-
中文名稱:人肺部活化調節趨化因子(PARC/CCL18)酶聯免疫試劑盒
-
貨號:CSB-E09941h
-
規格:96T/48T
-
價格:¥3200/¥2500
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
產品描述:人肺部活化調節趨化因子(PARC/CCL18)酶聯免疫試劑盒(CSB-E09941h)為雙抗夾心法ELISA試劑盒,定量檢測血清、血漿、組織培養上清液、組織勻漿樣本中的CCL18含量。CCL18是一種重要靶點。它屬于趨化因子家族,在免疫調節等生理過程中發揮作用。研究發現其在腫瘤微環境、免疫性疾病中表達異常。機制上,它能招募免疫細胞、影響細胞遷移和活化,為相關疾病的治療和研究提供了方向。試劑盒檢測范圍為31.25 pg/ml-2000 pg/ml,靈敏度為7.81 pg/ml。適用于體外實驗中探究肺部疾病模型、免疫調控機制、藥物干預效果等科研場景本品僅用于科研,不用于臨床診斷,產品具體參數及操作步驟詳見產品說明書。
-
別名:Alternative macrophage activation associated CC chemokine 1 ELISA Kit; Alternative macrophage activation-associated CC chemokine 1 ELISA Kit; AMAC-1 ELISA Kit; AMAC1 ELISA Kit; CC chemokine PARC ELISA Kit; CCL18 ELISA Kit; CCL18(4-69) ELISA Kit; CCL18_HUMAN ELISA Kit; CKb7 ELISA Kit; DC-CK1 ELISA Kit; DCCK1 ELISA Kit; DCCK1 ELISA Kit; Dendritic cell chemokine 1 ELISA Kit; Macrophage inflammatory protein 4 ELISA Kit; MIP-4 ELISA Kit; MIP4 ELISA Kit; PARC ELISA Kit; Pulmonary and activation regulated chemokine ELISA Kit; Pulmonary and activation-regulated chemokine ELISA Kit; SCYA18 ELISA Kit; Small inducible cytokine A18 ELISA Kit; Small inducible cytokine A18 ELISA Kit; Small-inducible cytokine A18 ELISA Kit
-
縮寫:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
樣本類型:serum, plasma, cell culture supernates, tissue homogenates
-
檢測范圍:31.25 pg/ml-2000 pg/ml
-
靈敏度:7.81 pg/ml
-
反應時間:1-5h
-
樣本體積:50-100ul
-
檢測波長:450 nm
-
研究領域:Immunology
-
測定原理:quantitative
-
測定方法:Sandwich
-
精密度:
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): CV%<8%
Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess.
Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): CV%<10%
Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty assays to assess.
Intra-Assay Precision
Inter-Assay Precision
Sample
1
2
3
1
2
3
n
20
20
20
20
20
20
Mean(ng/ml)
244.406
249.006
237.517
236.211
239.732
235.807
SD
0.045
0.055
0.052
0.066
0.072
0.078
CV(%)
4.011
4.685
4.510
5.820
6.081
6.915
-
線性度:
To assess the linearity of the assay, samples were spiked with high concentrations of human PARC/CCL18 in various matrices and diluted with the Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay.
Sample
Serum(n=4)
1:100
Average %
91
Range %
87-94
1:200
Average %
97
Range %
95-103
1:400
Average %
98
Range %
95-102
1:800
Average %
93
Range %
91-98
-
回收率:
The recovery of human PARC/CCL18 spiked to levels throughout the range of the assay in various matrices was evaluated. Samples were diluted prior to assay as directed in the Sample Preparation section.
Sample Type
Average % Recovery
Range
Serum (n=5)
91
87-94
EDTA plasma (n=4)
98
95-102
-
標準曲線:
These standard curves are provided for demonstration only. A standard curve should be generated for each set of samples assayed.
