Mouse Insulin,INS ELISA Kit
-
中文名稱(chēng):小鼠胰島素(INS)酶聯(lián)免疫試劑盒
-
貨號(hào):CSB-E05071m
-
規(guī)格:96T/48T
-
價(jià)格:¥3200/¥2500
-
其他:
產(chǎn)品詳情
-
產(chǎn)品描述:小鼠胰島素(INS)酶聯(lián)免疫試劑盒(CSB-E05071m)為雙抗夾心法ELISA試劑盒,定量檢測(cè)血清、血漿、組織培養(yǎng)上清液、組織勻漿、細(xì)胞裂解物樣本中的INS含量。INS即胰島素基因,在人體糖代謝中極為關(guān)鍵。它編碼的胰島素可促進(jìn)細(xì)胞攝取葡萄糖,降低血糖水平。研究主要圍繞其表達(dá)調(diào)控機(jī)制展開(kāi),以了解胰島素分泌異常與糖尿病等疾病關(guān)聯(lián),為開(kāi)發(fā)治療藥物和方案提供理論依據(jù)。試劑盒檢測(cè)范圍為15.6 nIU/mL-1000 nIU/mL,該產(chǎn)品適用于科研場(chǎng)景中評(píng)估胰島β細(xì)胞功能、分析胰島素分泌調(diào)控機(jī)制或篩選影響糖代謝的化合物,例如在建立糖尿病動(dòng)物模型后監(jiān)測(cè)胰島素動(dòng)態(tài)變化,或通過(guò)體外細(xì)胞實(shí)驗(yàn)探究藥物對(duì)胰島素合成與釋放的影響。本品僅用于科研,不用于臨床診斷,產(chǎn)品具體參數(shù)及操作步驟詳見(jiàn)產(chǎn)品說(shuō)明書(shū)。
-
別名:Ins1 ELISA Kit; Ins-1 ELISA Kit; Insulin-1 [Cleaved into: Insulin-1 B chain; Insulin-1 A chain] ELISA Kit
-
縮寫(xiě):
-
Uniprot No.:
-
種屬:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
樣本類(lèi)型:serum, plasma, cell culture supernates, tissue homogenates, cell lysates
-
檢測(cè)范圍:15.6 nIU/mL-1000 nIU/mL
-
靈敏度:3.9 nIU/mL
-
反應(yīng)時(shí)間:1-5h
-
樣本體積:50-100ul
-
檢測(cè)波長(zhǎng):450 nm
-
研究領(lǐng)域:Metabolism
-
測(cè)定原理:quantitative
-
測(cè)定方法:Sandwich
-
精密度:
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): CV%<8% Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess. Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): CV%<10% Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty assays to assess. -
線性度:
To assess the linearity of the assay, samples were spiked with high concentrations of mouse INS in various matrices and diluted with the Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay. Sample Serum(n=4) 1:100 Average % 90 Range % 84-95 1:200 Average % 93 Range % 90-96 1:400 Average % 95 Range % 90-100 1:800 Average % 94 Range % 87-99 -
回收率:
The recovery of mouse INS spiked to levels throughout the range of the assay in various matrices was evaluated. Samples were diluted prior to assay as directed in the Sample Preparation section. Sample Type Average % Recovery Range Serum (n=5) 98 92-102 EDTA plasma (n=4) 89 82-96 -
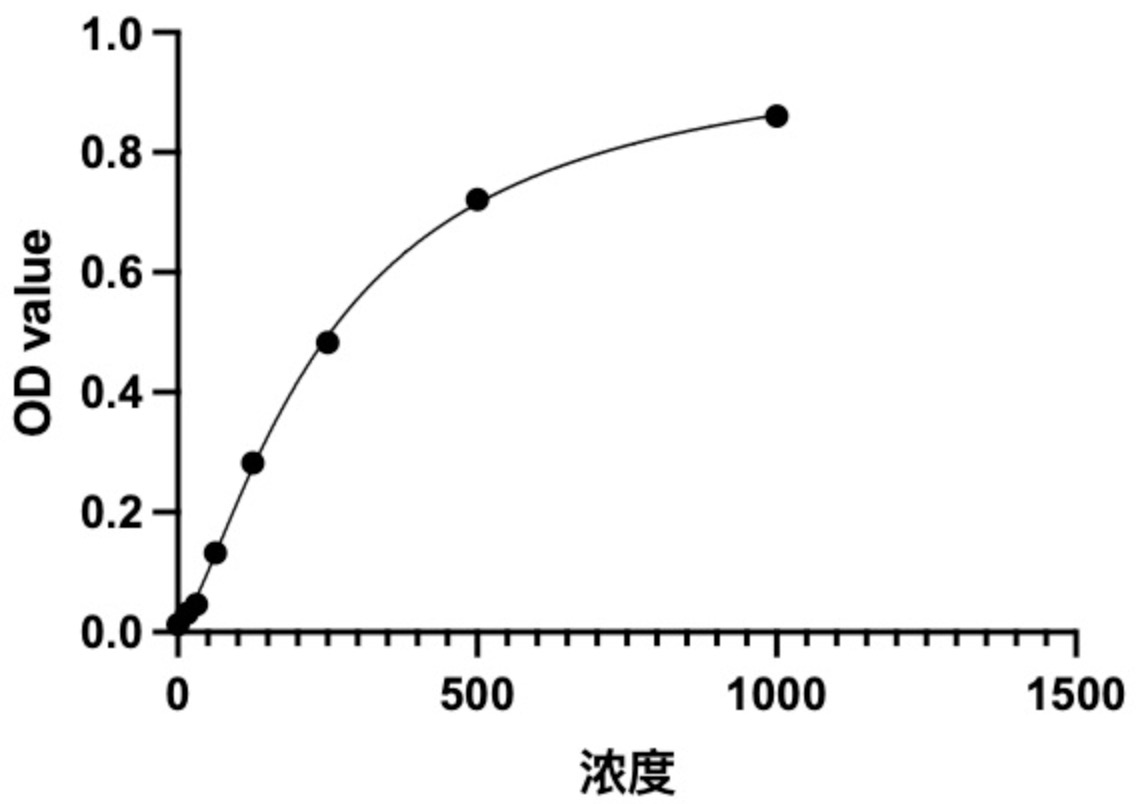
標(biāo)準(zhǔn)曲線:
These standard curves are provided for demonstration only. A standard curve should be generated for each set of samples assayed. 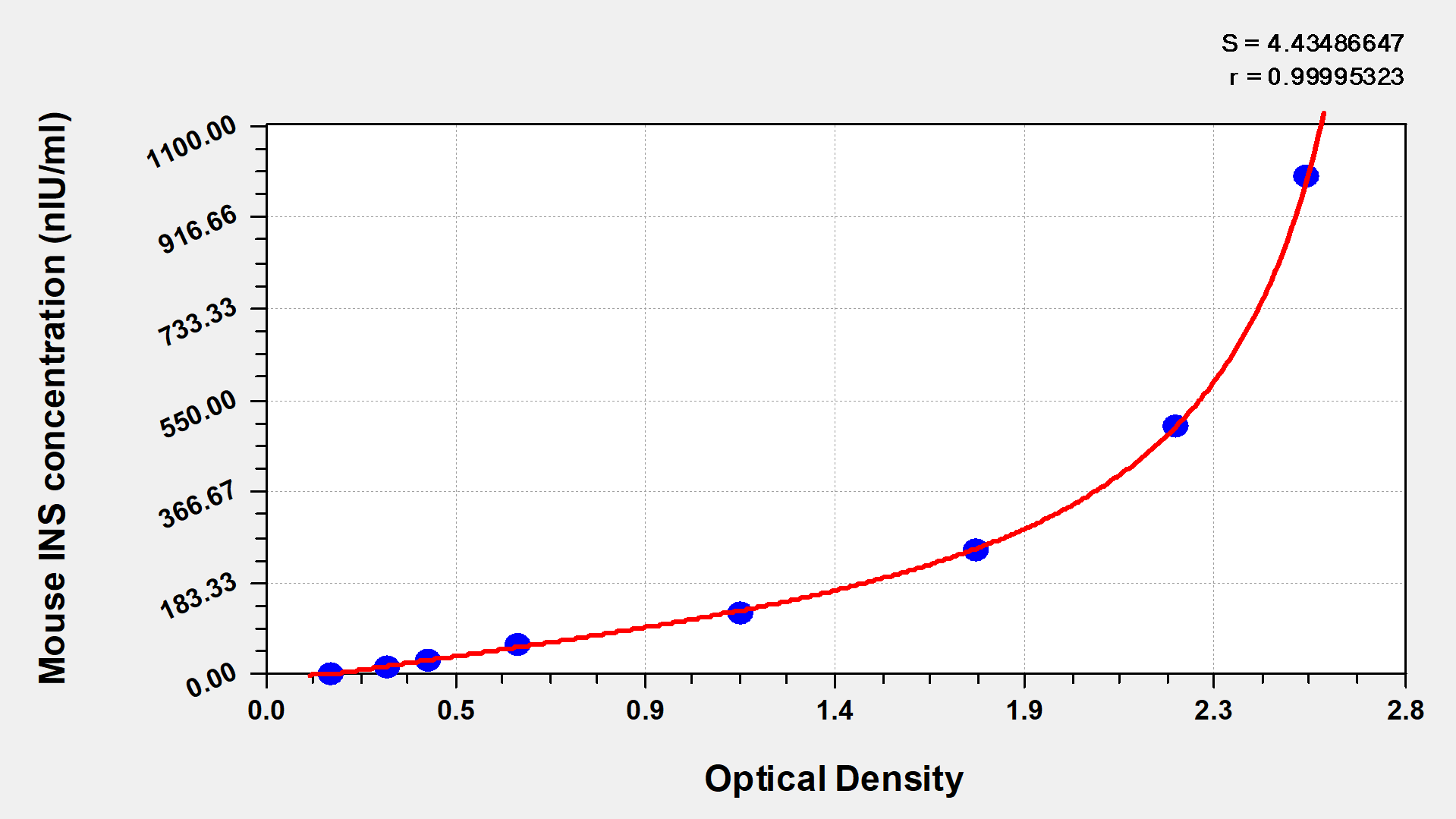
nIU/ml. OD1 OD2 Average Corrected 1000 2.546 2.598 2.572 2.396 500 2.231 2.267 2.249 2.073 250 1.745 1.769 1.757 1.581 125 1.198 1.163 1.181 1.005 62.5 0.648 0.628 0.638 0.462 31.2 0.426 0.407 0.417 0.241 15.6 0.302 0.326 0.314 0.138 0 0.173 0.179 0.176
-
數(shù)據(jù)處理:
-
貨期:3-5 working days
引用文獻(xiàn)
- HNF4α-CDKL3 axis restricts MASLD progression by targeting FoxO1 via non-canonical phosphorylation S Figure, S Table,Hepatology,/
- Naringenin cationic lipid-modified nanoparticles mitigate MASLD progression by modulating lipid homeostasis and gut microbiota L Dong, W Lou, C Xu, J Wang,Journal of Nanobiotechnology,2025
- Pathophysiological characterization of the ApoE?/?; db/db mouse: A model of diabetes and atherosclerosis M Paniagua-Sancho, AG Casanova,Methods,2025
- ANXA1-FPR2 axis mitigates the susceptibility to atrial fibrillation in obesity via rescuing AMPK activity in response to lipid overload P Liu, L Wang, Y Wang, L Jin, H Gong,Cardiovascular Diabetology,2024
- Network pharmacology and transcriptomics explore the therapeutic effects of Ermiao Wan categorized formulas for diabetes in mice Y Wang, Y Chen, X Liang, L Zhu, X Wen,Scientific Reports,2024
- Rescuing vascular dysfunction in dorsal pancreatic arteries prevents tacrolimus-induced glucose metabolism disorder H Wang, D Zhao, X Wang, C Tang, Y Lei,Authorea,2024
- Comprehensive Insights into Berberine's Hypoglycemic Mechanisms: A Focus on Ileocecal Microbiome in db/db Mice X Chen,Heliyon,2024
- The microbial metabolite agmatine acts as an FXR agonist to promote polycystic ovary syndrome in female mice C Yun,Nature metabolism,2024
- Gkongensin A, an HSP90β inhibitor, improves hyperlipidemia, hepatic steatosis, and insulin resistance K Miao,Heliyon,2024
- Sirt5 improves cardiomyocytes fatty acid metabolism and ameliorates cardiac lipotoxicity in diabetic cardiomyopathy via CPT2 de-succinylation M Wu,Redox biology,2024
- N1-methylnicotinamide impairs gestational glucose tolerance in mice X Wei,Journal of molecular endocrinology,2024
