-
中文名稱:大鼠α-突觸核蛋白(SNCA)酶聯免疫試劑盒
-
貨號:CSB-EL021912RA
-
規格:96T/48T
-
價格:¥3600/¥2500
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
產品描述:人α-突觸核蛋白(SNCA)酶聯免疫試劑盒(CSB-EL021912RA)為雙抗夾心法ELISA試劑盒,定量檢測血清、血漿、組織勻漿樣本中的SNCA含量。SNCA靶點編碼α - 突觸核蛋白,其基因突變或異常聚集與帕金森病等神經退行性疾病密切相關。研究機制主要圍繞其在神經元中的正常功能、錯誤折疊與聚集過程,以及對神經細胞的毒性作用,旨在為相關疾病的防治提供方向。試劑盒檢測范圍為0.625 ng/mL-40 ng/mL,可廣泛應用于神經退行性疾病模型構建、藥物干預效果評估或蛋白表達調控機制研究等領域,為探索SNCA相關病理生理過程提供可靠工具。本品僅用于科研,不用于臨床診斷,產品具體參數及操作步驟詳見產品說明書。
-
別名:Snca ELISA Kit; Alpha-synuclein ELISA Kit
-
縮寫:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
種屬:Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
-
樣本類型:serum, plasma, tissue homogenates
-
檢測范圍:0.625 ng/mL-40 ng/mL
-
靈敏度:0.156 ng/mL
-
反應時間:1-5h
-
樣本體積:50-100ul
-
檢測波長:450 nm
-
研究領域:Neuroscience
-
測定原理:quantitative
-
測定方法:Sandwich
-
精密度:
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): CV%<8% Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess. Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): CV%<10% Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty assays to assess. -
線性度:
To assess the linearity of the assay, samples were spiked with high concentrations of rat SNCA in various matrices and diluted with the Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay. Sample Serum(n=4) 1:1 Average % 86 Range % 82-90 1:2 Average % 102 Range % 97-105 1:4 Average % 98 Range % 94-101 1:8 Average % 98 Range % 91-102 -
回收率:
The recovery of rat SNCA spiked to levels throughout the range of the assay in various matrices was evaluated. Samples were diluted prior to assay as directed in the Sample Preparation section. Sample Type Average % Recovery Range Serum (n=5) 92 88-95 EDTA plasma (n=4) 94 87-97 -
標準曲線:
These standard curves are provided for demonstration only. A standard curve should be generated for each set of samples assayed. 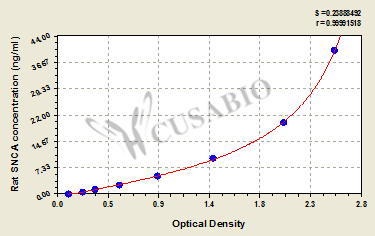
ng/ml OD1 OD2 Average Corrected 40 2.532 2.500 2.516 2.403 20 2.099 2.012 2.056 1.943 10 1.401 1.432 1.417 1.304 5 0.906 0.921 0.914 0.801 2.5 0.566 0.577 0.572 0.459 1.25 0.345 0.358 0.352 0.239 0.625 0.242 0.237 0.240 0.127 0 0.112 0.114 0.113 -
數據處理:
-
貨期:3-5 working days
引用文獻
- Unveiling Lobophytum sp. the neuroprotective potential of Parkinson's disease through multifaceted mechanisms, supported by metabolomic analysis and network pharmacology HT Bakhsh, DH Abu-Baih, RH Abu-Baih, EA Saber,Scientific Reports,2024
- Reactive astrocytes targeting with oral vitamin A: Efficient neuronal regeneration for Parkinson's disease treatment and reversal of associated liver fibrosis NS El‐Mezayen,CNS neuroscience & therapeutics,2023
- Brain Effects of SC-Nanophytosomes on a Rotenone-Induced Rat Model of Parkinson's Disease—A Proof of Concept for a Mitochondria-Targeted Therapy D Mendes,International journal of molecular sciences,2022
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Neuronal protein that plays several roles in synaptic activity such as regulation of synaptic vesicle trafficking and subsequent neurotransmitter release. Participates as a monomer in synaptic vesicle exocytosis by enhancing vesicle priming, fusion and dilation of exocytotic fusion pores. Mechanistically, acts by increasing local Ca(2+) release from microdomains which is essential for the enhancement of ATP-induced exocytosis. Acts also as a molecular chaperone in its multimeric membrane-bound state, assisting in the folding of synaptic fusion components called SNAREs (Soluble NSF Attachment Protein REceptors) at presynaptic plasma membrane in conjunction with cysteine string protein-alpha/DNAJC5. This chaperone activity is important to sustain normal SNARE-complex assembly during aging. Plays also a role in the regulation of the dopamine neurotransmission by associating with the dopamine transporter (DAT1) and thereby modulating its activity.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- Calcium binds to the C terminus of alpha-synuclein, therewith increasing its lipid-binding capacity. Using CEST-NMR, we reveal that alpha-synuclein interacts with isolated synaptic vesicles with two regions, the N terminus, already known from studies on SUVs, and additionally via its C terminus, which is regulated by the binding of calcium. PMID: 29459792
- alphasynuclein induces apoptosis of astrocytes by causing dysfunction of the endoplasmic reticulumGolgi compartment. PMID: 29749529
- induces the clustering of synaptic vesicles by double-anchor mechanism PMID: 27640673
- The results suggest that Zn caused Ubiquitin proteasome system impairment, resulting in alpha-synuclein aggregation subsequently leading to dopaminergic neurodegeneration, and that Zn-induced Parkinsonism exhibited positive L-Dopa response similar to sporadic PD. PMID: 29198021
