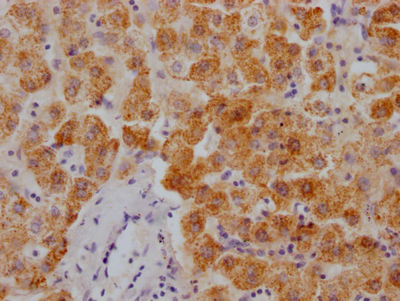
Phospho-KCND2 (S616) Antibody
-
中文名稱:磷酸化-KCND2 (S616)兔多克隆抗體
-
貨號:CSB-PA010505
-
規格:¥1090
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:KCND2
-
別名:KCD2 antibody; KCND 2 antibody; KCND2 antibody; KCND2_HUMAN antibody; KIAA1044 antibody; MGC119702 antibody; MGC119703 antibody; Potassium voltage gated channel Shal related subfamily member 2 antibody; Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily D member 2 antibody; RK 5 antibody; RK5 antibody; Voltage gated potassium channel Kv4.2 antibody; Voltage gated potassium channel subunit Kv4.2 antibody; Voltage sensitive potassium channel antibody; Voltage-gated potassium channel subunit Kv4.2 antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反應種屬:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Synthesized peptide derived from Human Kv4.2 around the phosphorylation site of S616.
-
免疫原種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
標記方式:Non-conjugated
-
抗體亞型:IgG
-
純化方式:The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
-
產品提供形式:Liquid
-
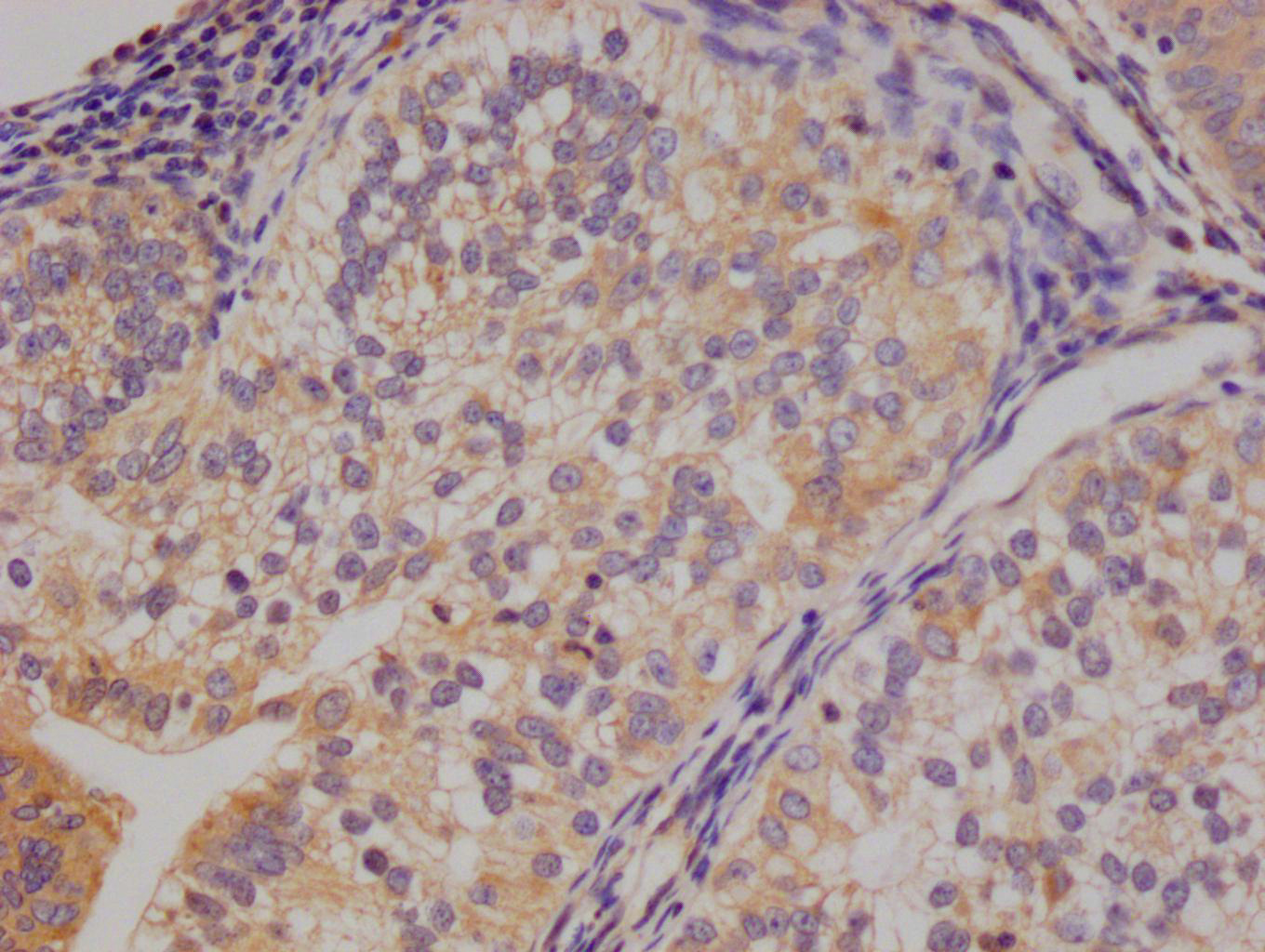
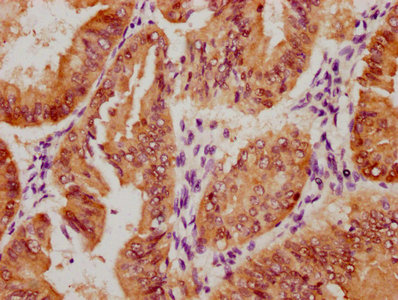
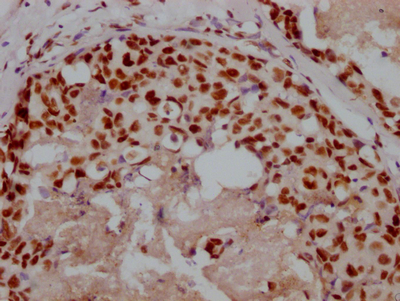
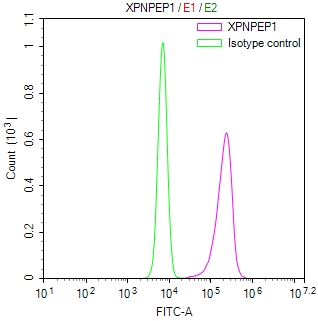
應用范圍:IHC, ELISA
-
推薦稀釋比:
Application Recommended Dilution IHC 1:100-1:300 ELISA 1:5000 -
Protocols:
-
儲存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
用途:For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Voltage-gated potassium channel that mediates transmembrane potassium transport in excitable membranes, primarily in the brain. Mediates the major part of the dendritic A-type current I(SA) in brain neurons. This current is activated at membrane potentials that are below the threshold for action potentials. It regulates neuronal excitability, prolongs the latency before the first spike in a series of action potentials, regulates the frequency of repetitive action potential firing, shortens the duration of action potentials and regulates the back-propagation of action potentials from the neuronal cell body to the dendrites. Contributes to the regulation of the circadian rhythm of action potential firing in suprachiasmatic nucleus neurons, which regulates the circadian rhythm of locomotor activity. Functions downstream of the metabotropic glutamate receptor GRM5 and plays a role in neuronal excitability and in nociception mediated by activation of GRM5. Mediates the transient outward current I(to) in rodent heart left ventricle apex cells, but not in human heart, where this current is mediated by another family member. Forms tetrameric potassium-selective channels through which potassium ions pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. The channel alternates between opened and closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane. Can form functional homotetrameric channels and heterotetrameric channels that contain variable proportions of KCND2 and KCND3; channel properties depend on the type of pore-forming alpha subunits that are part of the channel. In vivo, membranes probably contain a mixture of heteromeric potassium channel complexes. Interaction with specific isoforms of the regulatory subunits KCNIP1, KCNIP2, KCNIP3 or KCNIP4 strongly increases expression at the cell surface and thereby increases channel activity; it modulates the kinetics of channel activation and inactivation, shifts the threshold for channel activation to more negative voltage values, shifts the threshold for inactivation to less negative voltages and accelerates recovery after inactivation. Likewise, interaction with DPP6 or DPP10 promotes expression at the cell membrane and regulates both channel characteristics and activity.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- A mutation, V404M, in the Kv4.2 channel subunit is associated with infant-onset epilepsy and autism. V404M enhances inactivation of channels that have not opened but dramatically impairs inactivation after opening. Authors show that increased side-chain volume is largely responsible for these seemingly paradoxical effects. PMID: 29581270