- Enhancing β-cell function and identity in type 2 diabetes: The protective role of Coptis deltoidea C. Y. Cheng et Hsiao via glucose metabolism modulation and AMPK signaling activation S Zhang,Phytomedicine,2024
- N1-methylnicotinamide impairs gestational glucose tolerance in mice X Wei,Journal of molecular endocrinology,2023
- Vitamin D Alleviates Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by Mitigating Oxidative Stress-Induced Pancreatic β-Cell Impairment J Liu,Experimental and clinical endocrinology & diabetes,2023
- Irisin suppresses pancreatic β cell pyroptosis in T2DM by inhibiting the NLRP3-GSDMD pathway and activating the Nrf2-TrX/TXNIP signaling axis T Li,Diabetology & metabolic syndrome,2023
- Silencing of DIRAS3 improves the proliferation and insulin secretion of palmitic acid-treated pancreatic β?cells through regulating PI3K/AKT signaling Y Li,Springer link,2023
- Adoptive Transfer of Immature Dendritic Cells with High HO-1 Expression Delays the Onset of T1DM in NOD Mice X Yang,Available at SSRN 4563598,2023
- Serum and urine metabolomics study revealed the amelioration of Gynura bicolor extract on high fat diet-fed and streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic mice based on UHPLC-MS/MS X Ding,Journal of pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis,2023
- Astaxanthin supplementation assists sorafenib in slowing skeletal muscle atrophy in H22 tumsor‐bearing mice via reversing abnormal glucose metabolism P Ren,Molecular nutrition & food research,2023
- Bacillus sp. DU‐106 ameliorates type 2 diabetes by modulating gut microbiota in high‐fat‐fed and streptozotocin‐induced mice J Yan,Journal of applied microbiology,2023
- Inhibiting miR-182-3p Alleviates Gestational Diabetes Mellitus by Improving Insulin Resistance in Skeletal Muscle J Rao,Balkan medical journal,2023
- Ethanol extract from Ulva prolifera prevents high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance, oxidative stress, and inflammation response in mice Song W,BioMed research international,2023
- Simiao Wan modulates the gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism during improving type 2 diabetes mellitus in mice Yimeng Chen,Phytomedicine,2023
- Oroxin A from Oroxylum indicum prevents the progression from prediabetes to diabetes in streptozotocin and high-fat diet induced mice Sun W,Phytomedicine,2023
- Exerkine β-aminoisobutyric acid protects against atrial structural remodeling and atrial fibrillation in obesity via activating AMPK signaling and improving insulin sensitivity J Li,Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy,2024
- Jinkui Shenqi pills ameliorate diabetes by regulating hypothalamic insulin resistance and POMC/AgRP expression and activity H Li,Phytomedicine,2024
- Predictive Factors of Menstrual Recovery After Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Women with Obesity M Cai,Diabetes, metabolic syndrome and obesity,2023
- Augmented temperature fluctuation aggravates muscular atrophy through the gut microbiota Y Liu,Nature communications,2023
- Effects of folic acid supplementation in pregnant mice on glucose metabolism disorders in male offspring induced by lipopolysaccharide exposure during pregnancy WX Sun,Scientific reports,2023
- Derlin-1 ameliorates nonalcoholic hepatic steatosis by promoting ubiquitylation and degradation of FABP1 H You,/,2023
- Hepatic leucine carboxyl methyltransferase 1 (LCMT1) contributes to high fat diet-induced glucose intolerance through regulation of glycogen metabolism J Mo,The Journal of nutritional biochemistry,2023
- Hypoglycemic mechanisms of Polygonatum sibiricum polysaccharide in db/db mice via regulation of glycolysis/gluconeogenesis pathway and alteration of gut microbiota X Chen,Heliyon,2023
- Retinol dehydrogenase 10 reduction mediated retinol metabolism disorder promotes diabetic cardiomyopathy in male mice Y Wu,Nature communications,2023
- Melatonin increases susceptibility to atrial fibrillation in obesity via Akt signaling impairment in response to lipid overload X Qin,Journal of pineal research,2023
- Diabetes Mellitus Are Less Likely to Aortic Dissection: A 5-Year Single-Center Analysis on independent risk factors of Aortic Dissection in Diabetes Mellitus Patients X Yang,ResearchSquare,2022