- FKBP12 contributes to alpha-synuclein toxicity by regulating the calcineurin-dependent phosphoproteome. PMID: 29229832
- Exposure to the Functional Bacterial Amyloid Protein Curli Enhances Alpha-Synuclein Aggregation in Aged Fischer 344 Rats and Caenorhabditis elegans PMID: 27708338
- E46K alpha-synuclein pathological mutation causes cell-autonomous toxicity without altering protein turnover or aggregation. PMID: 28900007
- These findings provide evidence for a novel mechanism underlying the protective effects of PINK1 against alpha-syn-induced neurodegeneration and highlight a novel therapeutic target for Parkinson's disease treatment. PMID: 28933786
- Using single-molecule microscopy and photo-bleaching approaches, the authors most frequently found 70 alpha-synuclein-green fluorescent fusion proteins per vesicle. Although this number is high enough to modulate physical membrane properties, it is also strikingly similar to the number of synaptobrevins, a putative interaction partner of alpha-synuclein, per vesicle. PMID: 27477055
- TMEM175 deficiency impairs lysosomal and mitochondrial function and increases alpha-synuclein aggregation. PMID: 28193887
- we documented that ceftriaxone interacts with alpha-synuclein inhibiting its pathological aggregation and that a cyclical treatment with this molecule in a patient with adult-onset Alexander's disease halted, and partly reversed, the progression of neurodegeneration, suggests the possibility of a chaperone-like effect of ceftriaxone on protein involved in specific neurodegenerative diseases. PMID: 27133445
- The findings of this study confirm that alpha-synuclein interacts with membranes to affect Ca(2+) signalling in a structure-specific manner and the oligomeric beta-sheet-rich alpha-synuclein species ultimately leads to Ca(2+) dysregulation and Ca(2+)-dependent cell death. PMID: 26989132
- alpha-synuclein plays a crucial role in motor and sensory function regulation, in which, the underlying mechanism may be linked to the regulation of apoptosis associated with apoptotic gene (Bax, Bcl2) and neurotrophic factors expression (NGF, BDNF and NT3). PMID: 26822976
- the unaltered SNCA levels observed following ZSCAN21 down-regulation in the rat brain, possibly due to compensatory mechanisms, imply that ZSCAN21 is not a master regulator of SNCA in vivo. PMID: 26907683
- that loss of glucocerebrosidase function may contribute to SNCA accumulation through inhibition of autophagy via PPP2A inactivation PMID: 26378614
- We conclude that alphaSyn overexpression impairs neurite outgrowth and augments axonal degeneration, whereas axonal vesicle transport and autophagy are severely altered. PMID: 26158517
- The destabilization of physiological tetramers by PD-causing missense mutations and the neurotoxicity and inclusions induced by markedly decreasing tetramers suggest that decreased alpha-helical tetramers and increased unfolded monomers initiate pathogenesis. PMID: 26076669
- Results show that hydrostatic pressure is associated with a transition from monomeric to higher order alpha-synuclein aggregates and that increased pressure reduces the level of PLCbeta1 and the amount of alpha-synuclein/PLCbeta1 complexes. PMID: 26434717
- The data suggest that a-syn is involved in the regulation of synaptic plasticity in the ENS during early postnatal life and adult age. PMID: 25896939
- Mitochondrial impairment disturbs the autophagic flux and leads to the accumulation of exogenously applied alpha-synuclein PMID: 26212128
- the major toxic role of SNCA is related to its extracellular species and further supports a protective role of intracellular SNCA aggregation PMID: 25484190
- comparison between two types of alpha-synuclein showed that A53T mutated alpha-synuclein was more effective to establish a Parkinson disease (PD) model, and the model based A53T mutated alpha-synuclein was a suitable model for early-onset PD PMID: 26192120
- LRRK2 inhibition alleviates alpha-synuclein gene-induced neurodegeneration in the rat Parkinson's disease model. PMID: 26078453
- Cx3cl1 overexpression suppresses alpha-synuclein-mediated neurodegeneration. PMID: 25195598
- alpha-synuclein knockdown is neuroprotective in the rotenone model of PD and indicates that endogenous alpha-synuclein contributes to the specific vulnerability of dopaminergic neurons to systemic mitochondrial inhibition PMID: 26075822
- shed light on the potential roles of mutant alpha-synuclein in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease PMID: 24833599
