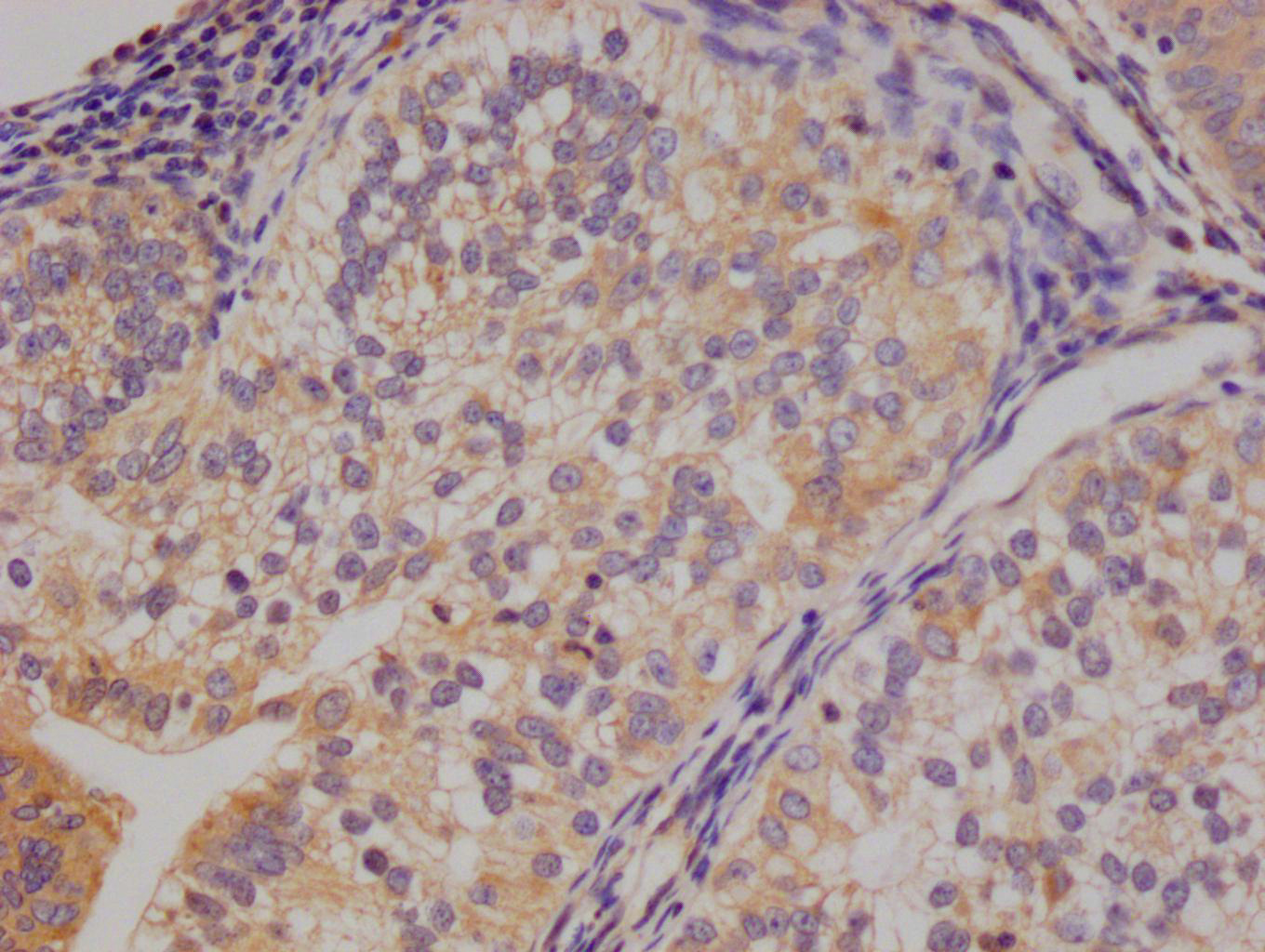
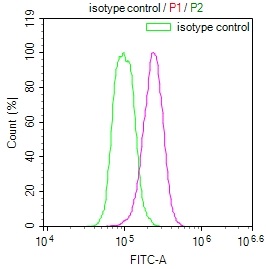
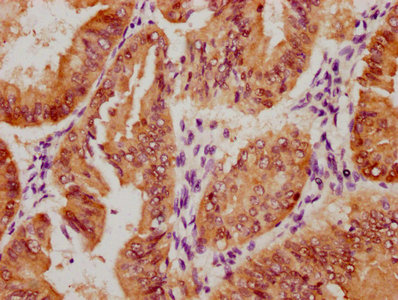
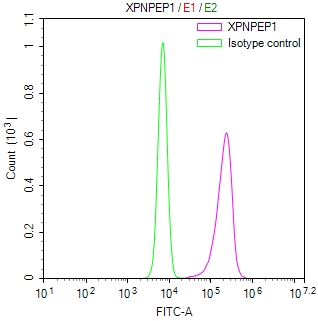
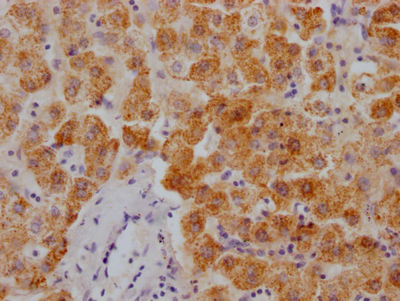
HEPACAM Antibody, HRP conjugated
-
中文名稱:HEPACAM兔多克隆抗體, HRP偶聯
-
貨號:CSB-PA010287LB01HU
-
規格:¥880
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
產品名稱:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) HEPACAM Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:
-
別名:FLJ25530 antibody; GlialCAM antibody; HECAM_HUMAN antibody; HEPACAM antibody; Hepatocyte cell adhesion molecule antibody; Protein hepaCAM antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反應種屬:Human
-
免疫原:Recombinant Human Hepatocyte cell adhesion molecule protein (265-415AA)
-
免疫原種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
標記方式:HRP
-
克隆類型:Polyclonal
-
抗體亞型:IgG
-
純化方式:>95%, Protein G purified
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300
Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4 -
產品提供形式:Liquid
-
應用范圍:ELISA
-
Protocols:
-
儲存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
用途:For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Involved in regulating cell motility and cell-matrix interactions. May inhibit cell growth through suppression of cell proliferation.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- On the whole, this study indicates that HepaCAM potentially represents a therapeutic target and PF3084014 may prove to a promising agent for use in the treatment of refractory prostate cancer. PMID: 29658567
- hepaCAM associates with connexin 43, a main component of gap junctions, and enhances connexin 43 localization to the plasma membrane at cellular junctions. PMID: 27819278
- this study revealed that hepaCAM was downregulated in CRC tissues and cell lines. Overexpression of hepaCAM inhibited CRC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in vitro. Furthermore, the tumorigenesis assay showed that increased expression of hepaCAM suppressed CRC tumor growth and metastasis in vivo. PMID: 28244854
- In a group of Egyptian patients with megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy, novel mutations were identified in HEPACAM. PMID: 27389245
- DNMT1 up-regulation induced by IL-6/STAT3 signaling was indispensable for IL-6-mediated hepaCAM loss in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) cell lines ACHN and 769-P, while DNMT3b up-regulation was crucial for hepaCAM loss in A498. PMID: 28093267
- Out of 20 patients, macrocephaly, classic MRI features, motor development delay and cognitive impairment were detected in 20(100%), 20(100%), 17(85%) and 4(20%) patients, respectively. 20(100%) were clinically diagnosed with MLC. 19(95%) were genetically diagnosed with 10 novel mutations in MLC1, MLC1 and GlialCAM mutations were identified in 15 and 4 patients, respectively PMID: 27322623
- HepaCAM depletion was discovered in bladder cancer tissues compared with adjacent normal tissues, and the decreased level was associated with the degradation of FoxO3. PMID: 28229220