- Selenoprotein F Knockout Caused Glucose Metabolism Disorder in Young Mice by Disrupting Redox Homeostasis M Li,Antioxidants,2022
- A Closed-Loop Autologous Erythrocyte-Mediated Delivery Platform for Diabetic Nephropathy Therapy. L Feng,Nanomaterials,2022
- Hypothalamic Hnscr regulates glucose balance by mediating central inflammation and insulin signal Y Liu,Cell proliferation,2022
- Systematic evaluation of antimicrobial food preservatives on glucose metabolism and gut microbiota in healthy mice P Li,NPJ science of food,2022
- RBM15 suppresses hepatic insulin sensitivity of offspring of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Mice via m6A-mediated regulation of CLDN4 J Fang,ResearchSquare,2022
- Exenatide regulates Th17/Treg balance via PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 pathway in db/db mice Q Xu,ResearchSquare,2022
- Paternal Zn-deficiency abolishes metabolic effects in offspring induced by diet type G Li,Animal Nutrition,2022
- The Mitochondrial-Derived Peptide MOTS-c Relieves Hyperglycemia and Insulin Resistance in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Y Yin,Pharmacological research,2021
- Acute and chronic metabolic effects of carvedilol in high-fructose, high fat diet-fed mice: Implication of β-arrestin2 pathway HMS Ahmed,Canadian journal of physiology and pharmacology,2021
- The tissue origin of human mesenchymal stem cells dictates their therapeutic efficacy on glucose and lipid metabolic disorders in type II diabetic mice Y Ma,Stem Cell Research & Therap,2021
- Pioglitazone Enhances β-Arrestin2 Signaling and Ameliorates Insulin Resistance in Classical Insulin Target Tissues S El-Fayoumi,Pharmacology,2021
- Early 1, 25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 Supplementation Effectively Lowers the Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus via Ameliorating Inflammation In KK-Ay Mice LIQ TIAN,Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology,2021
- Saturated fatty acids entrap PDX1 in stress granules and impede islet beta cell function M Zhang,Diabetologia,2021
- ZG02 Improved Hepatic Glucose Metabolism and Insulin Sensitivity via Activation of AMPK/Sirt1 Signaling Pathways in a High-fat Diet/Streptozotocin-induced Type 2 Diabetes Model Y Zhang,Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes.,2020
- Anti-Obesity and Antidiabetic Effects of Nelumbinis Semen Powder in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese C57BL/6 Mice SB Hwang,Nutrients,2020
- Alpha-ketoglutaric acid ameliorates hyperglycemia in diabetes by inhibiting hepatic gluconeogenesis via serpina1e signaling G Shu,Research Square,2020
- Polysaccharides from Armillariella tabescens mycelia ameliorate insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic mice R Yang,Food & Function,2020
- Genistein ameliorates inflammation and insulin resistance through mediation of gut microbiota composition in type 2 diabetic mice R Yang,European Journal of Nutrition,2020
- Dihydrotanshinone I Ameliorates Cardiac Hypertrophy in Diabetic Mice Induced by Chronic High-Fat Feeding S Li,Natural Product Communications,2020
- Effects of Exogenous Adiponectin Supplementation in Early Pregnant PCOS Mice on the Metabolic Syndrome of Adult Female Offspring M Zuo,Research Square,2020
- Insulin receptor substrate‐1 inhibits high‐fat diet‐induced obesity by browning of white adipose tissue through miR‐503 XF Man,FASEB J.,2020
- Gestational bisphenol A exposure induces fatty liver development in male offspring mice through the inhibition of HNF1b and upregulation of PPARγ Z Long,Cell Biology and Toxicology,2020
- Eicosapentaenoic and Docosahexaenoic acids Differentially Alter Gut Microbiome and Reverse High┸\Fat Diet┸\Induced Insulin Resistance P Zhuang,Mol Nutr Food Res,2020
- Depot-specific regulation of NAD+/SIRTs metabolism indentified in adipose tissue of mice in response to high-fat diet feeding or calorie restriction X Wei,The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry,2020
- Astaxanthin n-Octanoic Acid Diester Ameliorates Insulin Resistance and Modulates Gut Microbiota in High-Fat and High-Sucrose Diet-Fed Mice Y Gao,Int. J. Mol. Sci.,2020