- suggest that the N terminus of alpha-Syn is essential for the regulation of mitochondrial membrane permeability PMID: 25446002
- In the neuronal plasma membrane, alpha-synuclein caused synaptotoxic failure associated with a decrease in membrane proteins. PMID: 25669123
- a tight link between the intracellular level of alpha-synuclein and maturation capacity of primary oligodendrocyte progenitor cells PMID: 25019582
- These results suggest alpha-synuclein as a pathological link between chronic effects of traumatic brain injury and Parkinson's disease. PMID: 25251017
- It impairs maturation of oligodendrocyte progenitors thereby contributing to multiple system atrophy. PMID: 24698767
- CHIP can mediate the degradation of alpha synuclein aggregates in vivo PMID: 24664141
- extracellular ASN is involved in GSK-3beta-dependent Tau hyperphosphorylation, which leads to microtubule destabilization PMID: 24722055
- Results indicate the critical involvement of PAR2-NF-kappaB signaling in the upregulation of alpha-synuclein and motor dysfunction in the rodent model of Parkinsons disease. PMID: 24747612
- S-Nitrosylating protein disulphide isomerase plays a significant role in neurological disorders related to alpha-syn aggregation. PMID: 25090657
- LRRK2 expression in the wild-type rat midbrain remained undetected under nonpathological conditions, LRRK2 became highly expressed in iNOS-positive myeloid cells in the substantia nigra in response to alpha-synuclein overexpression or LPS exposures PMID: 24927544
- onjisaponin B was able to induce autophagy and accelerate both the removal of mutant huntingtin and A53T alpha-synuclein, which are highly associated with Huntington disease and Parkinson disease, respectively PMID: 24248062
- Changes in alpha-synuclein expression with age, including a baseline of accumulating synucleinopathies in the healthy aging submucosal plexus PMID: 23809578
- Our data show that changes in the S129 residue of alpha-synuclein influence the rate of pathology and neurodegeneration PMID: 23567651
- Extracellular alpha-synuclein induces calpain-dependent overactivation of cyclin-dependent kinase 5 in vitro. PMID: 23954626
- Inhibition of Nrf2/HO-1 leads to more alpha-syn aggregation and greater toxicity induced by iron, creating a vicious cycle of iron accumulation, alpha-syn aggregation and HO-1 disruption in PD. PMID: 23454680
- VDAC1 has a role in alpha-synuclein-induced dopaminergic neuron toxicity in rats PMID: 23291291
- Results suggest that macrophages play an active phagocytotic role in removing alpha-SYNC aggregates that accumulate with age in the neural circuitry of the gut. PMID: 23441091
- Accumulation of aggregated alpha-synuclein is triggered in substantia nigra in response to environmental toxins later in life. PMID: 23567316
- Exophagy, with or without expression of TPPP, may be an important physiological mechanism for unconventional secretion of alpha-synuclein from dopaminergic neurons. PMID: 23629650
- TFEB is a key player in the induction of alpha-synuclein-induced toxicity and Parkinson disease pathogenesis PMID: 23610405
- Our study is the first to evidence that enteric neurons are capable of secreting alpha-synuclein, thereby providing new insights into the role of the enteric nervous system in the pathophysiology of Parkinson disease. PMID: 23278133
- This study demonistrated that Deletion in exon 5 of the SNCA gene and exposure to rotenone leads to oligomerization of alpha-synuclein and toxicity to PC12 cells. PMID: 23128054
- Large alpha-Syn oligomers preferentially bind to the N-terminal domain of a vesicular SNARE protein, synaptobrevin-2, which blocks SNARE-mediated lipid mixing by preventing SNARE complex formation. PMID: 23431141
- Primary oligodendrocytes from rat brain and oligodendroglial cell lines take-up neuronal-secreted or exogenously added synuclein alpha from their conditioning medium. PMID: 23077527
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:Cytoplasm. Membrane. Nucleus. Cell junction, synapse. Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:Synuclein family
-
組織特異性:Found only in brain (hippocampus, brainstem and cortex). Specifically expressed in neuronal cell bodies and synapses.
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Human Transforming Growth factor β1,TGF-β1 ELISA kit
Detect Range: 23.5 pg/ml-1500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 5.8 pg/ml
-
-
-
Mouse Tumor necrosis factor α,TNF-α ELISA Kit
Detect Range: 7.8 pg/ml-500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 1.95 pg/ml
-
-
-
-