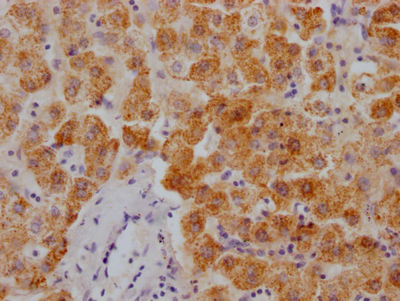
EYA4 Antibody, FITC conjugated
-
中文名稱:EYA4兔多克隆抗體, FITC偶聯(lián)
-
貨號(hào):CSB-PA007909LC01HU
-
規(guī)格:¥880
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
產(chǎn)品名稱:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) EYA4 Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:
-
別名:CMD1J antibody; Deafness, autosomal dominant 10 antibody; DFNA 10 antibody; DFNA10 antibody; dJ78N10.1 (eyes absent (Drosophila) homolog 4) antibody; dJ78N10.1 (eyes absent) antibody; EYA 4 antibody; eya4 antibody; EYA4_HUMAN antibody; Eyes absent 4 antibody; Eyes absent homolog 4 (Drosophila) antibody; Eyes absent homolog 4 antibody; HGNC:3522 antibody; OTTHUMP00000040267 antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反應(yīng)種屬:Human
-
免疫原:Recombinant Human Eyes absent homolog 4 protein (153-224AA)
-
免疫原種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
標(biāo)記方式:FITC
-
克隆類型:Polyclonal
-
抗體亞型:IgG
-
純化方式:>95%, Protein G purified
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300
Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4 -
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Liquid
-
儲(chǔ)存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
用途:For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
相關(guān)產(chǎn)品
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
功能:Tyrosine phosphatase that specifically dephosphorylates 'Tyr-142' of histone H2AX (H2AXY142ph). 'Tyr-142' phosphorylation of histone H2AX plays a central role in DNA repair and acts as a mark that distinguishes between apoptotic and repair responses to genotoxic stress. Promotes efficient DNA repair by dephosphorylating H2AX, promoting the recruitment of DNA repair complexes containing MDC1. Its function as histone phosphatase probably explains its role in transcription regulation during organogenesis. May be involved in development of the eye.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- Overexpression of EYA4 enhanced glioma cell proliferation, and EYA4 suppressed the expression of p27Kip1 directly in these cells. PMID: 30231237
- Although the clinical patient outcome of our 38 Colorectal Cancer patients was not associated with EYA4 promoter hypermethylation, the high frequency of this methylation and its high sensitivity and specificity to neoplastic cells may qualify EYA4 promoter methylation as a potential candidate screening marker in Iranian population and may help to improve early detection of CRC. PMID: 29436791
- Eyes absent homolog 4 (Drosophila) protein (EYA4) is frequently hypermethylated in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and may function as a tumor suppressor gene in the development of ESCC. PMID: 29660222
- identified novel EYA4 mutation can be considered responsible of the hearing loss observed in the proband and her father, while a dual molecular diagnosis was reached in the relatives co-segregating the EYA4 and the PAX3 mutations PMID: 29287889
- EYA4 hypermethylation is associated with colorectal cancer. PMID: 28351398
- EYA4 functions as tumor suppressor gene in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma via repressing beta-catenin/ID2 activation, and was an independent prognostic factor in PDAC. PMID: 27378242
- Low expression of EYA4 is associated with oral cancer. PMID: 27015871
- We discovered two genome-wide significant SNPs. The first was novel and near ISG20. The second was in TRIOBP, a gene previously associated with prelingual nonsyndromic hearing loss. Motivated by our TRIOBP results, we also looked at exons in known hearing loss genes, and identified two additional SNPs, rs2877561 in ILDR1 and rs9493672 in EYA4 (at a significance threshold adjusted for number of SNPs in those regions). PMID: 27764096
- Locus polymorphism of rs3813346 was associated with the risk of developing noise-induced hearing loss in the dominance model, the codominance model and the addictive model. Generalized multiple dimensionality reduction indicated that the combined interaction of the 2 loci-rs3813346 and rs9493627-significantly affected the incidence of noise-induced hearing loss. PMID: 27613755
- Up to now, merely 7 loci have been linked to mid-frequency hearing loss. Only four genetic mid-frequency deafness genes, namely, DFNA10 (EYA4), DFNA8/12 (TECTA), DFNA13 (COL11A2), DFNA44 (CCDC50), have been reported to date. [review] PMID: 27142990
- study identified EYA4 gene as targets for AML1-ETO and indicated it as a novel tumor suppressor gene. In addition, we provided evidence that EYA4 gene might be a novel therapeutic target and a potential candidate for treating AML1-ETO+ t (8;21) AML. PMID: 27231175