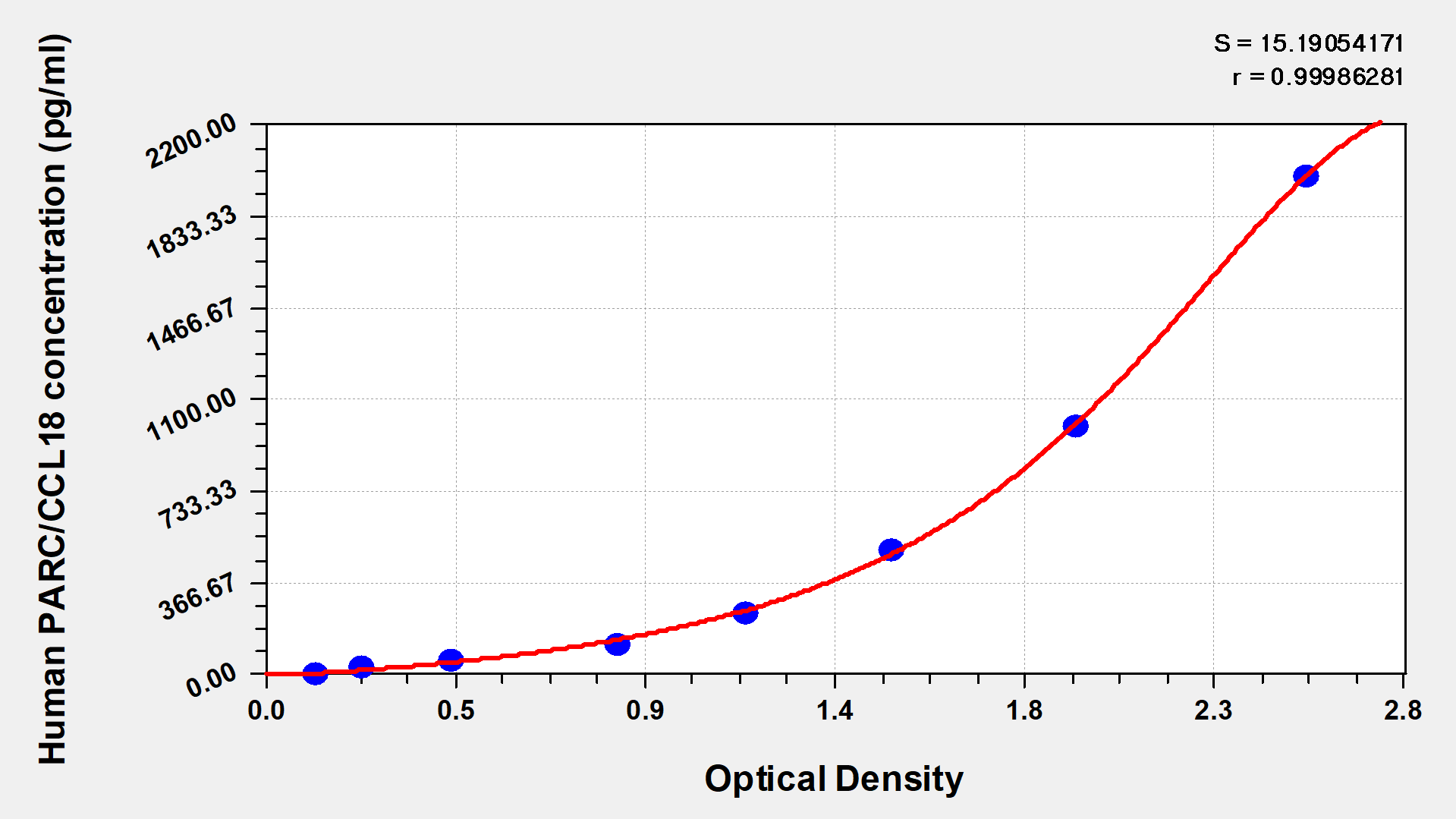
pg/ml
OD1
OD2
Average
Corrected
2000
2.466
2.585
2.526
2.394
1000
1.991
1.944
1.968
1.836
500
1.482
1.567
1.525
1.393
250
1.213
1.130
1.172
1.040
125
0.832
0.900
0.866
0.734
62.5
0.477
0.450
0.464
0.332
31.25
0.244
0.251
0.248
0.116
0
0.129
0.135
0.132
-
數據處理:
-
貨期:3-5 working days
引用文獻
- Circular RNA circ-CARD8 regulates alveolar macrophage pyroptosis through the miR-580-3p/CARD8 pathway in acute lung injury S Chen, L Wen, Y Wu, S Xiao, Y Lai, J Ou, Y Shen,PloS one,2024
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
最新研究進展:CCL18是一種趨化因子,在多種疾病的發病和發展中起著重要作用,如癌癥、肝病和心臟病等。最近的研究表明,CCL18在慢性阻塞性肺疾病(COPD)患者中的水平與氣流受限程度和炎癥程度相關。這些發現表明CCL18可能是COPD的潛在生物標志物,并提供了CCL18可能參與COPD發病機制的新證據。
-
功能:Chemotactic factor that attracts lymphocytes but not monocytes or granulocytes. May be involved in B-cell migration into B-cell follicles in lymph nodes. Attracts naive T-lymphocytes toward dendritic cells and activated macrophages in lymph nodes, has chemotactic activity for naive T-cells, CD4+ and CD8+ T-cells and thus may play a role in both humoral and cell-mediated immunity responses.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- miR-128 interacts with CCL18 3'UTR, reducing its expression in malignant melanoma. PMID: 30025750
- AMAP1 mediated CCL18-induce activation of NF-kappaB and promoted breast cancer metastasis. PMID: 28834540
- results of the study indicate that there could be a relationship between the expression of CCL-18 in nasal turbinate mucosa and the severity of allergic rhinitis PMID: 30102123
- chemokine CCL18 can be a mediator of peritoneal membrane failure associated with peritonitis episodes as well as providing a new potential therapeutic target. PMID: 29850544
- CCL18 was up-regulated in diffuse large B cell lymphoma and related to poor prognosis PMID: 29504526
- Serum C-C motif chemokine ligand 18 (CCL18) was elevated in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) and could serve as a new tumor biomarker, which also predicted a poor survival of the patient. PMID: 29036787
- In advanced lung adenocarcinoma, infiltration of CCL18(+) tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) was increased and higher expression of CCL18 by TAMs was associated with a favorable prognosis in lymph-node positive NSCLC PMID: 29970512
- This study study discovered a positive feedback loop between CTGF and CCL18 in hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. PMID: 28837877
- All patients with NPC1 mutations had high ChT activity, high CCL18/PARC concentrations and/or Niemann-Pick disease type C suspicion index scores >/=70. PMID: 28222799
- findings suggest that these pulmonary markers could be useful to assess CAP severity and, especially YKL-40 and CCL18 by helping predict CAP caused by atypical pathogens PMID: 29324810
- PARC activation of neutrophils by sterile immunogenic dying cells drives neutrophil-mediated residual cell killing. PMID: 28234357
- Matrigel invasion assays revealed that tumor ECM-educated macrophages efficiently stimulated cancer cell invasion through a mechanism involving CCL18. PMID: 28209528
- Our results indicate that CCL18 acts in an autocrine manner via Akt activation to stimulate oral squamous cell carcinoma cell growth and invasion during disease progression PMID: 26919103
- Our data indicate that hypoxic inhibition of JMJD3 activity reduces demethylation of H3K27me3, nucleosome removal, and hence induction of the STAT6 target gene CCL18, while induction of other STAT6-inducible genes such as SPINT2 remained unaffected by JMJD3. PMID: 27737800
