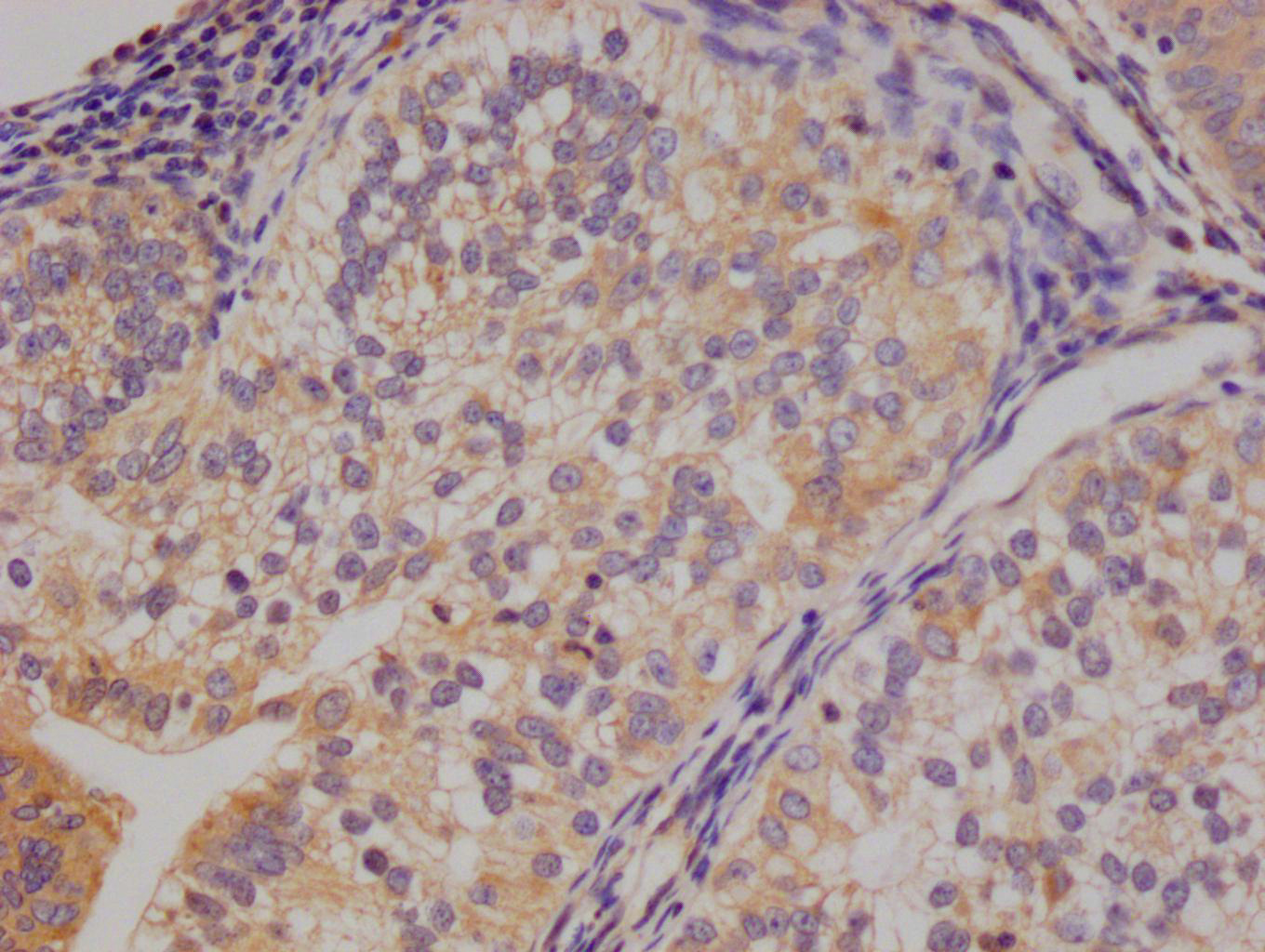
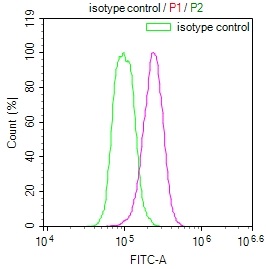
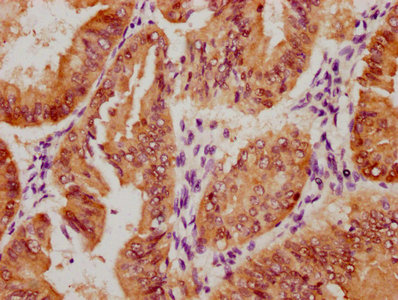
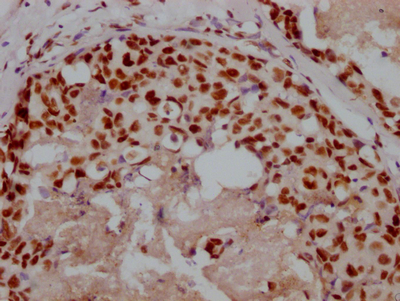
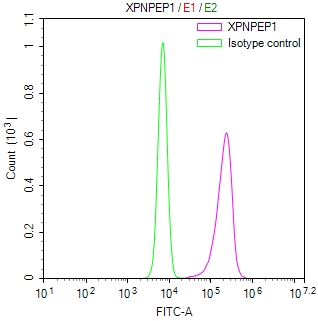
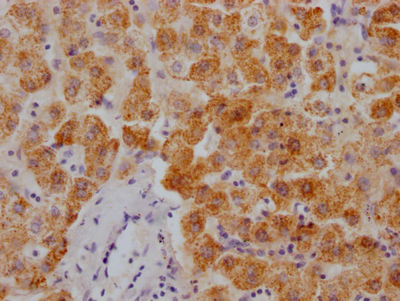
KLRD1 Antibody, FITC conjugated
-
中文名稱:KLRD1兔多克隆抗體, FITC偶聯(lián)
-
貨號(hào):CSB-PA615672LC01HU
-
規(guī)格:¥880
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
產(chǎn)品名稱:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) KLRD1 Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:
-
別名:CD 94 antibody; CD94 antibody; CD94 antigen antibody; Killer cell lectin like receptor subfamily D member 1 antibody; Killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily D member 1 antibody; KLRD 1 antibody; KLRD1 antibody; KLRD1 protein antibody; KLRD1_HUMAN antibody; KP 43 antibody; KP43 antibody; Natural killer cells antigen CD94 antibody; NK cell receptor antibody; OTTHUMP00000238754 antibody; OTTHUMP00000238755 antibody; OTTHUMP00000238756 antibody; OTTHUMP00000238758 antibody; OTTHUMP00000239093 antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反應(yīng)種屬:Human
-
免疫原:Recombinant Human Natural killer cells antigen CD94 protein (42-168AA)
-
免疫原種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
標(biāo)記方式:FITC
-
克隆類型:Polyclonal
-
抗體亞型:IgG
-
純化方式:>95%, Protein G purified
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300
Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4 -
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Liquid
-
儲(chǔ)存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
用途:For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
相關(guān)產(chǎn)品
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
功能:Immune receptor involved in self-nonself discrimination. In complex with KLRC1 or KLRC2 on cytotoxic and regulatory lymphocyte subsets, recognizes non-classical major histocompatibility (MHC) class Ib molecule HLA-E loaded with self-peptides derived from the signal sequence of classical MHC class Ia and non-classical MHC class Ib molecules. Enables cytotoxic cells to monitor the expression of MHC class I molecules in healthy cells and to tolerate self. Primarily functions as a ligand binding subunit as it lacks the capacity to signal.; KLRD1-KLRC1 acts as an immune inhibitory receptor. Key inhibitory receptor on natural killer (NK) cells that regulates their activation and effector functions. Dominantly counteracts T cell receptor signaling on a subset of memory/effector CD8-positive T cells as part of an antigen-driven response to avoid autoimmunity. On intraepithelial CD8-positive gamma-delta regulatory T cells triggers TGFB1 secretion, which in turn limits the cytotoxic programming of intraepithelial CD8-positive alpha-beta T cells, distinguishing harmless from pathogenic antigens. In HLA-E-rich tumor microenvironment, acts as an immune inhibitory