- Loss of EYA4 expression is associated with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. PMID: 27469137
- The identification of a novel EYA4 truncation mutation associated with DFNA10, rather than syndromic hearing loss, supports a previously reported genotype-phenotype correlation in this gene. PMID: 26015337
- results implicate Eya4/Six1 regulates normal cardiac function via p27/casein kinase-2alpha/histone deacetylase 2 and indicate that mutations within this transcriptional complex and signaling cascade lead to the development of cardiomyopathy. PMID: 26499333
- In a Dutch family with c.464del EYA4 mutation, hearing impairment begins as a mid-frequency hearing impairment in childhood and develops into a high-frequency, moderate hearing impairment later in life. PMID: 26331839
- Genetic variations in the EYA4, GRHL2 and DFNA5 genes and their interactions with occupational noise exposure may play an important role in the incidence of noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL). PMID: 26400775
- analysis of an EYA4 mutation causing hearing loss in a Chinese DFNA family PMID: 25963406
- A novel missense mutation c.1643C>G (p.T548R) in EYA4 may cause autosomal dominant non-syndromic hearing impairment. PMID: 25809937
- EYA4 mutations are associated with autosomal dominant non-syndromic hearing loss. PMID: 25781927
- Exome Sequencing Identifies a Mutation in EYA4 as a Novel Cause of Autosomal Dominant Non-Syndromic Hearing Loss PMID: 25961296
- EYA4 methylation may be identified in stool samples. PMID: 25620232
- Results provide molecular and clinical information in order to gain improved understanding of the pathogenesis of DFNA10 protein EYA4 mutations and the genotypephenotype correlations of DFNA10 hearing loss. PMID: 25242383
- Autosomal dominant hearing impairment due to a novel EYA4 frameshift mutation:a novel heterozygous frame-shift mutation (c.579_580insTACC, p.(Asp194Tyrfs*52)) in EYA4 was identified that truncates the so-called variable region of the protein. PMID: 25681523
- Low EYA4 expression is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. PMID: 24306662
- Work shows a clear role for EYA4 as a putative tumor suppressor genes in non-small-cell lung cancer. PMID: 24096489
- High methylation of the EYA4 gene is associated with ulcerative colitis with colorectal cancer. PMID: 23867875
- Serum methylation levels of TAC1, SEPT9, and EYA4 were significant discriminants between stage I colorectal cancer and healthy controls. PMID: 23862763
- Observational study and genome-wide association study of gene-disease association, gene-environment interaction, and pharmacogenomic / toxicogenomic. (HuGE Navigator) PMID: 21061259
- Clinical trial of gene-disease association and gene-environment interaction. (HuGE Navigator) PMID: 20379614
- EYA4 and hTERT mRNA expression increased with the severity of esophageal pathological changes and may be useful for identifying high-risk endoscopy candidates or for monitoring changes in premalignant esophageal lesions. PMID: 19939248
- Findings identify a role of EYA4 and possibly interacting SIX and DACH proteins in MPNSTs and suggest the EYA4 pathway as a rational therapeutic target. PMID: 19901965
- Mutation analysis of the EYA4 gene, which maps to 6q22.3, revealed an insertion of 4 bp (1558insTTTG) in affected family members with hereditary hearing impairment PMID: 12477971
- Mutation in the transcriptional coactivator EYA4 causes dilated cardiomyopathy and sensorineural hearing loss PMID: 15735644
- Results show the first definitive cardiac evaluations of DFNA10 hearing loss to support a correlation of EYA4 mutation with/without the of dilated cardiomyopathy, and will facilitate the counseling of patients with these phenotypes and EYA4 mutations. PMID: 17567890
- Study is the first report of a point mutation in EYA4 that is hypothesized to lead to aberrant pre-mRNA splicing and human disease. PMID: 17568404
- Mice lacking the orthologous gene have severe hearing deficits, suggesting that some human otitis media susceptibility reflects underlying genetic predisposition in genes such as this one. PMID: 18219393
顯示更多
收起更多
-
相關(guān)疾病:Deafness, autosomal dominant, 10 (DFNA10); Cardiomyopathy, dilated 1J (CMD1J)
-
亞細(xì)胞定位:Cytoplasm. Nucleus.
-
蛋白家族:HAD-like hydrolase superfamily, EYA family
-
組織特異性:Highly expressed in heart and skeletal muscle.
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-
-