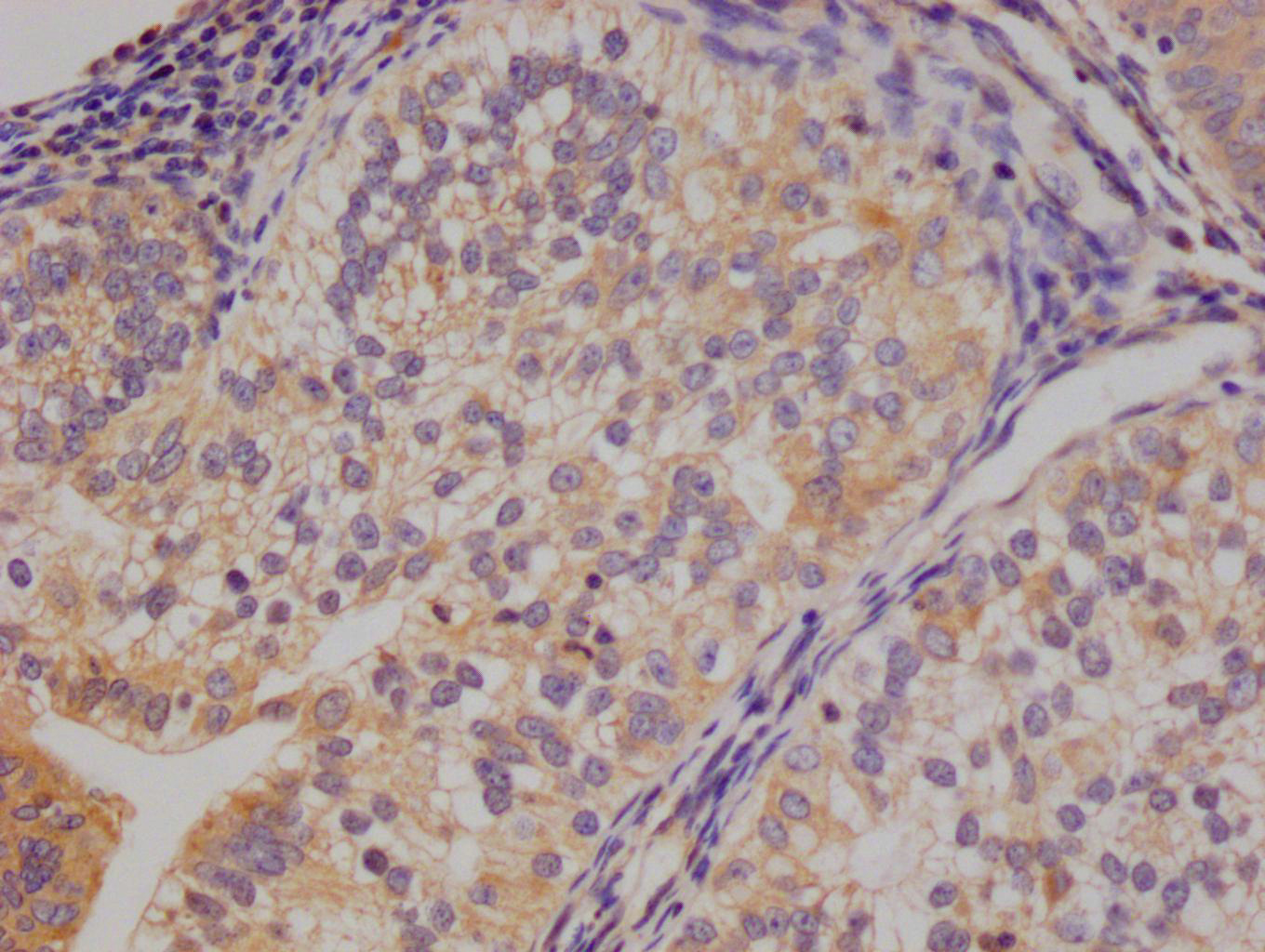
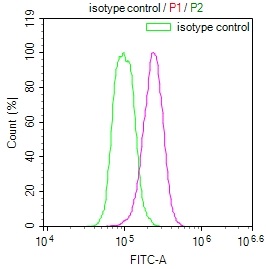
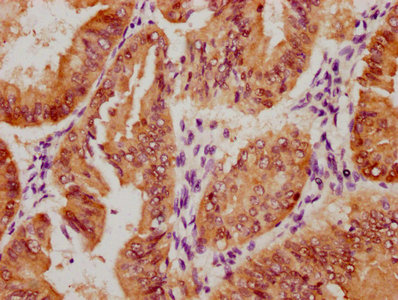
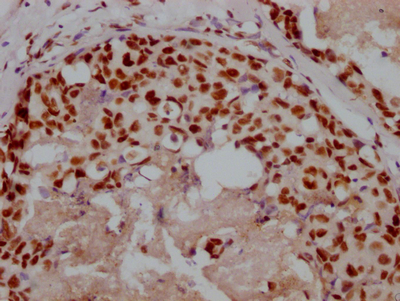
DTL Antibody, HRP conjugated
-
中文名稱:DTL兔多克隆抗體, HRP偶聯
-
貨號:CSB-PA889160LB01HU
-
規格:¥880
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
產品名稱:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) DTL Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:DTL
-
別名:Lethal(2) denticleless protein homolog antibody; CDW1 antibody; DCAF2 antibody; DDB1 and CUL4 associated factor 2 antibody; Ddb1- and Cul4-associated factor 2 antibody; Denticleless homolog antibody; Denticleless homolog (Drosophila) antibody; Denticleless protein homolog antibody; Dtl antibody; DTL_HUMAN antibody; L2DTL antibody; Lethal(2) denticleless protein homolog antibody; RA regulated nuclear matrix associated protein antibody; RAMP antibody; Retinoic acid regulated nuclear matrix associated protein antibody; Retinoic acid-regulated nuclear matrix-associated protein antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反應種屬:Human
-
免疫原:Recombinant Human Denticleless protein homolog protein (393-550AA)
-
免疫原種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
標記方式:HRP
-
克隆類型:Polyclonal
-
抗體亞型:IgG
-
純化方式:>95%, Protein G purified
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300
Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, PH 7.4 -
產品提供形式:Liquid
-
應用范圍:ELISA
-
Protocols:
-
儲存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
用途:For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Substrate-specific adapter of a DCX (DDB1-CUL4-X-box) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase complex required for cell cycle control, DNA damage response and translesion DNA synthesis. The DCX(DTL) complex, also named CRL4(CDT2) complex, mediates the polyubiquitination and subsequent degradation of CDT1, CDKN1A/p21(CIP1), FBH1, KMT5A and SDE2. CDT1 degradation in response to DNA damage is necessary to ensure proper cell cycle regulation of DNA replication. CDKN1A/p21(CIP1) degradation during S phase or following UV irradiation is essential to control replication licensing. KMT5A degradation is also important for a proper regulation of mechanisms such as TGF-beta signaling, cell cycle progression, DNA repair and cell migration. Most substrates require their interaction with PCNA for their polyubiquitination: substrates interact with PCNA via their PIP-box, and those containing the 'K+4' motif in the PIP box, recruit the DCX(DTL) complex, leading to their degradation. In undamaged proliferating cells, the DCX(DTL) complex also promotes the 'Lys-164' monoubiquitination of PCNA, thereby being involved in PCNA-dependent translesion DNA synthesis. The DDB1-CUL4A-DTL E3 ligase complex regulates the circadian clock function by mediating the ubiquitination and degradation of CRY1.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- Results suggest that CDK-mediated phosphorylation of Cdt2 inactivates its ubiquitin ligase activity by reducing its affinity to PCNA, an important strategy for regulating the levels of key proteins in the cell cycle. PMID: 29424068
- Findings suggest that DTL overexpression plays a crucial role in tumor cell proliferation in gastric carcinoma. PMID: 26472028
- CDT2 mediated XPG elimination from DNA damage sites clears the chromatin space needed for repair. PMID: 25483071