- HepaCAM proteins were significantly decreased in bladder carcinoma. Low hepaCAM was not statistically associated with clinicopathological characteristics of the patients. HepaCAM overexpression activated caspase 3/8/9, downregulated poly-ADP ribose polymerase and p-SMAD2/3, and decreased apoptosis. PMID: 26873485
- The suppressive roles of HEPACAM in NSCLC. PMID: 26392113
- Due to the ability to reactivate expression of hepaCAM and inhibit growth of bladder cancer cells, AZAC may represent an effective treatment for bladder cancer. PMID: 26677113
- The extracellular domain of GlialCAM is necessary for cell junction targeting and for mediating interactions with itself or with MLC1 and ClC-2. PMID: 26033718
- HepaCAM may prevent the translocation of PKCepsilon from cytosolic to particulate fractions, resulting in the inhibition of 786-0 cell proliferation. PMID: 24515280
- GlialCAM is able to interact with all CLC channels tested in this study, targeting them to cell junctions and activating them by stabilizing the open configuration of the common gate PMID: 25185546
- Results allow classifying the effect of HEPACAM gene mutations in different subtypes and authors indicate different cellular mechanisms that lead to megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy pathogenesis. PMID: 25044933
- we demonstrate an evolutionary conserved role for MLC1 in regulating glial surface levels of GLIALCAM, and this interrelationship explains why patients with mutations in either gene (MLC1 or GLIALCAM) share the same clinical phenotype. PMID: 24824219
- High expression of hepaCAM is associated with renal carcinoma. PMID: 24645843
- analysis of mutations in GLIALCAM in patients with megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts [case report] PMID: 24202401
- results suggested that HepaCAM acted as a tumor suppressor in prostate cancer PMID: 24811146
- Re-activation of hepaCAM gene by 5-aza-CdR can inhibit growth of cancer cells and arrest cells at G0/G1 phase PMID: 24324362
- results indicate GlialCAM is necessary for MLC1 protein expression, and its reduction affects the activity of volume-regulated anion currents (VRAC) which may cause astrocyte vacuolation; work extends the role of GlialCAM as a chaperone of MLC1 needed for proper VRAC activation PMID: 23793458
- No clear association between GLIALCAM mutations and an autism-epilepsy phenotype. PMID: 24580998
- Results suggest an important connection between HEPACAM and interferon-gamma, which may inhibit BIU-87 proliferation through HEPACAM re-expression and p21(WAF1) up-regulation to arrest cells at the G(0)/G(1) phase PMID: 22906662
- Research implies that the decrease in c-Myc protein expression, resulting from ectopic expression of hepaCAM, may contribute to the inhibition of proliferation in these cells. PMID: 21618595
- study presents more detailed characterization of the effect of mutations found in MLC1 and GLIALCAM megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts PMID: 21624973
