antibody; VAV 1 antibody; VAV 1 oncogene antibody; VAV antibody; Vav proto oncogene antibody; VAV_HUMAN antibody; VAV1 antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反應(yīng)種屬:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Synthesized peptide derived from Human Vav around the phosphorylation site of Y174.
-
免疫原種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
標(biāo)記方式:Non-conjugated
-
抗體亞型:IgG
-
純化方式:The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
-
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Liquid
-
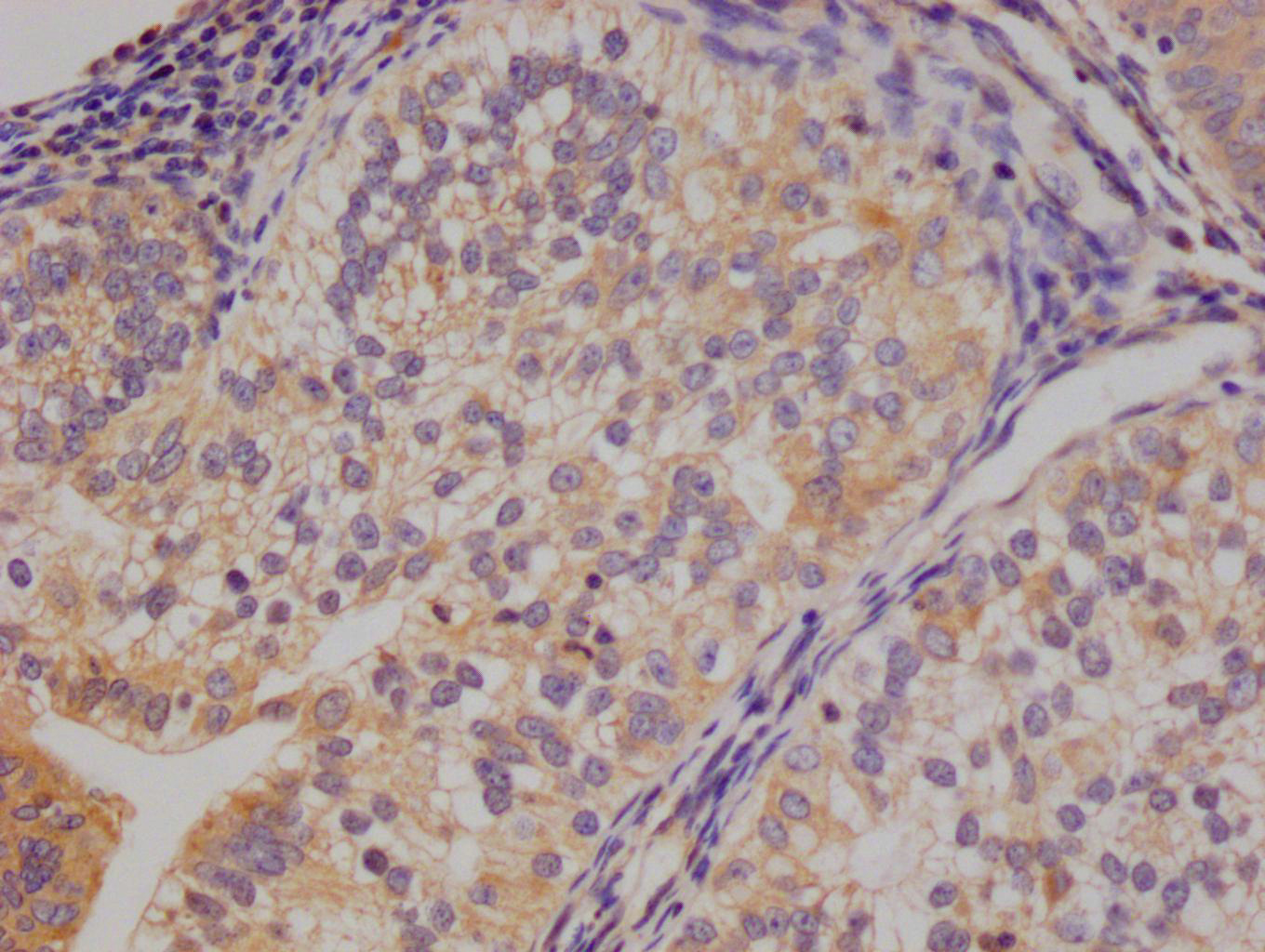
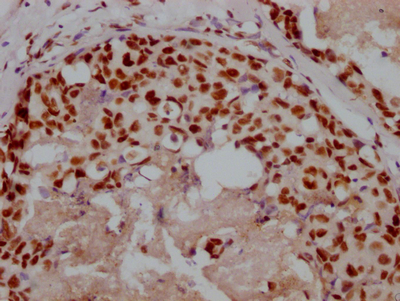
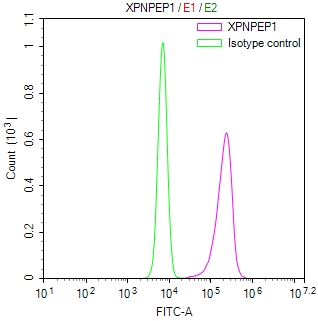
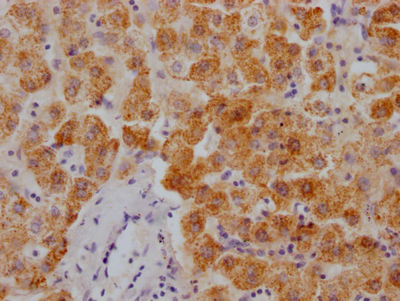
應(yīng)用范圍:WB, IHC, ELISA
-
推薦稀釋比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:2000 IHC 1:100-1:300 ELISA 1:5000 -
Protocols:
-
儲存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
用途:For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
相關(guān)產(chǎn)品
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
功能:Couples tyrosine kinase signals with the activation of the Rho/Rac GTPases, thus leading to cell differentiation and/or proliferation.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- Study identifies the residues on EZH2 that are critical for its interaction with VAV and demonstrate that EZH2 interactions with VAV proteins are crucial for the regulation of adhesion dynamics and cellular transformation. PMID: 28967906
- These results support a driver oncogenic role for VAV1 signaling in the pathogenesis of PTCL. PMID: 28062691
- no significant association of FoxP3 promoter rs3761548 or (GT) n repeat length with presumed immunological graft failure. The genotype frequencies of Vav1 intron polymorphisms did not significantly differ between patients with graft failure and matched controls. PMID: 28470865
- Data show that GEF Vav1 possesses tumor-suppressor functions in immature T cells. PMID: 29136506
- Polymorphisms of VAV1 gene is associated with Rheumatoid arthritis. PMID: 28053322
- Vav1 expression is increased in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, indicates poor prognosis, and can serve as a candidate molecular prognostic marker. PMID: 28336434
- TGFbeta induced the dissociation of DNMT1 from the VAV1 promoter, leading to demethylation and the subsequent ectopic expression of VAV1 in cancer cells via a SMAD4-dependent mechanism PMID: 27893715
- Our results suggest the existence of a Vav1/PU.1/miR-142-3p network that supports all-trans retinoic acid -induced differentiation in acute promyelocytic leukemia -derived cells PMID: 27480083
- revealed a new function for Vav1 in the negative feedback regulation of the phosphorylation of immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs within the zeta chains, CD3 delta, epsilon, gamma chains, as well as activation sites on the critical T cell tyrosine kinases PMID: 26043137
- Data indicate that only a single mutation in the proto-oncogene Vav1 enhances tumorigenicity. PMID: 25426554
- These findings establish VAV1 as a critical epigenetically regulated oncogene with a key role in MBSHH maintenance, and highlight its potential as a validated therapeutic target and prognostic biomarker for the improved therapy of medulloblastoma. PMID: 25531316
- The present study implies that estrogen-estrogen receptor modulates the transcription and expression of Vav1, which may contribute to the proliferation of cancerous cells. PMID: 24905577
