ABCC6 Antibody
-
中文名稱:ABCC6兔多克隆抗體
-
貨號:CSB-PA001065LA01HU
-
規(guī)格:¥440
-
圖片:
-
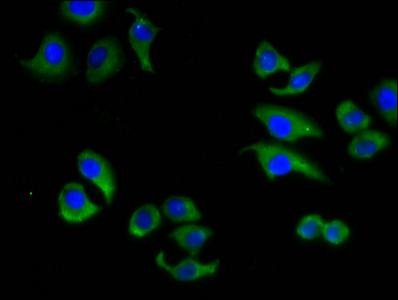
Immunofluorescence staining of A549 cells with CSB-PA001065LA01HU at 1:133, counter-stained with DAPI. The cells were fixed in 4% formaldehyde, permeabilized using 0.2% Triton X-100 and blocked in 10% normal Goat Serum. The cells were then incubated with the antibody overnight at 4°C. The secondary antibody was Alexa Fluor 488-congugated AffiniPure Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L).
-
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
產(chǎn)品名稱:Rabbit anti-Homo sapiens (Human) ABCC6 Polyclonal antibody
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:ABCC6
-
別名:ABC34 antibody; Abcc6 antibody; Anthracycline resistance-associated protein antibody; ARA antibody; ATP binding cassette sub family C (CFTR/MRP) member 6 antibody; ATP binding cassette sub family C member 6 antibody; ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 6 antibody; EST349056 antibody; GACI2 antibody; MLP1 antibody; MOAT E antibody; MOAT-E antibody; MOATE antibody; MRP 6 antibody; MRP6 antibody; MRP6_HUMAN antibody; Multi-specific organic anion transporter E antibody; Multidrug resistance associated protein 6 antibody; Multidrug resistance-associated protein 6 antibody; Multidrug resistance-associated protein 6, URG7 protein antibody; multispecific organic anion transporter E antibody; PXE antibody; PXE1 antibody; URG7 antibody; URG7 protein antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反應種屬:Human
-
免疫原:Recombinant Human Multidrug resistance-associated protein 6 protein (730-931AA)
-
免疫原種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
標記方式:Non-conjugated
本頁面中的產(chǎn)品,ABCC6 Antibody (CSB-PA001065LA01HU),的標記方式是Non-conjugated。對于ABCC6 Antibody,我們還提供其他標記。見下表:
-
克隆類型:Polyclonal
-
抗體亞型:IgG
-
純化方式:>95%, Protein G purified
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300
Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4 -
產(chǎn)品提供形式:Liquid
-
應用范圍:ELISA, IF
-
推薦稀釋比:
Application Recommended Dilution IF 1:50-1:200 -
Protocols:
-
儲存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
用途:For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
相關產(chǎn)品
靶點詳情
-
功能:ATP-dependent transporter of the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) family that actively extrudes physiological compounds, and xenobiotics from cells. Mediates ATP-dependent transport of glutathione conjugates such as leukotriene-c4 (LTC4) and N-ethylmaleimide S-glutathione (NEM-GS) (in vitro), and an anionic cyclopentapeptide endothelin antagonist, BQ-123. Does not appear to actively transport drugs outside the cell. Confers low levels of cellular resistance to etoposide, teniposide, anthracyclines and cisplatin.; Mediates the release of nucleoside triphosphates, predominantly ATP, into the circulation, where it is rapidly converted into AMP and the mineralization inhibitor inorganic pyrophosphate (PPi) by the ecto-enzyme ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase phosphodiesterase 1 (ENPP1), therefore playing a role in PPi homeostasis.; Inhibits TNF-alpha-mediated apoptosis through blocking one or more caspases.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- Serum levels of MRP8/MRP14 and MRP6 were up-regulated in patients with Graves' disease (GD) and Hashimoto's thyroiditis (HT). In addition, mRNA expression of MRP proteins in PBMCs and the thyroid gland was markedly elevated in these patients. PMID: 29656212
- High URG7 reduces the ER stress by decreasing the amount of unfolded proteins, by increasing both the total protein ubiquitination and the AKT activation and reducing Caspase 3 activation. PMID: 29704455
- Two compound heterozygous ABCC6 loss-of-function mutations, c.4182_4182delG (p.Lys1394Asnfs*9) and c.2900G > A (p.Trp967*), were found PMID: 29709427
- Genetic analysis revealed three nonsense, four frame-shift, one exon deletion and 13 missense mutations in 73 Japanese pseudoxanthoma elasticum patients. PMID: 28186352
- in a French cohort with pseudoxanthoma elasticum, study identified 538 mutational events with 142 distinct variants, of which 66 were novel PMID: 28102862
