-
中文名稱:大鼠神經膠質纖維酸性蛋白(GFAP)酶聯免疫試劑盒
-
貨號:CSB-E08602r
-
規格:96T/48T
-
價格:¥3600/¥2500
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
產品描述:大鼠神經膠質纖維酸性蛋白(GFAP)酶聯免疫試劑盒(CSB-E08602r)為雙抗夾心法ELISA試劑盒,定量檢測血清、血漿、組織勻漿樣本中的GFAP含量。GFAP即膠質纖維酸性蛋白,是星形膠質細胞的中間絲蛋白。其背景在于它在中樞神經系統發育、維持細胞結構等方面起重要作用。研究機制上,常作為星形膠質細胞活化標志物,用于神經系統疾病如腦損傷、神經退行性疾病等的病理研究。試劑盒檢測范圍為78 pg/mL-5000 pg/mL,適用于腦損傷模型評估、神經退行機制研究、膠質細胞活化分析及藥物神經保護效應篩選等科研場景,組織勻漿檢測功能可拓展至腦區特異性 GFAP 表達分析本品僅用于科研,不用于臨床診斷,產品具體參數及操作步驟詳見產品說明書。
-
別名:Gfap ELISA Kit; Glial fibrillary acidic protein ELISA Kit; GFAP ELISA Kit
-
縮寫:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
種屬:Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
樣本類型:serum, plasma, tissue homogenates
-
檢測范圍:78 pg/mL-5000 pg/mL
-
靈敏度:19.5 pg/mL
-
反應時間:1-5h
-
樣本體積:50-100ul
-
檢測波長:450 nm
-
研究領域:Neuroscience
-
測定原理:quantitative
-
測定方法:Sandwich
-
精密度:
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): CV%<8% Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess. Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): CV%<10% Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty assays to assess. -
線性度:
To assess the linearity of the assay, samples were spiked with high concentrations of rat GFAP in various matrices and diluted with the Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay. Sample Serum(n=4) 1:1 Average % 92 Range % 88-98 1:2 Average % 99 Range % 94-109 1:4 Average % 95 Range % 89-98 1:8 Average % 98 Range % 89-104 -
回收率:
The recovery of rat GFAP spiked to levels throughout the range of the assay in various matrices was evaluated. Samples were diluted prior to assay as directed in the Sample Preparation section. Sample Type Average % Recovery Range Serum (n=5) 104 98-108 EDTA plasma (n=4) 98 94-106 -
標準曲線:
These standard curves are provided for demonstration only. A standard curve should be generated for each set of samples assayed. 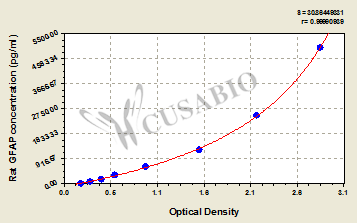
pg/ml OD1 OD2 Average Corrected 5000 2.804 2.925 2.865 2.664 2500 2.123 2.201 2.162 1.961 1250 1.529 1.507 1.518 1.317 625 0.936 0.914 0.925 0.724 312 0.590 0.576 0.583 0.382 156 0.424 0.432 0.428 0.227 78 0.309 0.300 0.305 0.104 0 0.204 0.198 0.201 -
數據處理:
-
貨期:3-5 working days
引用文獻
- The Histone Deacetylase Activator ITSA-1 Improves the Prognosis of Cardiac Arrest Rats by Alleviating Systemic Inflammatory Responses Following Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation C Zhang, H Wei, Q Zhang, H Zhan, Y Lu,Mediators of Inflammation,2025
- Biotin Mitigates Alcohol Withdrawal‐Induced Anxiety and Depression by Regulating Serotonin Metabolism, BDNF, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress in Rats D Hossaini, AK Alipour, M Sajjadi,Neuropsychopharmacology Reports,2025
- D Hossaini, MJ Nazari, KB Ghazanfar, ME Amiri,Addiction Neuroscience,2025
- Magnesium sulfate ameliorates nicotine withdrawal–induced anxiety and depression: implications for regenerative psychiatry M Haidary, MJ Nazari, SMJ Wasiq,Regenerative Medicine Reports,2024
- GABA Administration Ameliorates the Toxicity of Doxorubicin on CSF and the Brain of Albino Rats HM Abdelsalam,Annals of neurosciences,2024
- Establishment of a bio-industry-need hemisection of spinal cord rat model YH Lin,/,2024
- Comparison of the Effects of Botulinum Toxin Doses on Nerve Regeneration in Rats with Experimentally Induced Sciatic Nerve Injury S Hwang,Toxins,2023
- Adrenergic receptors blockade alleviates dexamethasone-induced neurotoxicity in adult male Wistar rats: Distinct effects on β-arrestin2 expression and molecular markers of neural injury RMSM Mohamed,Daru,2023
- Neuroprotective repositioning and anti-tau effect of carvedilol on rotenone induced neurotoxicity in rats: Insights from an insilico& in vivo anti-Parkinson's disease study RE Kamal,European journal of pharmacology,2022
- Neuroprotective Effects of SOX5 against Ischemic Stroke by Regulating VEGF/PI3K/AKT pathway W Zhang,Gene,2020
- Comparing the effects of progressive and mild intensity treadmill running protocols on neuroprotection of parkinsonian rats Mohammadi ZF,Life Sciences,2019
- Erythropoietin in the treatment of carbon monoxide neurotoxicity in rat Moallem SA. et al,Food Chem Toxicol,2015
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:GFAP, a class-III intermediate filament, is a cell-specific marker that, during the development of the central nervous system, distinguishes astrocytes from other glial cells.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- demonstrate increased DNA methylation coupled with decreased histone acetylation at the Gfap promoter leading to suppression of Gfap expression under maternal hypothyroidism PMID: 29852171