- The role of Vav1 in T leukemia survival by selectively triggering Rac2-Akt axis and elevating the expression of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2. PMID: 24880064
- results presented herein suggest a potential cross-talk between cancer cells and the microenvironment controlled by CSF1/Vav1 signaling pathways. PMID: 25313137
- our data provide evidence that Vav1 is the linker molecule that couples CD28 to PIP5Kalpha activation and strongly fit with a potential model in which CD28 regulates PIP2 synthesis and turnover in T lymphocytes. PMID: 25539813
- suggest that Vav1 promotes the matrix-degrading processes underlying tumor cell migration and further, under conditions of ectopic Vav1 expression, that Vav1 is a central regulator and major driver of invasive matrix remodeling by pancreatic tumor cells PMID: 24332539
- VAV1 overexpression in both SKOV3 and human ovarian surface epithelial cells demonstrated that its upregulation of an E-cadherin transcriptional repressor, Snail and Slug, was not confined to ovarian cancer cells PMID: 23856093
- The results highlight for the first time the potential role of Vav1 as an oncogenic stress activator in cancer and the p53 dependence of its pro-apoptotic effect in breast cells. PMID: 23342133
- study provides evidence the large GTPase Dyn2 regulates the small GTPase Rac1 to potentiate invasive migration of pancreatic tumor cells; Dyn2 plays an essential role in regulating Rac1-mediated pancreatic tumor cell migration through modulation of the Rac1 activator Vav1 via a direct interaction PMID: 23537630
- c-Abl tyrosine kinase plays a critical role in beta2 integrin-dependent neutrophil migration by regulating Vav1 activity. PMID: 23325923
- TCR-driven transendothelial migration of human effector memory CD4 T cells involves Vav, Rac, and myosin IIA. PMID: 23420881
- immunohistochemical experiments revealed that VAV1 is not expressed in glioma cells. Instead, VAV1 is found in non-tumoural astrocyte-like cells that are located either peritumouraly or perivascularly PMID: 22864683
- This study highlights the importance of the N-terminal 20 aa of Vav1 for CaM binding, and provides new insights into the distinguished and irreplaceable role of Vav1 in T cell activation and signal transduction. PMID: 23271736
- Suggest Vav1 as an autosomal dominant disease gene associated with common variable immunodeficiency with defective T-cell function. PMID: 23058036
- these results establish LIME as a transmembrane adaptor protein linking TCR stimulation to IS formation and integrin activation through activation of Vav(Vav guanine nucleotide exchange factor) PMID: 22395814
- both T cell activation and the association between SLP-76 and Nck. After T cell receptor stimulation, SLP-76 was phosphorylated, which enabled the binding of Nck. PMID: 22534133
- Substituting Vav1-specific residues into the C1b domain of PKCdelta, we identified five crucial residues (Glu(9), Glu(10), Thr(11), Thr(24), and Tyr(26)) along the rim of the binding cleft that weaken binding potency in a cumulative fashion. PMID: 22351766
- These data identify two regulatory mechanisms for vav1 expression: binding of c-Myb and CpG methylation of 5' regulatory sequences. PMID: 22253833
- results provide the first evidence that, at least in maturation of tumoral myeloid precursors, Vav1 is part of interconnected networks of functionally related proteins ended to regulate different aspects of gene expression PMID: 21856460