- There was no association between serial CCL18 concentrations with tumor response and overall survival. PMID: 28957436
- CCL-18 is a promising biomarker in COPD, as it is associated with frequency of exacerbations, particularly with severe COPD exacerbations requiring hospitalization, as well as with functional parameters and symptom scores. PMID: 28115842
- Data suggested that CCL18 upregulated Slug expression to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and stem cell-like features by activating the mTOR pathway in oral cancer. PMID: 28574664
- An increased lung protein expression of PARC in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients PMID: 28545096
- CCL18 can increase the invasive ability of non-small cell lung cancer cells by binding to its receptor Nir1. PMID: 26756176
- Results demonstrate that high levels of CCL18 are present in ovarian cancer (OC) ascites and that CCL18 is an important component of ascites for the ascites-mediated migration of OC cells. Ascites and CCL18 stimulate the phosphorylation and expression of Pyk2, which is critical for mediated CCL18-induced migration. PMID: 27613122
- Data suggest that circulating CCL18 and abdominal subcutaneous white adipose tissue-secreted CCL18 correlates with insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome risk score; because CCL18 is macrophage-specific and associates with adipose immune gene expression, it may constitute a marker of adipose tissue inflammation (panniculitis). PMID: 27459538
- Cytomegalovirus replication in the allograft causes an intrapulmonary increase of CCL-18 and CCL-20 and a systemic rise of CCL-20 serum levels. Strong intrapulmonary CCL-18 responses are associated with symptomatic HCMV disease, proposing that CCL-18 BALF levels could serve as a marker. PMID: 26910332
- Study determined that CCL18 expression was up-regulated in ovarian carcinoma suggesting that CCL18 may play an important role in the pathogenicity of epithelial ovarian cancer through the induction of regulators and the activation of signaling pathways including mTORC2 signaling pathways. PMID: 26457987
- CCL18 expression is significantly upregulated in human masticatory mucosa during wound healing PMID: 28005267
- release of CCL18 with greater non-small cell lung cancer tumor size is most likely due to the accompanied growth of leukocyte infiltrate PMID: 27630310
- this study shows that CCL18 has a correlation with cardiac function in patients with acute anterior myocardial infarction PMID: 27350631
- our findings establish a signaling role for CCL18 in gastric cancer cells and identify that the CCL18/ERK1/2/NF-kappaB signaling pathway is essential for tumor invasiveness in gastric cancer cells. PMID: 26242263
- CCL18 enhances hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) through the expression of PITPNM3 and the activation of the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. PMID: 26449829
- our findings suggest that CCL18 released from tumor-associated macrophages promotes angiogenesis and tumor progression in breast cancer. PMID: 26416449
- Findings suggest that down-regulation of miR98 and miR27b promotes CCL18-mediated invasion and migration of breast cancer cells. PMID: 26244871