- CDT2 likely is a non-oncogene to which transformed cells become addicted because of their enhanced cellular stress, such as replicative stress and DNA damage. PMID: 25115388
- These findings reveal C/EBPalpha regulates G1/S cell cycle arrest in response to DNA damage via the control of CRL4(Cdt2) mediated degradation of p21. PMID: 25483090
- CDK1 activity blocks CRL4CDT2 by preventing chromatin recruitment of the substrate receptor, CDT2. PMID: 25411249
- while interaction with PCNA was important for targeting p21 to the CRL4Cdt2 ligase re-localized to MVM replication centers PMID: 24699724
- CRL4(Cdt2)-dependent degradation of TDG occurs in S phase because of the requirement for TDG to interact with chromatin-loaded PCNA, and this degradation is important for preventing toxicity from excess TDG. PMID: 24962565
- Data shows that phosphorylation of Cdt2 at T464 is important fot its interaction with Cdt2. PMID: 25154416
- TGF-beta signaling promotes exit from the cell cycle and cellular migration through cullin cross-regulation: SCF-FBXO11 turns off CRL4-Cdt2. PMID: 23892434
- ubiquitination of p12 through CRL4(Cdt2) and subsequent degradation form one mechanism by which a cell responds to DNA damage to inhibit fork progression. PMID: 24022480
- Data indicate that depleting ubiquitin E3 ligase CRL4(CDT2/DCAF2) mimicked the pharmacological effects of MLN4924. PMID: 23995842
- Data indicate that CRL4(Cdt2) regulates the degradation of the p12 subunit of Pol delta4. PMID: 23913683
- Non-canonical CRL4A/4B(CDT2) interacts with RAD18 to modulate post replication repair and cell survival. PMID: 23555860
- The functional interaction between FBXO11 and CDT2 is evolutionary conserved from worms to humans and plays an important role in regulating the timing of cell-cycle exit. PMID: 23478441
- Migration of epithelial cells is stimulated by CRL1(FBXO11)-mediated downregulation of Cdt2 and the consequent stabilization of Set8. PMID: 23478445
- ATR, activated after DNA damage, phosphorylates Cdt2 and promotes the rapid degradation of Cdt1 after UV irradiation in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. PMID: 23029527
- CRL4 is a major regulator of CHK1 stability. CRL4CDT2 targets CHK1 for ubiquitination in the nucleoplasm, and for PCNA-independent degradation. CHK1 is required for G2 arrest in CDT2-depleted cells. PMID: 23109433
- The turnover of SET8 is accelerated after ultraviolet irradiation dependent on the CRL4(CDT2) ubiquitin ligase and PCNA. PMID: 21220508
- data identified miR-30a-5p as a tumor-suppressing miRNA in colon cancer cells exerting its function via modulation of DTL expression, which is frequently overexpressed in colorectal cancer PMID: 22287560
- CDT2, a 1q-located candidate gene encoding a protein involved in ubiquitin ligase activity and significantly overexpressed in 1qG Ewing sarcoma, was validated in vitro and in vivo proving its major contribution to this molecular and clinical phenotype PMID: 21822310
- Studies indicate the modular architecture of DDB1-CUL4 in complex with DDB2, CSA and CDT2 in DNA repair of UV-induced DNA lesions. PMID: 21550341
- Studies suggest that DNA damage-induced ubiquitination or sumoylation of PCNA prevents CRL4Cdt2-dependent degradation by inhibiting binding of Cdt1 to PCNA. PMID: 21846465
- N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine (MNNG) triggers MSH2 and Cdt2 protein-dependent degradation of the cell cycle and mismatch repair (MMR) inhibitor protein p21Waf1/Cip1. PMID: 21725088