- Data reveal a key role for Vav1-dependent T cell antigen receptor signaling in Foxp3 natural T(reg) cell development. PMID: 21948080
- EHD2 associates in the plasma membrane with Vav1, a Nek3-regulated GEF (guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor) for Rho GTPases. PMID: 21756249
- In tumoral promyelocytes, Vav1 is a component of lineage-specific transduction machineries that can be recruited by various differentiating agents. PMID: 21647562
- The integration of activating and inhibitory receptor signaling by regulated phosphorylation of Vav1 in NK cells. PMID: 21632469
- CDC25A, VAV1, TP73, BRCA1 and ZAP70 may be novel markers for predicting the effectiveness of radiotherapy in CRC patients. PMID: 21344162
- Vav1-mediated scaffolding interactions stabilize SLP-76 microclusters and contribute to antigen-dependent T cell responses. PMID: 21386095
- LFA-1-induced stabilization of ARE-containing mRNAs in T cells is dependent on HuR, and occurs through the Vav-1, Rac1/2, MKK3 and p38MAPK signaling cascade PMID: 21206905
- VAV1 protects Jurkat cells from apoptosis by promoting Bcl-2 transcription through its guanine nucleotide exchange factor activity. PMID: 21151158
- Vav-1 expression may be associated with activated B-cell DLBCL origin and higher proliferative activity, and indicate Vav-1 as a potential marker to identify tumours likely to respond to CD40-targeted therapies. PMID: 20155735
- Results define the composition, stoichiometry and specificity of interactions in the SLP-76, Nck and VAV1 complex, which is crucial for regulation of the actin machinery after T-cell activation. PMID: 20562827
- overexpression of a mutated form of Vav1, in which Y745 was replaced with a phenylalanine, significantly reduced the ATRA-induced CD11b expression and essentially abrogated the differentiation-related acquisition of the migratory capability PMID: 20028078
- gene knockdown blocks NK cell cytotoxicity triggered by NKG2D and 2B4 coengagement PMID: 20189481
- These data reveal unexpected negative roles for Vav1 and RasGRF2 in different stages of T-cell lymphoma progression. PMID: 20011522
- Study reports the structure and biophysical and cellular analyses of the five-domain autoinhibitory element of Vav1; the catalytic Dbl homology (DH) domain of Vav1 is controlled by two energetically coupled processes. PMID: 20141838
- IDO suppressed Vav1 mRNA and protein production in T cells. IDO inhibited TCR-activation-induced Vav1 phosphorylation. PMID: 19597340
- signaling is required for T-cell activation partly by inhibiting activation-induced proteolysis of Vav1. PMID: 19880579
- ATRA-induced increase of Vav1 expression and phosphorylation may be involved in recruiting PU.1 to the CD11b promoter and in regulating CD11b expression during the late stages of neutrophil differentiation of APL-derived promyelocytes. PMID: 19747912
- In vitro, Vav is a regulated guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor for Ras PMID: 11716957
- mechanisms by which Vav1 can regulate c-fos serum response element transcriptional activity PMID: 11859076
- Vav exchange factor counteracts Leu3a monoclonal antibody-mediated signals inducing apoptosis and mitochondrial damage in Jurkat T cells by decreasing Bax expression. PMID: 12055221
- Shb links SLP-76 and Vav with the CD3 complex in Jurkat T cells (SLP-76) PMID: 12084069
顯示更多
收起更多
-
組織特異性:Widely expressed in hematopoietic cells but not in other cell types.
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫鏈接: