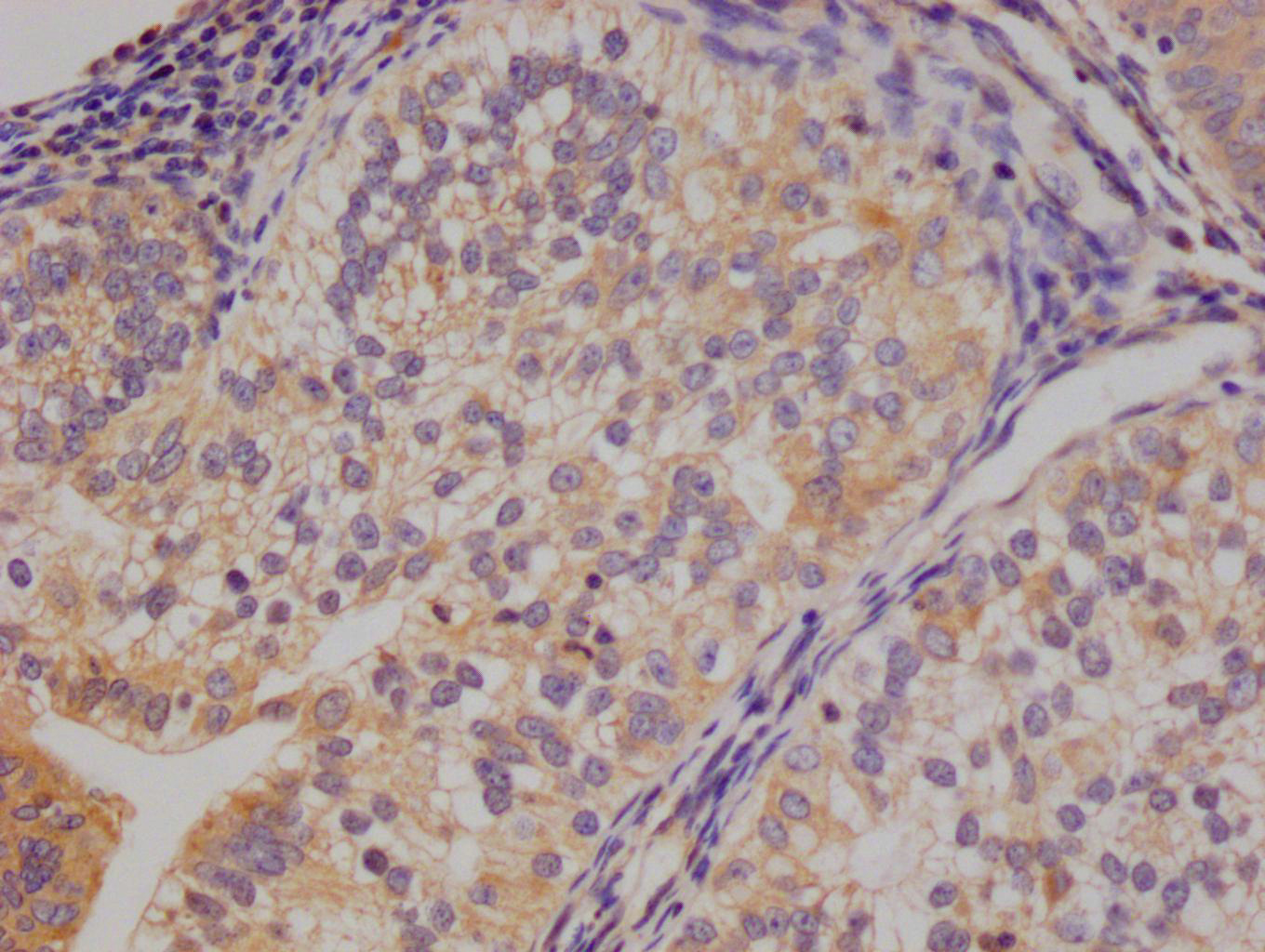
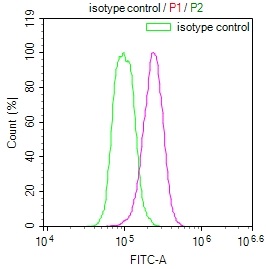
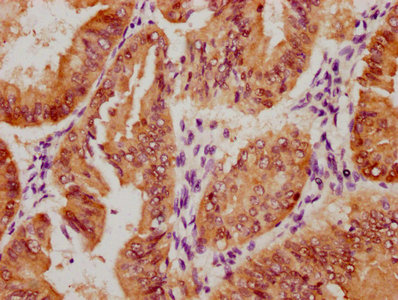
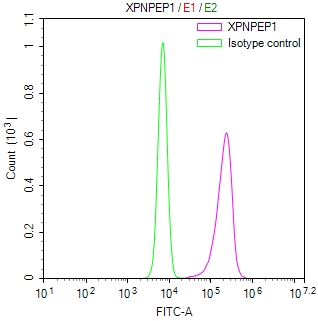
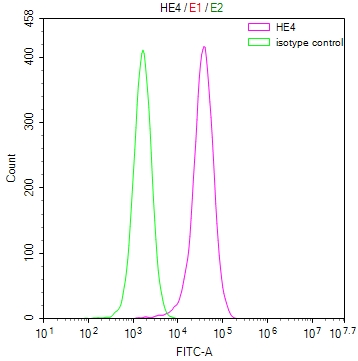
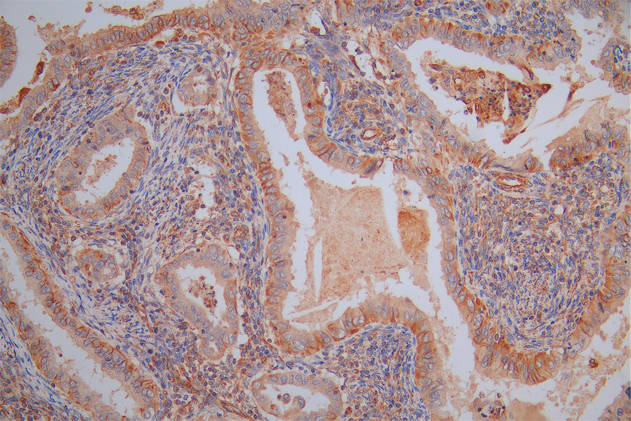
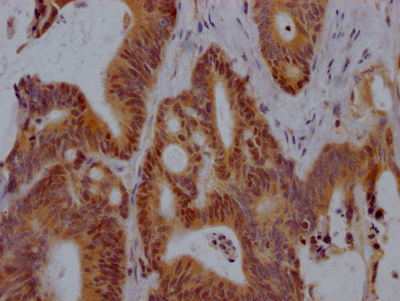
MMACHC Antibody
-
中文名稱:MMACHC兔多克隆抗體
-
貨號:CSB-PA014649GA01HU
-
規格:¥3,900
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:MMACHC
-
別名:1810037K07Rik antibody; BOS_3654 antibody; cblC antibody; DKFZp564I122 antibody; FLJ25671 antibody; Methylmalonic aciduria (cobalamin deficiency) cblC type with homocystinuria antibody; Methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria type C protein antibody; Methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria type C protein homolog antibody; MGC134307 antibody; MMAC_HUMAN antibody; MMACHC antibody; OTTHUMP00000009243 antibody; RP11 291L19.3 antibody; RP23-177C18.3 antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反應種屬:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Human MMACHC
-
免疫原種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
抗體亞型:IgG
-
純化方式:Antigen Affinity purified
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:PBS with 0.02% Sodium Azide, 50% Glycerol, pH 7.3. -20°C, Avoid freeze / thaw cycles.