- Cdt1 degradation following UV irradiation occurs rapidly at damaged sites due to PCNA chromatin loading and the recruitment of Cdt1 and CRL4(Cdt2), before DNA damage repair is completed PMID: 20929861
- Results demonstrate a central role of CRL4(Cdt2)-dependent cell-cycle regulation of Set8 for the maintenance of a stable epigenetic state essential for cell viability. PMID: 20932471
- CRL4(Cdt2)-dependent destruction of Set8 in S phase preserves genome stability by preventing aberrant chromatin compaction during DNA synthesis. PMID: 20932472
- This study identifies CRL4-Cdt2 ubiquitin ligase to promote the ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis of the histone H4 methyltransferase Set8 during S-phase of the cell cycle and after UV-irradiation in a reaction that is dependent on PCNA. PMID: 20932471
- miR-215, through the suppression of DTL expression, induces a decreased cell proliferation leading to an increase in chemoresistance PMID: 20433742
- PCNA, L2DTL and the DDB1-CUL4A complex play critical and differential roles in regulating the protein stability of p53 and MDM2/HDM2 in unstressed and stressed cells. PMID: 16861890
- L2DTL and PCNA interact with CUL4/DDB1 complexes and are involved in CDT1 degradation after DNA damage. PMID: 16861906
- These studies uncover diverse substrate receptors for Cul4 and identify Cdt2 as a conserved component of the Cul4-Ddb1 E3 that is essential to destroy Cdt1 and ensure proper cell cycle regulation of DNA replication. PMID: 16949367
- DTL promotes genomic stability through two distinct mechanisms. First, it is an essential component of the CUL4-DDB1 complex that controls CDT1 levels, thereby preventing rereplication. Second, it is required for the early G2/M checkpoint. PMID: 17085480
- L2DTL encodes a nuclear protein with centrosome targeting in mitosis, and plays important roles in DNA synthesis, cell cycle progression, cytokinesis, proliferation, and differentiation. PMID: 17106265
- roles of DTL/RAMP in growth of breast cancer cells and suggest that DTL/RAMP might be a promising molecular target for treatment of breast cancer. PMID: 18542055
- CDK inhibitor p21 is degraded by a proliferating cell nuclear antigen-coupled Cul4-DDB1Cdt2 pathway during S phase and after UV irradiation PMID: 18703516
- RAMP plays an oncogenic role in gastric carcinogenesis PMID: 19672268
- CDT2/DTL functions as a substrate recognition factor for the Cul4-DDB1-Roc1 E3 ubiquitin ligase to promote PCNA-dependent ubiquitylation and degradation of the CDK inhibitor CDKN1A, both in S-phase of the cell cycle and after UV irradiation. PMID: 18794347
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:Nucleus. Nucleus membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Nucleoplasmic side. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Chromosome. Note=Nuclear matrix-associated protein. Translocates from the interphase nucleus to the metaphase cytoplasm during mitosis.
-
蛋白家族:WD repeat cdt2 family
-
組織特異性:Expressed in placenta and testis, very low expression seen in skeletal muscle. Detected in all hematopoietic tissues examined, with highest expression in thymus and bone marrow. A low level detected in the spleen and lymph node, and barely detectable leve
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-