- Our results do not support the notion that accessory KChIP2 binding is a prerequisite for dendritic trafficking and functional surface expression of Kv4.2 channels, however, accessory KChIP2 binding may play a potential role in Kv4.2 modulation during intrinsic plasticity processes. PMID: 29385176
- Ca(2+)/calcineurin (CaN)/nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) c4 axis is required for neuritin-induced Kv4.2 transcriptional expression and potentiation of IA densities in cerebellum granule neurons. PMID: 27307045
- closed-state inactivation in Kv4.2 channels is a multistep process PMID: 26745419
- The study provides the first piece of evidence for the role of H2S in regulating Ito potassium channels and also the specific motif in an ion channel labile for H2S regulation. PMID: 25756524
- The stoichiometry of the Kv4.2-DPP10 complex was variable depending on the relative expression level of each subunit, with a preference for 4:2 stoichiometry PMID: 26209633
- The findings of this study suggest that variations in KCND2 genes are associated with both mild and severe persistent breast pain after breast cancer surgery. PMID: 25599232
- A rare genetic mutation of the KCND2 gene, p.D612N, was identified in a single patient. Co-expression of mutant and wild-type KCND2 with KChIP2 demonstrated a gain-of-function phenotype. PMID: 25214526
- study identified a de novo variant p.Val404Met in KCND2 in a family with identical twins affected with autism and severe seizures; findings suggest KCND2 is the causal gene for epilepsy in this family and has a role in the etiology of autism PMID: 24501278
- Subunit counting by single-molecule imaging revealed that the bound number of KChIP4 in each Kv4.2.KChIP4 complex was dependent on the expression level of KChIP4. PMID: 24811166
- reflected in the immunoblotting data KV4.2 receptors were detected at higher levels of expression in patient with cortical dysplasia with intractable epilepsy. PMID: 25003238
- KCND2 is expressed in human skin, but has not been associated with aging. PMID: 24037343
- WT PrP(C), in a DPP6-dependent manner, modulated Kv4.2 channel properties, causing an increase in peak amplitude PMID: 24225951
- Our results support the hypothesis that KChIPs enhances Kv4.2 functional expression by a 1 : 1 suppression of the N-terminal FERN domain and by producing additional positive regulatory effects on functional channel expression. PMID: 23692269
- Autoantibodies from patients with encephalitis are specific for DPPX (a subunit of Kv4.2) without reacting to Kv4.2. PMID: 23225603
- Seizures in Kv4.2 transgenic mice rapidly redistribute K+ channel subunit Kv4.2 to the neuronal surface, implicating a molecular substrate for the increased K+ current. PMID: 22122031
- KChIP2 differentially regulates total and cell surface Kv4.2 protein expression and Kv4 current densities. PMID: 20709747
- MiRP3 modulates Kv4.2 current activation, inactivation and recovery from inactivation. MiRP3 shifts the half-maximal voltage for activation and slows time to peak ~ 100%. PMID: 20498229
- PSD-95 increased the amount of Kv1.4, but not Kv4.2, in lipid rafts. PMID: 14559911