- Guava Leaf Extract Attenuates Insulin Resistance via the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway in a Type 2 Diabetic Mouse Model Q Yang,Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes,2020
- Distinct cardiac energy metabolism and oxidative stress adaptations between obese and non-obese type 2 diabetes mellitus X Li,Theranostics,2020
- Overexpression of Galectin 3 in Pancreatic β Cells Amplifies β-Cell Apoptosis and Islet Inflammation in Type-2 Diabetes in Mice I Petrovic,Frontiers in Endocrinology,2020
- Exendin-4 inhibits lipotoxicity?induced oxidative stress in β?cells by inhibiting the activation of TLR4/NF?κB signaling pathway Ximei Shen,International Journal of Molecular Medicine,2020
- VEGF-Modified PVA/Silicone Nanofibers Enhance Islet Function Transplanted in Subcutaneous Site Followed by Device-Less Procedure. Yang B,Int J Nanomedicine,2020
- TAK-875 Mitigates β-Cell Lipotoxicity-Induced Metaflammation Damage through Inhibiting the TLR4-NF-κB Pathway Chen X,Journal of Diabetes Research,2019
- Baicalein reduces hepatic fat accumulation by activating AMPK in oleic acid-induced HepG2 cells and high-fat diet-induced non-insulin-resistant mice Sun W,Food & Function,2019
- Obesity-induced RCAN1 Overexpression Leads to β-Cell Failure through Mitophagy Pathway Inhibition Li X, et al,Antioxidants and Redox Signaling,2019
- Melatonin ameliorates SGLT2 inhibitor-induced diabetic ketoacidosis by inhibiting lipolysis and hepatic ketogenesis in type 2 diabetic mice Jae-Hyung Park, et al,Journal of Pineal Research,2019
- Downregulation of osteopontin inhibits browning of white adipose tissues through PI3K-AKT pathway in C57BL/6 mice Yi Lu, et al,European Journal of Pharmacology,2019
- A New Possible Mechanism by which Punicalagin Protects Against Liver Injury Induced by Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Upregulation of Autophagy via the Akt/FoxO3a Signaling Pathway Zhang Y, et al,Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2019
- Oleic acid antagonizes the action of high fructose high fat diet on insulin secretion and adipose tissue β-arrestin signaling Mansour R M E S, et al,J. Pharm. Sci,2019
- Generation of insulin-secreting cells from mouse gallbladder stem cells by small molecules in vitro Chen F, et al,Stem Cell Research & Therapy,2019
- Caspase/AIF/apoptosis pathway: a new target of puerarin for diabetes mellitus therapy Liang T, et al,Molecular Biology Reports,2019
- Glucose metabolic effects of oat noodles with different processing in type 2 diabetic mice LijuanWang,Journal of Cereal Science,2019
- Long-term liraglutide ameliorates nigrostriatal impairment via regulating AMPK/PGC-1a signaling in diabetic mice Ma D, et al,Brain research,2019
- Ergosterol Ameliorates Diabetic Nephropathy by Attenuating Mesangial Cell Proliferation and Extracellular Matrix Deposition via the TGF-β1/Smad2 Signaling Pathway Dong Z, et al,Nutrients,2019
- The effects of decabromodiphenyl ether on glycolipid metabolism and related signaling pathways in mice Zhu Y, et al,Chemosphere,2019
- Dendrobium huoshanense polysaccharide regulates hepatic glucose homeostasis and pancreatic β-cell function in type 2 diabetic mice Hong-YanWang, et al,Carbohydrate Polymers,2019
- Chronic treatment with five vascular risk factors causes cerebral amyloid angiopathy but no Alzheimer pathology in C57BL6 mice Foidl BM, et al,Brain Behavior And Immunity,2019
- Hyperglycaemia Stress-Induced Renal Injury is Caused by Extensive Mitochondrial Fragmentation, Attenuated MKP1 Signalling, and Activated JNK-CaMKII-Fis1 Biological Axis Zhang Y, et al,Cellular physiology and biochemistry,2018
- Loss of pigment epithelium-derived factor leads to ovarian oxidative damage accompanied by diminished ovarian reserve in mice Li XH, et al,Life Sciences,2018
- miR-335-5p induces insulin resistance and pancreatic islet β-cell secretion in gestational diabetes mellitus mice through VASH1-mediated TGF-β signaling pathway Tang XW.et al,journal of cellular physiology,2018
- Effects of diet zinc level on circadian rhythms and lipid metabolism in male mice Guan-ya Li.et al,biological rhythm research,2018
- The analysis of fagopyritols from tartary buckwheat and their anti-diabetic effects in KK-Ay type 2 diabetic mice and HepG2 cells WeijingWu.et al,Journal of Functional Foods,2018