-
產品提供形式:Liquid
-
應用范圍:ELISA,WB
-
Protocols:
-
儲存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
用途:For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Cobalamin (vitamin B12) cytosolic chaperone that catalyzes the reductive decyanation of cyanocob(III)alamin (cyanocobalamin, CNCbl) to yield cob(II)alamin and cyanide, using FAD or FMN as cofactors and NADPH as cosubstrate. Cyanocobalamin constitutes the inactive form of vitamin B12 introduced from the diet, and is converted into the active cofactors methylcobalamin (MeCbl) involved in methionine biosynthesis, and 5'-deoxyadenosylcobalamin (AdoCbl) involved in the TCA cycle. Forms a complex with the lysosomal transporter ABCD4 and its chaperone LMBRD1, to transport cobalamin across the lysosomal membrane into the cytosol. The processing of cobalamin in the cytosol occurs in a multiprotein complex composed of at least MMACHC, MMADHC, MTRR (methionine synthase reductase) and MTR (methionine synthase) which may contribute to shuttle safely and efficiently cobalamin towards MTR in order to produce methionine. Also acts as a glutathione transferase by catalyzing the dealkylation of the alkylcob(III)alamins MeCbl and AdoCbl, using the thiolate of glutathione for nucleophilic displacement to generate cob(I)alamin and the corresponding glutathione thioether. The conversion of incoming MeCbl or AdoCbl into a common intermediate cob(I)alamin is necessary to meet the cellular needs for both cofactors. Cysteine and homocysteine cannot substitute for glutathione in this reaction.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- The epimutation is present in three generations and results from PRDX1 mutations that force antisense transcription of MMACHC. PMID: 29302025
- Partial CblC-type inherited Methylmalonic acidemia (MMACHC heterozygous mutation exonl: c. 80A >G, c. 609G >A) can onset with severe metabolic Atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. PMID: 29068997
- The crystal structure of ceCblC provides insights into how architectural differences at the alpha- and beta-faces of cobalamin promote the thiol oxidase activity of ceCblC but mute it in wild-type human CblC. PMID: 28442570
- Sequencing of the MMACHC gene is used for confirming the diagnosis of cblC disease. MMACHC mutations were found in all the nine patients. 7 different mutations were identified, including c.609G>A, c.455_457delCCC, c.394C>T, c.445_446insA, c.658_660delAAG, c.452A>G and IVS1+1G>A. The most frequent mutation was c.609G>A (6/9). Two patients had homozygous mutations (c.445_446insA/c.445_446insA and c.609G>A/c.609G>A). PMID: 26563984
- Case Report: c.567dupT,p.(Ile190Tyrfs*13) MMACHC heterozygous mutation underlying methylmalonic academia in infant. PMID: 27383490
- Five different known mutations in either MUT or MMACHC genes were identified in seven of the eight Chinese patients with methyl malonic acidemia. PMID: 25982642
- MMACHC mutation was found in children diagnosed with hemolytic uremic syndrome secondary to cobalamin C disorder. PMID: 26253414
- the MMACHC-MMADHC complex is a 1:1 heterodimer, where the interaction region overlaps with the MMACHC-Cbl binding site PMID: 26483544
- These results indicated that hypergonadotropic hypogonadism may be a novel clinical manifestation of cblC disease, but more reports on additional patients are needed to support this hypothesis. PMID: 26283149
- an adult patient with bull's eye macular lesions and no clinically relevant systemic symptoms was diagnosed with cblC by genetic screening and follow-up biochemical laboratory tests. PMID: 25687216
- A novel mutation p.G155R of the MMACHC gene is identified in prenatal diagnosis of combined methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria. PMID: 26149271
- Results propose a model whereby membrane-bound LMBD1 and ABCD4 facilitate the vectorial delivery of lysosomal vitamin B12 to cytoplasmic MMACHC. PMID: 25535791