- CCL18 is significantly up-regulated in breast cancer vs benign tumors or normal breast. It increased with the size of tumors, the number of lymph node metastasis, and advancing tumor stage. PMID: 26294068
- A common CCL18 polymorphism together with intraventricular hemorrhage had an additive influence on cerebral palsy susceptibility. PMID: 26113374
- The CCL18 levels in serum and synovial fluid are correlated with the severity of osteoarthritis. PMID: 25794928
- Combined functions of CCL18 in mesenchymal and cancer cells might accelerate the progression of PDAC by promoting the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion and migration of pancreatic cancer cells. PMID: 25502147
- Increased CCL18 levels characterize chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection and pulmonary obstruction in patients with cystic fibrosis. PMID: 25142483
- upregulation of CCL18 may be involved in the malignant progression of prostate cancer. PMID: 25197632
- CCL-18 and IGFBP-6 were identified as new potential serum biomarkers for prostate cancer. PMID: 24747338
- CCL18 expression was positively correlated with malignancy in EC. PMID: 25275026
- Pyk2 and Src are important in CCL18-induced breast cancer metastasis PMID: 24142406
- CCL18 is an antimicrobial protein with bacteriocidal activity against E. coli and S. aureus. PMID: 12949249
- CCL18 from tumor-associated macrophages induces cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition, forming a positive feedback loop, in coculture systems and humanized mice. PMID: 24823638
- Further development of A1AT as a diagnostic biomarker for BCa is warranted. PMID: 24011266
- the Cys10-Cys34 disulfide bond is involved in the function of CCL18. PMID: 23742785
- genetic polymorphism is associated with lung function in Hutterites, who are a founder population of European descent in North America PMID: 23932459
- In patients with systemic sclerosis-related interstitial lung disease, CCL18 was a predictor of short-term decline in forced vital capacity. It was not a longterm prognostic indicator. PMID: 23588945
- Data indicate that PYK2 N-terminal domain interacting receptor 1 (Nir1) could induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition by stabilising Snail via the PI3K/Akt/GSK3beta/Snail signalling pathway through binding to CCL18. PMID: 24001613
- this review focuses on the potential role, in asthma and lung immunity, of CCL18 a chemokine both constitutively expressed at high levels in the lung and induced in inflammatory conditions PMID: 23786278
- Identification of human CCR8 as a CCL18 receptor. PMID: 23999500
- A high CCL18 level might be an independent biomarker for predicting better survival of patients with colorectal cancer. PMID: 23433718
- CCL18 may be an interesting therapeutic target for NSCLC PMID: 23349697
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:Intercrine beta (chemokine CC) family
-
組織特異性:Expressed at high levels in lung, lymph nodes, placenta, bone marrow, dendritic cells present in germinal centers and T-cell areas of secondary lymphoid organs and macrophages derived from peripheral blood monocytes. Not expressed by peripheral blood mono
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Human Transforming Growth factor β1,TGF-β1 ELISA kit
Detect Range: 23.5 pg/ml-1500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 5.8 pg/ml
-
-
-
Mouse Tumor necrosis factor α,TNF-α ELISA Kit
Detect Range: 7.8 pg/ml-500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 1.95 pg/ml
-
-
-
-