- The present study found that social isolation during adolescence resulted in abnormal locomotor, emotional and cognitive behaviors and increased the expression of GFAP, ANXA2 and VIM in PFC of adult rats PMID: 28705472
- GFAP-positive structures were present and exhibited a tendency to become linear on both sides, with an increased density on the left. NFAP-positive expression was present in the left treated limb with a disorganized pattern PMID: 28652433
- We found that GFAP exhibited enhanced stability upon the addition of two equivalents of each ligands with ceftriaxone imparting a more spontaneous interactions and a more ordered complex system than phenytoin PMID: 27133445
- reduction of GFAP+ cell density was in agreement with a lower expression of GFAP protein PMID: 27579183
- Astrocyte expression of GLAST/GFAP was reduced via JAK1/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway after exposure to sevoflurane. PMID: 27003918
- Upon ependymal stem cells differentiation, Cx50 expression favors glial cell fate, since higher expression levels, endogenous or by over-expression of Cx50, augmented the expression of the astrocyte marker GFAP and impaired the neuronal marker Tuj1. PMID: 26561800
- It is likely that a plastic change in GFAP expression in astrocytes selectively occurs around Oxytocin (OXT) neurons at proestrus and facilitates OXT release. PMID: 26994384
- investigated temporal profile of astrocytic and neuronal injury markers after TBI; different mechanisms underlie clearance of UCH-L1 and GFAP in CSF and serum PMID: 25763798
- Its antibody is able to protect cells from oxidative stress, which is due to changed protein expressions of the actin cytoskeleton. PMID: 25837926
- GFAP release in hippocampus is significantly increased in a model of traumatic brain injury. PMID: 25898931
- Hippocampal glucose uptake defects correlate with NeuN immunoreactivity in the latent phase and GFAP immunoreactivity in the chronic phase. PMID: 25798055
- paracrine factors inhibit p38 MAPK and JNK, and most likely by regulating their downstream targets, p53 and STAT1, to promote astrocyte survival associated with GFAP downregulation after ischemic stroke in vitro PMID: 25752945
- The down-regulation of histone deacetylase SIRT1 abrogating the effect of cocoa on glial fibrillary acidic protein up-regulation and on Lys310-RelA/p65 acetylation by silencing or blockage was clearly demonstrated herein in vivo and in vitro. PMID: 25448608
- Data indicate that glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) was up-regulated in satellite glial cells (SGCs) in dorsal root ganglia 14 days after streptozotocin injection. PMID: 25312986
- increased in nucleus ambiguous after recurrent or superior laryngeal nerve injury PMID: 25181319
- Diametric expression of GFAP and a different morphological pattern of caspase-3 labelling, although no changes in the cell number, were observed in the neurons of young and old animals. PMID: 25182537
- Progesterone promotes neuroprotection following traumatic brain injury by inhibiting the expression of Nogo-A and GFAP, and increasing GAP-43 expression. PMID: 24567055
- GFAP expression study also showed that cortical layer I usually contained multiple large astrocytes with branching processes, as well as numerous smaller processes with high intensity of expression. PMID: 25282817
- GFAP repression is mediated through direct binding of p-PPARgamma (S112) to its promoter region. PMID: 24481447
- GFAP is an important marker in determining the severity of traumatic brain injury. PMID: 24379073
- To clarify whether GFAP-positive neoplastic astrocytes exist in rat spontaneous oligodendrogliomas and mixed gliomas or not, immunohistochemical examination was performed on spontaneous oligodendrogliomas (26 cases) and mixed gliomas. PMID: 23076037
- Findings indicate the reciprocal relationships between GFAP expression and astrocyte neurotrophic activity by linking the ERalpha to ERbeta ratio to GFAP expression. PMID: 23515288
- TMJ inflammation induced significant upregulation of GFAP (an astroglial marker) in the trigeminal subnucleus caudalis. PMID: 23110394
- Western blot analysis showed that the chronic stress downregulated GFAP but upregulated NDRG2 protein PMID: 22610521