- Polytherapy with Reserpine and Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Improves the Symptoms in Streptozotocin-Induced Type-1 Diabetic Mice by Reducing Inflammation and Inducting Beta Cell Regeneration Skurikhin.et al,Stem Cell Research & Therapy,2018
- ERα and/or ERβ activation ameliorates cognitive impairment, neurogenesis and apoptosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus mice Su-Su Tang.et al,Experimental Neurology,2018
- DUSP1 recuses diabetic nephropathy via repressing JNK-Mff-mitochondrial fission pathways Junqin Sheng.et al,Journal of cellular physiology,2018
- SIRT3 Facilitates Amniotic Fluid Stem Cells to Repair Diabetic Nephropathy Through Protecting Mitochondrial Homeostasis by Modulation of Mitophagy Feng J.et al,Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry,2018
- HIF1α deletion facilitates adipose stem cells to repair renal fibrosis in diabetic mice Tang Q.et al,In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim,2018
- Praeruptorin B improves diet-induced hyperlipidemia and alleviates insulin resistance via regulating SREBP signaling pathway Zu-Guo Zheng.et al, RSC Adv,2018
- Targeted inhibition of RAGE reduces amyloid-β influx across the blood-brain barrier and improves cognitive deficits in db/db mice Wang H.et al,Neuropharmacology,2017
- Improved Sp1 and Betaine Homocysteine-S-Methyltransferase Expression and Homocysteine Clearance Are Involved in the Effects of Zinc on Oxidative Stress in High-Fat-Diet-Pretreated Mice Li Wu,Biological Trace Element Research,2024
- Oat bran β-glucan improves glucose homeostasis in mice fed on a high-fat diet Yuliang Cheng.et al, RSC Adv,2017
- Role of Sertoli and Leydig Cells in the Regulation of Spermatogonial Stem Cell and Development of Reproductive Disorders in Male C57Bl/6 Mice with Type 1 Skurikhin EG.et al,Bull Exp Biol Med,2017
- Serine prevented high-fat diet-induced oxidative stress by activating AMPK and epigenetically modulating the expression of glutathione synthesis-related genes Zhou X.et al,Biochim Biophys Acta,2017
- 6-Shogaol ameliorates diabetic nephropathy through anti-inflammatory, hyperlipidemic, anti-oxidative activity in db/db mice Xu Y.et al,Biomed Pharmacother,2017
- Baicalein improves insulin resistance via regulating SOCS3 and enhances the effect of acarbose on diabetes prevention WenlongSun.et al,Journal of Functional Foods,2017
- Berberine Improves Diabetic Encephalopathy through SIRT1/ER Stress Pathway in db/db Mice Li HY.et al,Rejuvenation Res ,2017
- Regenerative Potential of Spermatogonial Stem Cells, Endothelial Progenitor Cells, and Epithelial Progenitor Cells of C57Bl/6 Male Mice with Metabolic Disorders Skurikhin EG.et al,Bull Exp Biol Med.,2017
- Arachidonic acid sex-dependently affects obesity through linking gut microbiota-driven inflammation to hypothalamus-adipose-liver axis Zhuang P.et al,BBA-MOL BASIS DIS ,2017
- Involvement of receptor-interacting protein 140 in palmitate-stimulated macrophage infiltration of pancreatic beta cells Runmei Zou.et al,Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine,2017
- Standardized Mori ramulus extract improves insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity in C57BLKS/J db/db mice and INS-1 cells Soo-yeon Park.et al,Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,2017
- Lycopene Improves Insulin Sensitivity through Inhibition of STAT3/Srebp-1c-Mediated Lipid Accumulation and Inflammation in Mice fed a High-Fat Diet Zeng Z.et al,Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes.,2017
- Kukoamine A attenuates insulin resistance and fatty liver through downregulation of Srebp-1c Guangyun Li.et al,Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,2017
- Trivaric acid, a new inhibitor of PTP1b with potent beneficial effect on diabetes. ,Life Sciences,2016
- PPARγ agonists regulate bidirectional transport of amyloid-β across the blood-brain barrier and hippocampus plasticity in db/db mice. Wang H.et al,Br J Pharmacol.,2016
- Dicaffeoylquinic Acid-Enriched Fraction of Cichorium glandulosum Seeds Attenuates Experimental Type 1 Diabetes via Multipathway Protection. Tong J.et al,J Agric Food Chem.,2015
- Combinatorial Treatment of Bone Marrow Transplantation and Regulatory T Cells Improves Glycemia in Streptozotocin-diabetic Mice. Min H.et al,Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes.,2015
