APOA1 Antibody
-
中文名稱:APOA1兔多克隆抗體
-
貨號:CSB-PA005772
-
規格:¥1090
-
圖片:
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:
-
別名:Apo-AI antibody; ApoA I antibody; ApoA-I antibody; APOA1 antibody; APOA1_HUMAN antibody; Apolipoprotein A-I(1-242) antibody; Apolipoprotein A1 antibody; Apolipoprotein AI antibody; Apolipoprotein of high density lipoprotein antibody; ApolipoproteinAI antibody; Brp14 antibody; high density lipoprotein uptake antibody; Ltw1 antibody; Lvtw1 antibody; MGC117399 antibody; Sep1 antibody; Sep2 antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反應種屬:Human,Mouse
-
免疫原:Synthesized peptide derived from the Internal region of Human ApoA-I.
-
免疫原種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
標記方式:Non-conjugated
-
抗體亞型:IgG
-
純化方式:The antibody was affinity-purified from rabbit antiserum by affinity-chromatography using epitope-specific immunogen.
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:Liquid in PBS containing 50% glycerol, 0.5% BSA and 0.02% sodium azide.
-
產品提供形式:Liquid
-
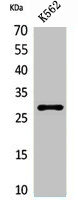
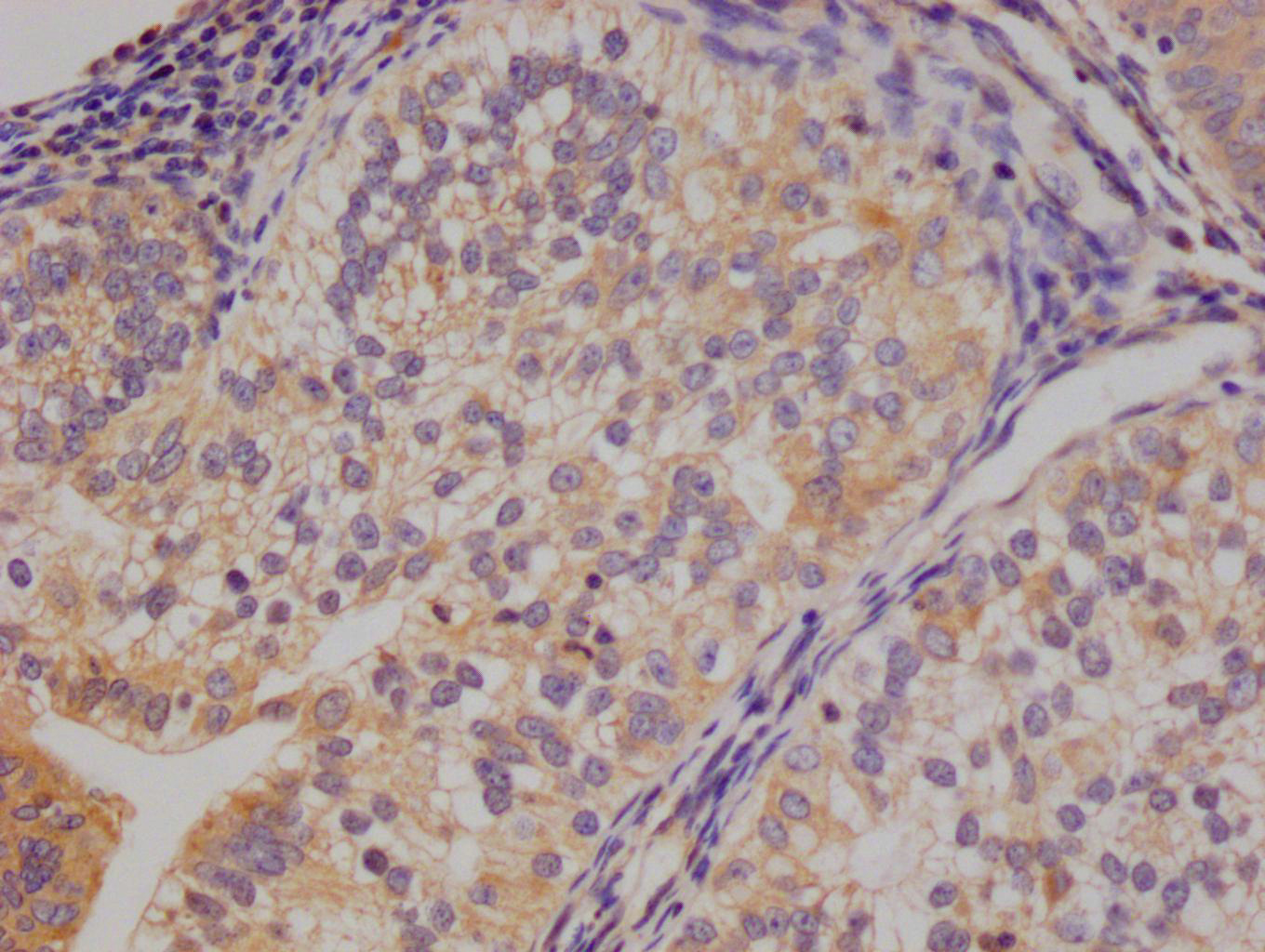
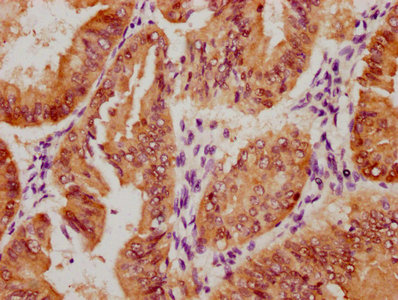
應用范圍:WB, ELISA
-
推薦稀釋比:
Application Recommended Dilution WB 1:500-1:2000 ELISA 1:20000 -
Protocols:
-
儲存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
用途:For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Participates in the reverse transport of cholesterol from tissues to the liver for excretion by promoting cholesterol efflux from tissues and by acting as a cofactor for the lecithin cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT). As part of the SPAP complex, activates spermatozoa motility.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- Plasma apoA-I proteolysis is augmented in aortic valve stenosis and cathepsin S exerts the most deleterious effects on apoA-I integrity in humans. PMID: 29915952
- This study explores how the high-density lipoproteins lipid composition influences amyloid deposition by apoA-I and related proteins. PMID: 27768903
- Site-specific, covalent modifications of apoA-I (lysines or arginines) led to altered protein structure, reduced lipid binding capability and a reduced ability to catalyze cholesterol efflux from macrophages, partly in a modification-specific manner. PMID: 29802959
- assessing the quality of ApoA1 and, in turn, that of HDL in circulating blood can serve as an early diagnostic tool for cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). In this study, we developed monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) specific to modified ApoA1 with its tyrosine residue at the 166th position nitrated to 3-nitrotyrosine PMID: 30132720
- Vitreous levels of APOA1 and RBP4 in human rhegmatogenous retinal detachment associated with choroidal detachment reflects the severity of disease. PMID: 29618920
- The objective of this study was to evaluate whether apolipoprotein gene polymorphisms confer susceptibility to osteonecrosis of the femoral head. PMID: 30119683
- Case Report: recurrence of non-familial hereditary apolipoprotein A-I amyloidosis in Japanese transplant recipient with two novel APOA1 mutations. PMID: 29968409