checkpoint and may contribute to progressive loss of effector functions of NK cells and tumor-specific T cells, a state known as cell exhaustion. Upon HLA-E-peptide binding, transmits intracellular signals through KLRC1 immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motifs (ITIMs) by recruiting INPP5D/SHIP-1 and INPPL1/SHIP-2 tyrosine phosphatases to ITIMs, and ultimately opposing signals transmitted by activating receptors through dephosphorylation of proximal signaling molecules.; KLRD1-KLRC2 acts as an immune activating receptor. On cytotoxic lymphocyte subsets recognizes HLA-E loaded with signal sequence-derived peptides from non-classical MHC class Ib HLA-G molecules, likely playing a role in the generation and effector functions of adaptive NK cells and in maternal-fetal tolerance during pregnancy. Regulates the effector functions of terminally differentiated cytotoxic lymphocyte subsets, and in particular may play a role in adaptive NK cell response to viral infection. Upon HLA-E-peptide binding, transmits intracellular signals via the adapter protein TYROBP/DAP12, triggering the phosphorylation of proximal signaling molecules and cell activation.; (Microbial infection) Viruses like human cytomegalovirus have evolved an escape mechanism whereby virus-induced down-regulation of host MHC class I molecules is coupled to the binding of viral peptides to HLA-E, restoring HLA-E expression and inducing HLA-E-dependent NK cell immune tolerance to infected cells. Recognizes HLA-E in complex with human cytomegalovirus UL40-derived peptide (VMAPRTLIL) and inhibits NK cell cytotoxicity.; (Microbial infection) May recognize HLA-E in complex with HIV-1 gag/Capsid protein p24-derived peptide (AISPRTLNA) on infected cells and may inhibit NK cell cytotoxicity, a mechanism that allows HIV-1 to escape immune recognition.; (Microbial infection) Upon SARS-CoV-2 infection, may contribute to functional exhaustion of cytotoxic NK cells and CD8-positive T cells. On NK cells, may recognize HLA-E in complex with SARS-CoV-2 S/Spike protein S1-derived peptide (LQPRTFLL) expressed on the surface of lung epithelial cells, inducing NK cell exhaustion and dampening antiviral immune surveillance.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- an early response by KLRD1-expressing Natural killer cells may control influenza infection. PMID: 29898768
- it is not clear if high expression of CD94 on peripheral blood NK cells is related to abnormal activity of endometrial NK cells. PMID: 24975965
- Synergistic inhibition of natural killer cells by the nonsignaling molecule CD94. PMID: 24082146
- Studies indicate that HLA-E interacts with CD94/NKG2 receptors expressed mainly on the surface of natural killer (NK) cells, thus confining its role to the regulation of NK-cell function. PMID: 22576308
- Loss of CD94 is associated with rheumatoid arthritis. PMID: 22102879