- Dominant HEPACAM mutations can cause either macrocephaly and mental retardation with or without autism or benign familial macrocephaly. PMID: 21419380
- Downregulation of hepaCAM expression plays an important role in the tumorigenesis and development of bladder cancer PMID: 20628239
- There is a close relationship between hepaCAM and VEGF in urothelial carcinoma PMID: 20593288
- The truncation mutant of hepaCAM failed to promote cell-ECM adhesion and migration, and lost the inhibitory effects on cell growth, suggesting a regulatory role of the cleavage in hepaCAM functions. PMID: 20514407
- HepaCAM is involved in cell adhesion and growth control, and its expression is frequently silenced in TCCB. The extracellular domain of hepaCAM is essential to its physiological and biological functions. PMID: 20205955
- Observational study of gene-disease association. (HuGE Navigator) PMID: 20237496
- HEPN1 is frequently silenced in HCC, and exogenous HEPN1 exhibits antiproliferative effect on HepG2 cells, suggesting that silencing of HEPN1 may be associated with carcinogenesis of hepatocytes. PMID: 12971969
- encodes an Ig-like transmembrane glycoprotein and is involved in cell adhesion and growth control PMID: 15885354
- the cytoplasmic domain of hepaCAM is essential to its function on cell-matrix interaction and cell motility PMID: 15917256
- study examined the glycosylation of the GlialCAM (hepaCAM) extracellular domain expressed in HEK and CHO cells PMID: 18082421
- GlialCAM, an immunoglobulin-like cell adhesion molecule is expressed in glial cells of the central nervous system. PMID: 18293412
- the expression of hepaCAM in MCF7 cells not only inhibits cell growth but also induces cellular senescence through the p53/21 pathway PMID: 18845560
- hepaCAM is partially localized in the lipid rafts/caveolae and interacts with Cav-1 through its first immunoglobulin domain. PMID: 19059381
- The data suggest that an intact hepaCAM protein is critical for establishing a stable physical association with the actin cytoskeleton; and such association is important for modulating hepaCAM-mediated cell adhesion and motility. PMID: 19142852
- high expression of hepaCAM significantly accelerated cell adhesion but inhibited cell proliferation and migration; cell differentiation was noticeably less apparent in cells expressing low-level hepaCAM PMID: 19507233
顯示更多
收起更多
-
相關疾病:Leukoencephalopathy, megalencephalic, with subcortical cysts, 2A (MLC2A); Leukoencephalopathy, megalencephalic, with subcortical cysts, 2B (MLC2B)
-
亞細胞定位:Cytoplasm. Membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Note=In MCF-7 breast carcinoma and hepatic Hep 3B2.1-7 and Hep-G2 cell lines, localization of HEPACAM is cell density-dependent. In well spread cells, localized to punctate structures in the perinuclear membrane, cytoplasm, and at cell surface of protusions. In confluent cells, localized predominantly to the cytoplasmic membrane, particularly in areas of cell-cell contacts. Colocalizes with CDH1.
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-