- TNFalpha differently regulated the levels of PPARalpha, LXRalpha, and LXRbeta binding to the apoA-I gene promoter in THP-1 cells. Obtained results suggest a novel tissue-specific mechanism of the TNFalpha-mediated regulation of apoA-I gene in monocytes and macrophages and show that endogenous ApoA-I might be positively regulated in macrophage during inflammation. PMID: 29442267
- An increased apo B/apo A1 ratio was independently associated with all-cause mortality and cardiovascular events in peritoneal dialysis patients. PMID: 29776362
- he present study reveals that there may be a racial/ethnic- and/or gender-specific association between the APOA1 rs964184 SNP and serum lipid parameters in our study populations PMID: 29747660
- In this study the APOA1 (rs670) gene showed important effects on body weight, adiposity, LDL-cholesterol levels and insulin resistance after 12weeks of the dietary intervention PMID: 29859275
- Residues 26-43 of one APOA1 in the smaller particle form a hinge on the disc edge, which displaces the C-terminal domain of the other APOA1 to the phospholipid surface PMID: 29712830
- H1 receptor signaling is a novel pathway of apo A1 gene expression PMID: 29378195
- genetic polymorphisms of ApoA1 rs5070 A/G may play a role in the susceptibility to large artery atherosclerosis among male diabetic patients. PMID: 28238629
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in APOA1 gene is associated with dyslipidemia. PMID: 29758034
- rs670, rs2854116, and rs662799 single nucleotide polymorphisms of the APOA1-C3-A5 cluster are associated with ischemic stroke in the northern Chinese Han population. PMID: 28635360
- Higher levels of TG, LPO (P<0.0001), nonHDL/HDL and ApoB/ApoA1 (P<0.001, 0.05, respectively), and lower levels of HDL-c, ApoA1, and PON1 (P<0.0001) were observed in T2DM subjects than in controls. PMID: 29626583
- Data suggest that N(epsilon)-(carboxyethyl)lysine (CEL) modification of ApoA1 is up-regulated in serum from patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD); CEL-ApoA1 is a kind of advanced glycation end product; this leads to up-regulation of anti-CEL-ApoA1 IgM in early disease. Both CEL and anti-CEL IgM may serve as AD biomarkers. PMID: 29680706
- The osteonecrosis of the femoral head patients had higher A/A genotype proportions on the apolipoprotein A1 gene 75bp, compared to the control group, while the G/A genotype frequency was lower in the affected patients. This suggests that the G/A mutation on Apo A1 promoter might be one of the predisposing factors for osteonecrosis of the femoral head. PMID: 28770971
- Independent evidence indicated LpAI:A-II has a diameter 20% smaller than LpAI, consistent with a model having two apoA-I and one apoA-II PMID: 27526664
- ApoA1 combined with 9alpha,11ss-PGF2 represents a useful composite biomarker of anaphylaxis, achieving superior diagnostic power over either factor alone. PMID: 28378321
- Low-dose lipid-free apoA-I treatment in atherosclerotic mice preserves and restores collecting lymphatic vessels function by direct and indirect mechanisms. PMID: 28939717