- ABCC6 overexpression may also contribute to nilotinib and dasatinib resistance in vitro. With nilotinib and dasatinib now front line therapy options in the treatment of CML, concomitant administration of ABCC6 inhibitors may present an attractive option to enhance TKI efficacy PMID: 29385210
- Using an integrated pathway-based approach, we identified polymorphisms in ABCC6, ABCB1 and CYP2C8 associated with overall survival. These associations were replicated in a large independent cohort, highlighting the importance of pharmacokinetic genes as prognostic markers in Ewing sarcoma PMID: 27287205
- ABCC6 knockdown HepG2 cells show: 1) intracellular reductive stress; 2) cell cycle arrest in G1 phase; 3) upregulation of p21Cip p53 independent; and 4) downregulation of lamin A/C. the absence of ABCC6 profoundly changes the HepG2 phenotype, suggesting that Pseudoxanthoma elasticum syndrome is a complex metabolic disease that is not exclusively related to the absence of pyrophosphate in the bloodstream. PMID: 28536638
- ABCC6 deficiency can be rescued by 4-phenylbutyrate therapy in a mouse model expressing human variants PMID: 27826008
- Biochemical and cell biological analyses demonstrate these mutations influence multiple steps in the biosynthetic pathway, minimally altering local domain structure but adversely impacting ABCC6 assembly and trafficking. The differential impacts on local and global protein structure are consistent with hierarchical folding and assembly of ABCC6. PMID: 27994049
- The results suggest that a transmembrane domain is not required for transport function and that a cytosolic loop maintains ABCC6 in a targeting-competent state for the basolateral membrane and might be involved in regulating the nucleotide binding domains. PMID: 26942607
- The results of this study showed that mtDNA(atp6) variants were actively involved in schizophrenia in some families with maternal inheritance of this PMID: 26822593
- Pseudoxanthoma elasticum is due to mutation of the ABCC6 gene on chromosome 16. PMID: 26564082
- Membrane insertion and topology of the amino-terminal domain TMD0 of multidrug-resistance associated protein 6 PMID: 26545497
- A direct relationship between reduced ABCC6 levels and the expression of pro-mineralization genes in hepatocytes. PMID: 25169437
- Minimal rescue of the morpholino-induced phenotype was achieved with eight of the nine mutant human ABCC6 mRNAs tested, implying pathogenicity. This study demonstrates that the Chinese PXE population harbors unique ABCC6 mutations. PMID: 25615550
- Virtual screening expands this possibility to explore more compounds that can interact with ABCC6, and may aid in understanding the mechanisms leading to pseudoxanthoma elasticum PMID: 25062064
- The increase in ABCC6 expression accompanied by the induction of cholesterol biosynthesis supposes a functional role for ABCC6 in human lipoprotein and cholesterol homeostasis. PMID: 25064003
- ABCC6 gene is important to determine the genotype of patients diagnosed with pseudoxanthoma elasticum. PMID: 23675997
- Hepatic ABCC6-mediated ATP release is the main source of circulating PPi, revealing an unanticipated role of the liver in systemic PPi homeostasis. PMID: 24969777
- This study describes the URG7 expression in E.coli and a structural study of it by using circular dichroism and fluorescence spectroscopy. PMID: 24555429
- This study showed that the expression of ABCC6 in liver is an important determinant of calcification in cardiac tissues in response to injuries PMID: 24479134
- Case Report:ABCC6 mutations in pseudoxanthoma elasticum families from different ethnic backgrounds. PMID: 23572048
- analysis of pseudoxanthoma elasticum-causing missense mutants of ABCC6, and the correction of their mislocalization by chemical chaperone 4-phenylbutyrate PMID: 24352041
- Our findings provide additional evidence that the ABCC6 gene product inhibits calcification under physiologic conditions and confirm a second locus for generalized arterial calcification of infancy. PMID: 24008425