- Nr2e1 Deficiency Augments Palmitate-Induced Oxidative Stress in Beta Cells Shi X.et al,Oxid Med Cell Longev.,2016
- Whole Body Vibration Improves Insulin Resistance in db/db Mice: Amelioration of Lipid Accumulation and Oxidative Stress Liu Y.et al,Appl Biochem Biotechnol.,2016
- PPAR緯 agonists regulate bidirectional transport of amyloid-尾 across the blood-brain barrier and hippocampus plasticity in db/db mice Wang H.et al,Br J Pharmacol.,2016
- Nuclear orphan receptor TLX affects gene expression, proliferation and cell apoptosis in beta cells. Shi X.et al,Biochem Biophys Res Commun.,2015
- Dicaffeoylquinic acid-enriched fraction of Cichorium glandulosum seeds attenuates experimental type 1 diabetes via multi-pathway protection Tong J. et al,J Agric Food Chem,2015
- Combined Transfection of the Three Transcriptional Factors, PDX-1, NeuroD1, and MafA, Causes Differentiation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Insulin … Guo Qing-Song et al,Experimental Diabetes Research,2012
- The multimerization and secretion of adiponectin are regulated by TNF-alpha He Y. et al,Endocrine,2015
- Nicotinamide Facilitates Mesenchymal Stem Cell Differentiation Into Insulin-Producing Cells and Homing to Pancreas in Diabetic Mice Yang SF. et al,Transplant Proc,2015
- Antidiabetic drugs restore abnormal transport of amyloid-ß across the blood-brain barrier and memory impairment in db/db mice Chen F. et al,Neuropharmacology,2015
- Dan-Qi prescription ameliorate insulin resistance through overall corrective regulation of glucose and fat metabolism Xie Z. et al,J Ethnopharmacol.,2015
- Homoarginine supplementation improves blood glucose in diet-induced obese mice Stockebrand M. et al,Amino Acids. ,2015
- High-throughput sequencing reveals altered expression of hepatic microRNAs in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-related fibrosis. Leti F, et al,Transl Res,2015
- RIP140 mediates hyperglycemia-induced glucotoxicity in ß-cells via the activation of JNK and ERK1/2 signaling pathways Zou R et al,Diabetes Res Clin Pract,2013
產(chǎn)品評(píng)價(jià)
樣品類(lèi)型:血漿(抗凝劑) EDTA抗凝劑
樣品信息:小鼠
稀釋比:其他 按說(shuō)明書(shū)1:200稀釋
產(chǎn)品評(píng)價(jià): 我用CSB-E05071m檢測(cè)正常lean鼠血漿,1:200稀釋?zhuān)琌D值為0.422,在標(biāo)準(zhǔn)曲線范圍內(nèi),絕對(duì)值也符合正常濃度。
By 王老師
樣品類(lèi)型:血清
樣品信息:小鼠
稀釋比:沒(méi)有稀釋
產(chǎn)品評(píng)價(jià): 使用Mouse Insulin,INS ELISA Kit檢測(cè)小鼠血清中insulin濃度,OD值為0.7813,在標(biāo)準(zhǔn)曲線范圍內(nèi),絕對(duì)值也符合正常濃度。標(biāo)曲見(jiàn)附圖
By 顏老師
樣品類(lèi)型:血清
樣品信息:小鼠
稀釋比:1:100
產(chǎn)品評(píng)價(jià): 我用CSB-E05071m檢測(cè)正常小鼠血清的胰島素濃度,OD值為:景景:0.2241,0.2555,0.3090,使用方便,快捷
By 王老師
相關(guān)產(chǎn)品
靶點(diǎn)詳情
-
最新研究進(jìn)展:胰島素是由胰島的 β細(xì)胞分泌的蛋白質(zhì)激素,用于調(diào)節(jié)血糖水平。最新的研究表明,INS還具有抗炎作用,可以調(diào)節(jié)免疫細(xì)胞的活性,并促進(jìn)炎癥的清除。INS對(duì)心血管健康、神經(jīng)保護(hù)等方面的重要性也得到了更多的認(rèn)識(shí)。
-
功能:Insulin decreases blood glucose concentration. It increases cell permeability to monosaccharides, amino acids and fatty acids. It accelerates glycolysis, the pentose phosphate cycle, and glycogen synthesis in liver.
-
基因功能參考文獻(xiàn):
- Impairment in the insulin-Snail1 axis may contribute to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in obesity. PMID: 30013137
- Feeding of high fat diet leads to impairment of brain insulin signaling linked with neuroinflammation. Insulin resistance due to high fat diet associated with biochemical changes in markers related with Alzheimer disease pathology. PMID: 27771511
- High INS1 expression is associated with weight gain and obesity. PMID: 29122848
- psychological stress impairs insulin signaling and results in hippocampal deficits. PMID: 29970188
- Our data shed light on the putative role of Kv1.3 in weight gain and insulin-dependent responses contributing to knowledge about adipocyte physiology. PMID: 29947924
- Data suggest that hybrid insulin peptides (HIPs), formed in insulin-secreting-cells by fusion of insulin C-peptide fragments to peptide fragments of chromogranin A or islet amyloid polypeptide, and reactivity of CD4+-T-lymphocytes to HIPs may act as biomarkers of autoimmunity in type 1 diabetes. PMID: 29976617
