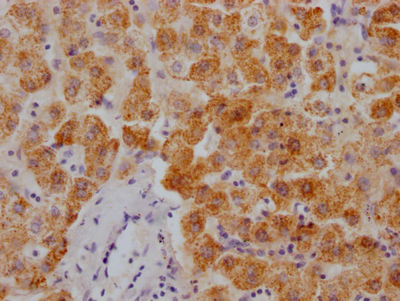
KIAA0319 Antibody, Biotin conjugated
-
中文名稱:KIAA0319兔多克隆抗體, Biotin偶聯
-
貨號:CSB-PA22689D0Rb
-
規格:¥880
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
產品名稱:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) KIAA0319 Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:KIAA0319
-
別名:DLX 2 antibody; DLX2 antibody; DYLX 2 antibody; DYLX2 antibody; Dyslexia susceptibility 2 antibody; Dyslexia-associated protein KIAA0319 antibody; DYX 2 antibody; DYX2 antibody; K0319_HUMAN antibody; Kiaa0319 antibody; MGC176717 antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反應種屬:Human
-
免疫原:Recombinant Human Dyslexia-associated protein KIAA0319 protein (153-268AA)
-
免疫原種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
標記方式:Biotin
-
克隆類型:Polyclonal
-
抗體亞型:IgG
-
純化方式:>95%, Protein G purified
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300
Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4 -
產品提供形式:Liquid
-
應用范圍:ELISA
-
Protocols:
-
儲存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
用途:For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Involved in neuronal migration during development of the cerebral neocortex. May function in a cell autonomous and a non-cell autonomous manner and play a role in appropriate adhesion between migrating neurons and radial glial fibers. May also regulate growth and differentiation of dendrites.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- By suggesting the presence of common biological processes underlying reading (dis)ability, these findings represent initial support for a generalist effect of the non-additive interdependence between READ1 and the KIAA0319 risk haplotype and can help in clinically assessing the individual risk for Developmental dyslexia. PMID: 29066855
- These findings suggest that DNA methylation patterns in the KIAA0319 promoter region might be associated with cognitive control processes that are necessary to perform well in the forced-attention conditions. PMID: 28958754
- The study corroborates the importance of rs2038137-KIAA0319, and rs6935076-KIAA0319 in the aetiology of dyslexia. The relevance of rs2038137-KIAA0319, and rs6935076-KIAA0319 was further supported by the meta-analysis. PMID: 27312598
- a meta-analysis of association studies involving KIAA0319 polymorphisms and Developmental Dyslexia risk, is reported. PMID: 27464509
- Missense variant in DYX2 gene is associated with reading disability. PMID: 28866788
- Two SNPs in the KIAA0319 gene were nominally associated with rapid naming, and these associations were stable across different ages in longitudinal data set from the Dutch Dyslexia Program. PMID: 28074887
- Study establishes KIAA0319 as a novel player in axon growth and regeneration with the ability to repress the intrinsic growth potential of axons; describes a novel regulatory mechanism operating during peripheral nervous system and central nervous system axon growth, and offers novel targets for the development of effective therapies to promote axon regeneration PMID: 28334068
- This study indicated that genetic polymorphisms of KIAA0319 are associated with an increased risk of DD in the Uyghur population. PMID: 27098879
- The KIAA0319 gene is associated with both reading ability and general cognition, but in different ways. The effect on IQ appears to occur earlier in development and is transient, whereas the effect of reading ability occurs later and is moderated by antenatal maternal stress. PMID: 27465261
- Markers in DYX2 genes KIAA0319 and FAM65B were associated with cortical thickness in the left developing orbitofrontal region and global fractional anisotropy, respectively. KIAA0319 and ACOT13 were suggestively associated with overall fractional anisotropy and left pars opercularis cortical thickness, respectively. PMID: 25953057
- These results indicate that KIAA0319L is the fourth of four candidate dyslexia susceptibility genes that is involved in neuronal migration, which supports the association of abnormal neuronal migration with developmental dyslexia. PMID: 23831424
- the association of DCDC2 and KIAA0319 with Developmental dyslexia in Chinese population should be further validated PMID: 25230923