- APOA1 gene may be associated with low HDL-cholesterol disease in the pastoral area of northwest China. PMID: 28969676
- Our results strongly suggest that plasma concentrations of EPA and DHA influence aspirin effects on lipid mediators of CVD event risk where their concentrations are most beneficial when moderate, not high or low. These effects on HDL-C cholesterol and apoA-I exchange are novel. PMID: 29031392
- A multidisciplinary approach, including circular dichroism, dynamic light scattering, spectrofluorometric and atomic force microscopy analyses, monitored the effect of target cells on the conformation and fibrillogenic pathway of the two AApoAI amyloidogenic variants AApoAI(L75P) and AApoAI(L174S). Specific cell milieus selectively affect conformation, aggregation propensity and fibrillogenesis of these variants. PMID: 29174954
- we demonstrated a 21.6% decrease in serum ApoA-I in FA patients compared with non-affected controls PMID: 29447225
- Smaller apolipoprotein(a) isoform size and increased lipoprotein(a) concentration are independent and causal risk factors for coronary heart disease. PMID: 28408323
- In conclusion, decreasing levels of apolipoproteins B and A1 were associated with increased risk of venous thrombosis. PMID: 28540474
- Serum ApoA-I level was negatively correlated with the formation of vocal fold polyps, suggesting ApoA-I may reduce the risk of vocal fold polyps. PMID: 27816355
- data indicate that low apoA1 levels are an independent predictor of the poor clinical outcomes in invasive ductal carcinoma patients. PMID: 28595037
- Data suggest that Apolipoprotein A1 (ApoA-1) might be a promising therapeutic target to reduce recurrence and metastasis for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients after resection. PMID: 27683106
- The generated structures provide evidence for the discoidal, antiparallel arrangement of apoA-I in nascent HDL, and propose two preferred conformations of the flexible N-termini PMID: 28754383
- identified that apolipoprotein-A1 and haptoglobin had significant predictive values for the prediction of recovery at 12 weeks in DILI, enabling the construction of a new prognostic panel, the DILI-ActiTest, which needs to be independently validated PMID: 29287080
- ApoA1 is associated with neurite outgrowth after mechanical injury by mediating polymerisation of actin and restricting inflammatory responses after injury which are deleterious to healing. PMID: 27100352
- A retractable lid in lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase provides a structural mechanism for activation by apolipoprotein A-I PMID: 29030428
- Lower ApoA1 improves the risk prediction of new type 2 diabetes PMID: 28502492
- Following ETC-216 administration to normal human volunteers, an initial dose-dependent HDL-C elevation was observed. Thereafter, subjects transiently acquired a lipoprotein profile similar to that of AIM carriers, including reduced HDL-C and mild hypertriglyceridemia. PMID: 27155060
- The different anti-inflammatory mechanisms of the ApoA-I cysteine mutants might be associated with the regulation of ATF3 level. PMID: 28093456