- Our findings, focusing on energy balance, provide a mechanistic understanding of the promising effect of early insulin initiation on lipotoxicity. Insulin, by recovering UCP3 activity, alleviated energy surfeit and potentiated AMPK-mediated lipid homeostasis in skeletal muscle cells following exposure to PA and in gastrocnemius of mice fed HFD. PMID: 29039450
- In the present study, the mRNA expression of the two mouse insulin genes Ins1 and Ins2 was investigated in MIN6 cells treated with different concentrations of melatonin, and insulin secretion was detected under the same conditions. Following the overexpression or silencing of MTNR1B, the activities of components of the MAPK signaling pathway PMID: 29207116
- diabetic gastroparesis was an aggressive process due to the successive damages of myenteric cholinergic neurones and ICC by impairing the insulin/InsR and IGF-1/IGF-1R signaling. Insulin therapy in the early stage may delay diabetic gastroparesis PMID: 28931726
- nNOS mediates insulin- and oxidative stress-induced glucose uptake in skeletal muscle myotubes. PMID: 28666850
- Data (including data from studies using knockout mice) suggest that Ins1 and Ins2 are required for pancreatic beta-cell maturation; thus, Ins1 and Ins2 are needed for normal beta-cell development and for maintenance of normal beta-cell function. PMID: 29029025
- Despite higher endogenous insulin concentrations following feeding, arcuate nucleus phosphorylation of Akt (pAkt) levels were significantly lower in the pregnant group compared with the nonpregnant group. PMID: 29029017
- Our current results reinforce the notion that the AT2R has a physiological role in the conservation of insulin action PMID: 27979738
- E4-ORF1 activation of PI3K in adipocytes recapitulates insulin regulation of FoxO1 but not regulation of Glut4. This uncoupling of PI3K effects occurs despite E4-ORF1 activating PI3K and downstream signaling to levels achieved by insulin PMID: 28009298
- These data support a role for islet NGF in fine-tuning insulin secretion. PMID: 27424144
- PDX1 and ISL1 regulation of insulin gene expression in pancreatic beta cells, was investigated. PMID: 26994512
- insulin and aPC converge on a common spliced-X-box binding protein-1 (sXBP1) signaling pathway to maintain endoplasmic reticulum (ER) homeostasis. PMID: 28687614
- Insulin stimulation of Akt1 and Akt2 signaling in Cystic fibrosis airway cells was diminished compared with that observed in airway cells expressing wild-type CFTR. PMID: 28213469
- These data implicate the insulin-FoxM1/PLK1/CENP-A pathway-regulated mitotic cell-cycle progression as an essential component in the beta cell adaptation to delay and/or prevent progression to diabetes. PMID: 28286049
- Rac1 activation is caused by membrane translocation of a guanine nucleotide exchange factor FLJ00068 in Akt2-mediated insulin signaling in mouse skeletal muscle. PMID: 27163697
- Netrin-1 enhanced insulin secretion by promoting beta-cell Ca(2+) influx and cAMP production. PMID: 27520508
- This study identifies AR as a novel receptor that enhances beta cell function. PMID: 27133133
- The effects were abolished by using pharmacological inhibition of PI3K/Akt with LY294002 and paralleled by transfecting DCs with klotho siRNA. In conclusion, the regulation of klotho sensitive DC function by IGF-1 or insulin is mediated through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in BMDCs. PMID: 27808000
- Overexpression of either ca-Nfatc2 or ca-Nfatc1 in mouse islets enhanced insulin secretion, whereas only ca-Nfatc2 was able to promote b-cell proliferation, suggesting distinct molecular pathways mediating insulin secretion vs. b-cell proliferation are regulated by NFAT PMID: 27935966
- BMP-7 therefore is an attractive candidate for tackling a multifaceted disease such as diabetes, since it not only reduces body fat, but also strengthens insulin signaling, causing improved glucose uptake and ameliorating peripheral insulin resistance. PMID: 28186649
- these findings demonstrate, for the first time, that miR-155 is a positive regulator of insulin sensitivity with potential applications for diabetes treatment. PMID: 27711113
- Maternal chromium restriction leads to glucose metabolism imbalance in mice offspring through insulin signaling and Wnt signaling pathways. PMID: 27782077
- Hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia blunts the Insulin-Inpp5f negative feedback loop in the diabetic heart. PMID: 26908121