- our findings suggest that KIAA0319 is associated with a reading-related cognitive skill PMID: 25015435
- KIAA0319 and ROBO1 genes, and developmental dyslexia (DD), related neuropsychological phenotypes and comorbid language and mathematical (dis)abilities in a large cohort of 493 Italian nuclear families ascertained through a proband with a diagnosis of DD. PMID: 24430574
- This study demonstrated the association of developmental dyslexia with rs4504469 of KIAA0319 and not with any single-nucleotide polymorphisms of DCDC2. PMID: 23677054
- results suggested that the 931C > T variant in KIAA0319, but not the -3G > A in DYX1C1, was significantly associated with the risk of dyslexia PMID: 23065966
- The results of this study found that KIAA0319 gene contained polymorphisms that were significantly associated with white matter volume in the left temporo-parietal region and that white matter volume influenced reading ability. PMID: 22683091
- Association study of a functional genetic variant in KIAA0319 in German dyslexics. PMID: 21934641
- Mutations in cilia co-expressed DCDC2, DYX1C1 and KIAA0319 genes are associated with a cognitive neurological disorder, dyslexia. PMID: 22558177
- The Kiaa0319 plays a role in neuronal migration during embryonic development, and that early interference with this gene results in an array of behavioral deficits including impairments in rapid auditory processing and simple spatial learning. PMID: 22326444
- The results of this study confirmed that both FOXP2 and KIAA0319/TTRAP/THEM2 genes play an important role in human language development, but probably through different cerebral pathways. PMID: 22262880
- We provide further support for the role of KIAA0319 and DCDC2 in contributing to reading abilities PMID: 21457949
- We identified four rare variants that were significantly associated with the late MMN component. PMID: 21104116
- At this point, there is no statistical evidence of association between the allelic variation in the three candidate genes and DD in our sample. PMID: 21203818
- These results support previous studies indicating the 5' region of the KIAA0319 gene as the location of risk alleles contributing to RD. PMID: 21207242
- KIAA0319 not only has a direct role in neuronal migration but may also have additional signaling functions. PMID: 20943657
- acetylated H3 histones in KIAA0319 have a role in reading disabilities PMID: 19588467
- The results provide additional supportive evidence linking candidate dyslexia susceptibility genes to migrational disturbances during brain development, and extends the role of Kiaa0319 to include growth and differentiation of dendrites. PMID: 19679544
- Strong evidence that KIAA0319 on chromosome 6p is a susceptibility gene for developmental dyslexia. PMID: 15717286
- The risk haplotype on chromosome 6p22.2 down-regulates the KIAA0319 gene which is required for neuronal migration during the formation of the cerebral neocortex. PMID: 16600991
- a multilocus effect in or near KIAA0319 may influence variation in reading ability. PMID: 17597587
- widely expressed in adult brain; alternative splicing variants are detected PMID: 17846832
- results suggest that KIAA0319 could be involved not only in cell-cell interactions, but also in signalling PMID: 18063668
- we found a nominally significant association for the quantitative dimension "word reading" and KIAA0319 genotype PMID: 18810304
- KIAA0319 protein is associated with dyslexia. PMID: 18829873
- identified seven single-nucleotide polymorphisms on the risk haplotype immediately upstream of KIAA0319 and determined that three of these are strongly associated with multiple reading-related traits PMID: 19325871
- The dyslexia-associated protein KIAA0319 interacts with adaptor protein 2 and follows the classical clathrin-mediated endocytosis pathway. PMID: 19419997
顯示更多
收起更多
-
相關疾病:Dyslexia 2 (DYX2)
-
亞細胞定位:Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Early endosome membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein.
-
組織特異性:Detected in adult brain cortex and fetal frontal lobe (at protein level). Highly expressed in brain cortex, putamen, amygdala, hippocampus and cerebellum.
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-