- In the hippocampus, thalamus, and piriform cortex both vascular laminin and astrocytic GFAP expression are upregulated following kainic acid injection. PMID: 22475395
- Increases in c-fos and GFAP were triggered by the combined stress of non-thermal irradiation and the toxic effect of picrotoxin on cerebral tissues. PMID: 21524663
- There was a reduction in GFAP levels in the hippocampus of non-trained diabetic animals, which was not found in trained diabetic group. PMID: 21892662
- Zuogui Pill may have protective effects on the optic nerve and retina ganglion cells after contusion by promoting nestin and GFAP expressions in Muller cells of the retina. PMID: 21906524
- Activation of a pro-survival IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 cascade contributes to cholera toxin-induced GFAP expression. PMID: 21470923
- Cesarean section might increase GFAP expression in the hippocampus and frontal cortex, and trigger neuronal apoptosis of hippocampus region. PMID: 21211284
- GFAP-positive temporomandibular joint disc cells were characterized by broader processes and existed exclusively in the deeper area. PMID: 21679183
- GFAP expression was down-regulated while GAP-43 expression upregulated in the retinal ganglial cells after peripheral nerve transplantation. PMID: 20423852
- Region-specific alterations in the gene expression of GFAP, VEGF, and FGF-2 and their receptors in the aged brain correspond to changes in astrocytic reactivity, supporting astrocytic heterogeneity and demonstrating a differential aging effect. PMID: 21385309
- GFAP content was diminished after a long-term administration of progesterone in hippocampus. PMID: 21683086
- There is a differential expression pattern of GFAP in the rat brain during pregnancy and the beginning of lactation that is associated with changes in brain function during these reproductive stages. PMID: 20732387
- Data show that astrocyte structural proteins GFAP and vimentin are induced by chronic leptin administration, suggesting astrocytes participating in leptin modulated synaptic inputs. PMID: 21343257
- Butylphthalide may protect the neuron-vascular unit of the hippocampus of Alzheimer model rats by inhibiting the expression of GFAP and increasing the expression of VEGF. PMID: 20197608
- Pax3 negatively regulates GFAP expression during astrocyte differentiation in vitro PMID: 21371476
- these results indicate that intracellular cAMP levels regulate the expression of NPP1 in rat C6 glioma cells by a signalling pathway that is different from the GFAP signal transduction pathway PMID: 21168404
- hyperbaric oxygenation treatment for cerebral infarction, can increase the expression of Map-2 and decrease the expression of GFAP. PMID: 19141977
- Amniotic fluid-GFAP levels appear to correlate with spinal cord injury as gestation proceeds in fetal rats with myelomeningocele. PMID: 21284970
- Retinal injury induces an upregulation of a complement of four intermediate filament proteins, including synemin and nestin, in Muller cells. PMID: 21139996
- Chondroitinase ABC can reduce the expression of GFAP after spinal cord injury. PMID: 21046809
- retinoic acid and cytokines have a synergistic effect on the regulation of glial fibrillary acidic protein expression PMID: 20876578
- There was no significant increase in GFAP immunoreactivity in the white matter in a weight drop model of mild cerebral contusion injury in the rat. PMID: 20479526
- Alcohol could repress the expression of GFAP and S100 of astrocytes. PMID: 16986516
- S100 protein and glial fibrillary acidic protein expression increased significantly in the hippocampal astrocytes of rats with Alzheimer disease, and were inhibited by butylphthalide. PMID: 19726345
- Brain concussion induced the expression of GFAP. PMID: 16850587
- expression of 25-kDa synaptosomal-associated protein and glial fibrillary acidic protein, were significantly enhanced in the cerebellum of rats with treadmill training after cerebral infarct PMID: 19661770
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:Cytoplasm.
-
蛋白家族:Intermediate filament family
-
組織特異性:Expressed in the cortex and hippocampus. Expression decreases following acute and chronic corticosterone treatment.
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Human Transforming Growth factor β1,TGF-β1 ELISA kit
Detect Range: 23.5 pg/ml-1500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 5.8 pg/ml
-
-
-
Mouse Tumor necrosis factor α,TNF-α ELISA Kit
Detect Range: 7.8 pg/ml-500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 1.95 pg/ml
-
-
-
-