- Kv4.2 and K+ channel-interacting protein 2 make up a complex of Ito channels PMID: 14623880
- Data show that KChIP1, KChIP2.1, and KChIP2.2 could form homo- as well as hetero-oligomers, and that this oligomerization did not perturb their interaction with Kv4.2 potassium channel. PMID: 15358149
- mutations in KCND2 and KCND3 are not a frequent cause of long QT syndrome PMID: 15563876
- Data show that the Kv4.2 voltage-dependent potassium channel acts as a fast-responding steroid sensor in human granulosa cells. PMID: 15991246
- Traffic of Kv4.2 is coat protein complex I (COPI)-dependent. PMID: 16260497
- the C-terminal domain of Kv4.2 plays a critical role in voltage-dependent activation and functional expression that is mediated by direct interaction between the Kv4.2 C terminus and KChIP2 PMID: 16820361
- Electrophysiological analysis indicates attenuated K+ current density in cells expressing this Kv4.2-N587fsX1 mutant channel, which is consistent with a model of aberrant neuronal excitability characteristic of TLE. PMID: 16934482
- two Ca2+-dependent posttranslational events regulate the activity of DREAM on Kv4.2 channel function PMID: 17102134
- Our results further suggest distinct mechanisms for Kv4.2 gating modulation by KChIPs and DPPs. PMID: 17981906
- biophysical and biochemical methods indicate that I(SA) channels carry four subunits each of Kv4.2 and DPP6. PMID: 18364354
- rodent and human Abeta are effective in modulating K currents PMID: 18463498
- An ALA-scanning mutagenesis in the S4-S5 linker region, the initial part of S5, and the distal part of S6, in X. laevis oocytes showed that temporary uncoupling at the interface between V sensor and cytoplasmic gate may underlie closed-state inactivation. PMID: 19171772
- SAP97 is a major partner for surface expression and CaMKII-dependent regulation of cardiac Kv4.2 and kv4.3 channels. PMID: 19213956
- the inhibition of maximal amplitude of Kv4.2 channels by arachidonic acid can explain the inhibition of somatodendritic I(A) in hippocampal neurons PMID: 19453640
- This study indicated that Kv4.2 is expressed in both neuronal and glial cells and its regulation may involve potassium channel interacting proteins, alterations in the subcellular localization of the channel. PMID: 19596445
顯示更多
收起更多
-
相關疾病:KNCD2 mutations have been found in a family with autism and epilepsy and may play a role in disease pathogenesis. Autism is a complex multifactorial, pervasive developmental disorder characterized by impairments in reciprocal social interaction and communication, restricted and stereotyped patterns of interests and activities, and the presence of developmental abnormalities by 3 years of age. Epilepsy is characterized by paroxysmal transient disturbances of the electrical activity of the brain that may be manifested as episodic impairment or loss of consciousness, abnormal motor phenomena, psychic or sensory disturbances, or perturbation of the autonomic nervous system.
-
亞細胞定位:Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell projection, dendrite. Cell junction, synapse. Perikaryon. Cell junction, synapse, postsynaptic cell membrane. Cell projection, dendritic spine. Cell junction.
-
蛋白家族:Potassium channel family, D (Shal) (TC 1.A.1.2) subfamily, Kv4.2/KCND2 sub-subfamily
-
組織特異性:Detected in ovary, in corpus luteum and in granulosa and theca cells in the follicle (at protein level). Highly expressed throughout the brain. Detected in amygdala, caudate nucleus, cerebellum, hippocampus, substantia nigra and thalamus. Expression is no
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-
-