- Data suggest that resveratrol acts on differentiating preadipocytes by inhibiting insulin signaling, mitochondrial biogenesis, and lipogenesis. PMID: 26968895
- elevating nuclear O-GlcNAc increases intracellular insulin levels and preserves glucose-stimulated insulin secretion during chronic hyperglycemia PMID: 26598517
- Data (including data from studies in knockout/transgenic mice) suggest INS is required for lipogenic effects of activation of LXRalpha in liver; INS is not required to down-regulate gene expression in ER stress or inflammation (as seen in diabetes). PMID: 26511317
- the insulin-InsR signaling drives multipotent progenitors differentiation into lymphoid lineages in early lymphopoiesis. PMID: 26573296
- The target miRNAs are closely associated with dysregulation of insulin/PI3K-AKT signaling, suggesting that the Cmah-null mice could be a useful model for studying diabetes. PMID: 25243123
- the inhibitory effect of CRFR2 signaling on insulin action is mediated by cAMP in a mammalian target of rapamycin-dependent manner. PMID: 25875045
- This study discloses age-dependent changes in insulin CSF/serum ratios in humans. In the elderly, cerebral insulin resistance might be partially attributed to an impaired transport of insulin into the central nervous system PMID: 25965336
- adiponectin. Taken together, our results show that adiponectin is stored in a unique vesicular compartment, and released through a regulated exocytosis pathway that is dependent on insulin signalling. PMID: 26330614
- LKB1 is essential for mitochondrial maintenance and negatively regulates a distal step of insulin secretion. PMID: 26139601
- ubiquitin-like protein 4A (Ubl4A) plays a crucial role in insulin-induced Akt plasma membrane translocation. PMID: 26195787
- synaptotagmin-7 is directly activated by GLP-1 signaling and may serve as a drug target for boosting insulin secretion. PMID: 26216970
- The paracrine actions of Ucn3 activate a negative feedback loop that promotes somatostatin release to ensure the timely reduction of insulin secretion upon normalization of plasma glucose. PMID: 26076035
- Tcf7l2 is regulating proinsulin expression directly via Isl1, Ins1 and indirectly via MafA, NeuroD1 and Pdx1. PMID: 25015099
- elevated adiponectin levels improve systemic lipid metabolism in the near absence of insulin. PMID: 25339419
- the RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway is involved in insulin release through the up-regulation of Cx36 expression in 3D-cultured MIN6 cells. PMID: 25129107
- Analyzed was insulin translation in islets and in INS-1 cells. Insulin translational levels were significantly increased in islets of mice fed a high-fat diet to meet systemic demand, without altering its transcriptional levels. PMID: 25686499
- Data indicate that Src homology-2 domain containing protein B (SHB) deficiency causes a chronic increase in beta-cell focal adhesion kinase (FAK) activity that perturbs the normal insulin secretory characteristics of beta-cells. PMID: 25274988
- The activation of Cav-1 during the adipocyte differentiation process could facilitate the maintenance of insulin sensitivity by mature adipocytes isolated from additional external stimuli. PMID: 24751908
- GX sPLA2 negatively regulated pancreatic insulin secretion by augmenting COX-2-dependent PGE2 production. PMID: 25122761
- Diet-induced obesity mice exhibited significant increases in body weight, plasma glucose, insulin, and IGF1. PMID: 24914941
- The over-expression of miR-200a in the hypothalamus of obese mice is linked to leptin and insulin signaling impairment. PMID: 24394757
- Mouse Ins2 and Ins1 promoters were transiently activated in mouse fetal hepatocytes of embryonic days 13.5 and 16.5, respectively. PMID: 24258027
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細(xì)胞定位:Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:Insulin family
-
數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Human Transforming Growth factor β1,TGF-β1 ELISA kit
Detect Range: 23.5 pg/ml-1500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 5.8 pg/ml
-
-
-
Mouse Tumor necrosis factor α,TNF-α ELISA Kit
Detect Range: 7.8 pg/ml-500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 1.95 pg/ml
-
-
-
-