- Anti-apoA-1 IgG are independent predictors of nonfatal incident coronary artery disease in the general population. The strength of this association is dependent on a functional polymorphism of the CD14 receptor gene, a finding suggesting a gene-autoantibody interaction for the development of CAD. PMID: 29074586
- In vitro proteolysis of the apoA-I-Cy5.5 probe by a variety of proteases including serine, cysteine, and metalloproteases resulted in an up to 11-fold increase in fluorescence, allowing for quantification of apolipoprotein A-I proteolytic degradation. PMID: 28167355
- Using atomic force microscopy, detail the ring-shaped coarse structure, and the three detailed structures of apoA-I directly derived from spherical HDL through NP-40-induced lipid depletion. PMID: 28279834
- These data suggest that high doses of insulin downregulate apoA-I gene expression in HepG2 cells through redistribution of FOXO1/LXRbeta complex, FOXA2, and LXRalpha on hepatic enhancer of apoA-I gene. PMID: 27404023
- Our findings suggest that serum ApoA-I level should be evaluated as a predictor of survival in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma PMID: 27444612
- Inflammatory markers modify the risk of recurrent coronary events associated with apolipoprotein A-I in postinfarction patients PMID: 28391888
- Serum Apo-A1 was significantly lower in term SGA newborns compared to control term newborns. PMID: 28304324
- This study showed that the predictive value of apolipoprotein B/A-I ratio for coronary artery calcification may differ according to kidney function. PMID: 28957410
- Findings suggest that the ABCG1-mediated efflux of cholesterol, but not of 7-ketocholesterol, shows specificity for structural domains of apoA-I bound to reconstituted HDL. Although the mid region alone of apoA-I associated to rHDL can promote ABCG1-mediated cholesterol efflux, deletion of carboxyl-terminal region 185-243 from full-length apoA-I diminishes ABCG1-mediated cholesterol efflux. PMID: 23826352
- Low APOA1 expression is associated with coronary artery disease severity. PMID: 28038449
- Data suggest that activation of SR-BI by APOAI down-regulates sphingosine 1-phosphate/S1PR2-mediated inflammation in vascular endothelial cells by activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway; oxidized-LDL does the opposite. (APOA1 = apolipoprotein A-I; SR-BI/SCARB1 = scavenger receptor class B type I; S1PR2 = sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 2; PI3K = phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; Akt = proto-oncogene c-akt) PMID: 28181168
- The minor alleles of rs662799 (APOA5) and rs5072 (APOA1) modulate TG levels in Mexican children PMID: 27171122
顯示更多
收起更多
-
相關疾病:High density lipoprotein deficiency 2 (HDLD2); High density lipoprotein deficiency 1 (HDLD1); Amyloidosis 8 (AMYL8)
-
亞細胞定位:Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:Apolipoprotein A1/A4/E family
-
組織特異性:Major protein of plasma HDL, also found in chylomicrons. Synthesized in the liver and small intestine. The oxidized form at Met-110 and Met-136 is increased in individuals with increased risk for coronary artery disease, such as in carrier of the eNOSa/b
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-