- mutation analysis of the MMACHC gene in four patients revealed novel heterozygous mutations at nucleotide 276 (c.276G > A [p.Glu926Glu] and c.276G > T [p.Glu92Asp]), which is located at the end of exon 2. PMID: 24853097
- HCFC1 plays a role in craniofacial development, which is in part mediated through the regulation of MMACHC expression PMID: 25281006
- The gene responsible for cblC, named MMACHC, catalyzes the reductive decyanation of cyanocobalamin. PMID: 24577983
- data suggest that the interaction of methionine synthase with MMACHC may play a role in the regulation of the cellular processing of cobalamins that is required for cobalamin cofactor synthesis PMID: 23825108
- Subcellular location of MMACHC and MMADHC, two human proteins central to intracellular vitamin B(12) metabolism. PMID: 23270877
- The function of MMADHC is exerted through its structured C-terminal domain via interactions with MMACHC. PMID: 22832074
- a structural framework provides a framework for understanding catalytic function and disease mechanism for the multifunctional MMACHC complex. PMID: 22642810
- MMADHC was confirmed as a binding partner for MMACHC both in vitro (SPR) and in vivo (bacterial two-hybrid system). PMID: 21071249
- defects occurring in the MMACHC gene are the major cause of this disease in Chinese patients with combined methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria PMID: 20631720
- MMACHC-wt and MMACHC-R161Q are both very thermolabile proteins in their apo forms, with melting temperatures (T(m)) of 39.3+/-1.0 and 37.1+/-0.7 degrees C, respectively PMID: 20219402
- Mutations in MMACHC are associated with altered cellular oxidative stress and apoptosis processes in the presence or absence of vitamin B(12). PMID: 19760748
- MMACHC with the G147D mutation is unable to bind either cyanocobalamin or hydroxocobalamin, providing a straight forward explanation for the absence of response to either vitamin form. PMID: 19700356
- Diverse and clinically significant structural heart defects appear to be highly prevalent in cblC type methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria. PMID: 19767224
- Data show that the catalytic turnover numbers for the dealkylation of methylcobalamin and 5'-deoxyadenosylcobalamin by MMACHC are 11.7 +/- 0.2 and 0.174 +/- 0.006 h(-1) at 20 degrees C, respectively. PMID: 19801555
- One mutation, 271dupA, in MMACHC accounted for 40% of all disease alleles. PMID: 16311595
- Mutation analysis of the MMACHC gene showed that both patients were homozygous for 394C --> T which suggests a founder effect in Late onset cobalamin C disorder. PMID: 17431913
- c.271dupA (accounting for 55% of the MMACH alleles in our cohort) followed by c.394C>T (16%) and c.331C>T (9%) were the most frequent mutations. PMID: 18164228
- Most patients (eight of nine patients investigated) were compound heterozygotes for the 271dupA mutation and a missense mutation. PMID: 18245139
- MMACHC catalyzes a reductive decyanation reaction that removes the cyanide group in vitamin B(12) or cyanocobalamin PMID: 18779575
- A new mutation (146_154 del CCTTCCTGG) in the MMACHC gene was detected in a Chinese family with methylmalonic aciduria. PMID: 19199254
- Epigenetic inactivation of the MMACHC gene is responsible for methionine dependence in human melanoma cell line MeWo-LC1. PMID: 19200761
- MMACHC was sequenced from the DNA of 118 cblC individuals. Eleven novel mutations were identified.Genotype-phenotype correlations of common mutations were apparent. PMID: 19370762
- These studies suggest that the CblC protein is responsible for early processing of both CNCbl (decyanation) and alkylcobalamins (dealkylation) in mammalian cells. PMID: 19447654
顯示更多
收起更多
-
相關疾病:Methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria type cblC (MMAHCC)
-
亞細胞定位:Cytoplasm, cytosol.
-
蛋白家族:MMACHC family
-
組織特異性:Widely expressed. Expressed at higher level in fetal liver. Also expressed in spleen, lymph node, thymus and bone marrow. Weakly or not expressed in peripheral blood leukocytes.
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-