- ABCC6 prevents ectopic mineralization seen in pseudoxanthoma elasticum by inducing cellular nucleotide release. PMID: 24277820
- nonsense mutations in the ABCC6 gene have a role in pseudoxanthoma elasticum and may be suppressed by PTC124 PMID: 23702584
- The virus-mediated anti-apoptotic effect of URG7 could arise from the C-terminal cytosolic tail binding a pro-apoptotic signaling factor and retaining it to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. PMID: 23912081
- ABCC6 is in the basolateral membrane, mediating the sinusoidal efflux of a metabolite from the hepatocytes to systemic circulation. PMID: 23625951
- Mutations in the underlying disease genes ENPP1, ABCC6, NT5E, and SLC20A2, respectively, lead to arterial media calcification. PMID: 23122642
- The expression pattern of ABCC6P2 in 39 human tissues was highly similar to that of ABCC6 and ABCC6P1 suggesting similar regulatory mechanisms for ABCC6 and its pseudogenes. PMID: 22873774
- We identified three DNase I hypersensitive sites (HSs) specific to cell lines expressing ABCC6. PMID: 22763786
- ABCC6 mutations accounted for a significant subset of generalized arterial calcification of infancy patients, and ENPP1 mutations could also be associated with pseudoxanthoma elasticum lesions in school-aged children. PMID: 22209248
- ABCC6 does not transport adenosine. PMID: 21813308
- The heterozygosity for ABCC6 R1141X did not associate with risk of ischemic heart disease, myocardial infarction, ischemic cerebrovascular disease, or ischemic stroke. PMID: 21831958
- These results show that VK3GS is not the essential metabolite transported by ABCC6 from the liver and preventing the symptoms of pseudoxanthoma elasticum. PMID: 22056557
- The nucleotide-binding domain 2 of the human transporter protein MRP6. PMID: 21748403
- Angioid streaks in pseudoxanthoma elasticum are associated with the p.R1268Q mutation in the ABCC6 gene. PMID: 21179111
- regulatory pathway of ABCC6 expression showing that the ERK1/2-HNF4alpha axis has an important role in regulation of the gene PMID: 20463007
- The R1141X loss-of-function mutation of the ABCC6 gene is a strong genetic risk factor for coronary artery disease. PMID: 19929409
- Nine novel deletion mutations in ABCC6 cause pseudoxanthoma elasticum. PMID: 20075945
- The classic forms of pseudoxanthoma elasticum are due to loss-of-function mutations in the ABCC6 gene, which encodes ABCC6, a transmembrane efflux transporter expressed primarily in the liver PMID: 20032990
- Studies show that individuals homozygous for the c.3775delT mutation in the ABCC6 gene can have a highly variable phenotype. PMID: 19904211
- Loss of ATP-dependent transport activity in pseudoxanthoma elasticum-associated mutants of human ABCC6 (MRP6). PMID: 11880368
- Presence of the R1141X mutation in the ABCC6 gene is associated with a sharply increased risk of premature coronary artery disease PMID: 12176944
- We suggest that the severity of the Pseudoxanthoma elasticum phenotype is not directly correlated with the level of ABCC6/MRP6 activity. PMID: 12673275
- A specific founder effect for the R1141X mutation exists in Dutch patients with PXE (pseudoxanthoma elasticum). PMID: 12714611
- Using linkage analysis and mutation detection techniques, mutations in the ABCC6 gene were recently implicated in the etiology of pseudoxanthoma elasticum. PMID: 12850230
- Asn15, which is located in the extracellular N-terminal region of human ABCC6, is the only N-glycosylation site in this protein. PMID: 12901863
- Twenty-three different mutations were identified, among which 11 were new, in Italian patients with pseudoxanthoma elasticum PMID: 15459974
顯示更多
收起更多
-
相關疾病:Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE); Arterial calcification of infancy, generalized, 2 (GACI2)
-
亞細胞定位:[Isoform 1]: Basolateral cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein.; [Isoform 2]: Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Single-pass membrane protein.
-
蛋白家族:ABC transporter superfamily, ABCC family, Conjugate transporter (TC 3.A.1.208) subfamily
-
組織特異性:Expressed in kidney and liver. Very low expression in other tissues.
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-