- increased expression on natural killer cells in women with recurrent spontaneous abortion after IVIG therapy PMID: 19811464
- human CD56(bright) NK cells progress through a continuum of differentiation that ends with a CD94(low)CD56(dim) phenotype. PMID: 19897577
- Conservation and variation in human and chimpanzee CD94 genes PMID: 11751968
- A critical role of CD94-dependent MHC-I recognition for the regulation of IFN-gamma production and target lysis was demonstrated. PMID: 12149421
- TCR specificity dictates CD94/NKG2A expression by CTL. PMID: 12387742
- CD94 gene expression is regulated by distal and proximal promoters that transcribe unique initial exons specific to each promoter, resulting in two species of transcripts--the previously described CD94 mRNA and a novel CD94C mRNA. PMID: 14607929
- Aberrant expression of natural killer (NK) receptors CD94/NKG2A may have an impact on the magnitude and direction of dendritic cell activation of T cells under pathological conditions, such as chronic hepatitis C virus infection. PMID: 15528343
- A CD94 alternatively spliced transcript paired with an NKG2B isoform may contribute to the plasticity of the natural killer cell immunological synapse by insuring an adequate inhibitory signal. PMID: 16237464
- Cytolytic activity levels of purified CD94-expressing cells from 7-day cultures with FK506 were much higher than those from 7-day cultures without FK506. PMID: 16378079
- results indicate that the SNPs of the inhibitory receptor CD94/NKG2A and its haplotypes, as well as its ligand HLA-E, are associated with Behcet's disease immune systems PMID: 17767552
- identified molecular characteristics of an aggressive subset of pediatric patients with AML through a prospective evaluation of CD56+ neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) and CD94 expression PMID: 18323797
- Uncommon endocytic and trafficking pathway of the natural killer cell CD94/NKG2A inhibitory receptor is described. PMID: 18363778
- Under the influence of interleukin-12 stimulation, CD94/NKG2A is transiently inducible in natural killer (NK) cells bearing the homologous CD94/NKG2C-activating receptor, providing a potential negative regulatory feedback mechanism. PMID: 19124726
- In this work, the glycan ligands of NKG2D and CD94 for the first time were resolved. PMID: 19303396
- NKG2D and CD94 bind to heparin and sulfate-containing polysaccharides. PMID: 19555665
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細(xì)胞定位:Cell membrane; Single-pass type II membrane protein.
-
組織特異性:Expressed in NK cell subsets (at protein level). Expressed in memory/effector CD8-positive alpha-beta T cell subsets (at protein level). Expressed in melanoma-specific cytotoxic T cell clones (at protein level). Expressed in terminally differentiated cyto
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-